Digital Colour Imaging Systems Operating Instructions
Table Of Contents
- Operating Instructions
- Conventions
- Table of Contents
- Getting To Know Your Machine
- Basic Fax Transmission
- Fax Transmission Procedure
- Entering a Destination
- Transmission with Destination Monitoring
- Talking to the Remote Party Before Transmission
- Setting Original Quality
- Setting the Original Size
- Transmitting 2-Sided Originals
- Verification Stamp
- Transmitting a Document Stored in Memory
- Job Build and SADF
- Direct Transmission
- Verifying Communication Status
- Rotated Transmission
- Batch Transmission
- Getting an Outside Line Using PIN Code Access
- Using Program Keys
- Cancelling a Communication
- Dial Prefix
- Convenient Fax Features
- Fax Reception
- Internet Fax
- What is Internet Fax?
- What Internet Fax Can Do
- Tips for Internet Fax
- Preparing to Use Internet Fax
- Sending an Email Procedure
- Entering an Email Address
- Using Cc, Bcc and From
- Setting a File Type and a File Name
- Emailing an A3-Sized Document
- Setting Message Delivery Notice (MDN)
- When Email Transmission Fails
- Using a Completion Notice
- Receiving an Email
- Receiving an Email on a Computer
- Inbound Routing
- Using the Relay Feature
- Relayed Transmission from Internet Fax
- Relayed Transmission from PC
- Result of Relayed Transmission
- Useful Terms to Remember
- Handling Communication Reservation Files
- Program Destinations/Program Keys
- Reading Reports/Lists
- Solving Problems
- Appendix
40
Chapter 2 Basic Fax Transmission
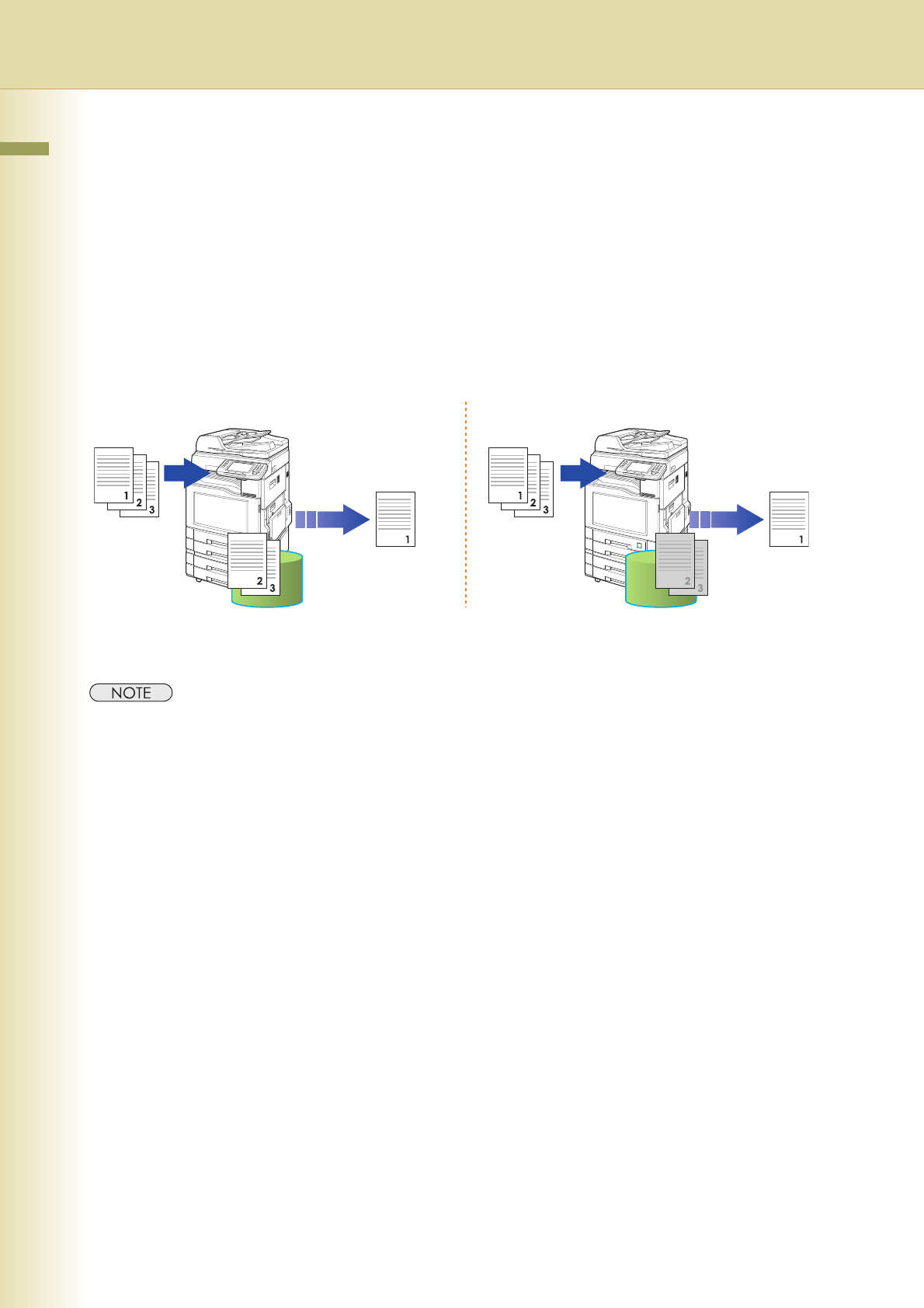
Transmitting a Document Stored in Memory
Documents can be quickly scanned and stored in the memory before transmission.
This feature allows you to send the documents to multiple destinations without having to scan the
same documents over again. It also allows you to retrieve your original(s) immediately without having
to wait for the Fax transmission to complete.
In addition to the Memory transmission, the machine supports the Direct transmission feature. In Direct
transmission, a document is transmitted without storing it into the memory.
z If the memory overflows while original(s) are being scanned for transmission to a single destination, the
machine will operate in the following manner:
If the Quick Memory Transmission feature is set to “Valid” in Function Parameters
The document is transmitted up to the portion that was stored into the memory.
If the Quick Memory Transmission feature is set to “Invalid” in Function Parameters
The document is transmitted up to the portion that was stored in the memory, and then switches to Direct
transmission and transmits the remaining original(s) in the ADF during the same phone call.
z If the memory overflows while original(s) are being scanned for transmission to multiple destinations, a
message appears asking whether to transmit the successfully stored documents in memory or to cancel the
transmission. Select “Yes” to start transmitting, or “No” to cancel. If no action is taken within 10 seconds, the
machine will start transmitting the stored documents.
z The transmission of a document terminates if memory overflows when the first page is transmitted.
z The standard setting of Memory transmission is “On” and it can be changed with the Function Parameter “05
Memory (HOME)” (Fax/Email Settings > Fax Parameters). For instructions on how to change the standard
setting, refer to Fax/Email Settings in the Operating Instructions (For Function Parameters) of provided CD-
ROM.
z The Function Parameter “82 Quick Memory XMT” (Fax/Email Settings > Fax Parameters) can be configured
to start transmitting a document when the first page is stored. This transmission mode is called “Quick Memory
Transmission”. The standard setting of Quick Memory transmission is “Valid”. For instructions on how to
change the standard setting, refer to Fax/Email Settings in the Operating Instructions (For Function
Parameters) of provided CD-ROM.
z Your machine is preset to transmit all documents from memory.
Original(s)
Original(s)
Stores all the
original(s) into
memory first, and
then starts its
transmission.
Starts transmitting
when the first page
is stored in the
memory.
Memory
Memory
Destination
machine(s)
Quick Memory TransmissionMemory Transmission
Destination
machine(s)










