- NX series User's Manual POWER SUPPLY
84(86)
Fault tracing
9
9. FAULT TRACING
When a fault is detected by the frequency converter control electronics, the drive is stopped and
the symbol
F
together with the ordinal number of the fault, the fault code and a short fault
description appear on the display. The fault can be reset with the Reset button on the control
keypad or via the I/O terminal. The faults are stored in the Fault history menu (M5) which can be
browsed. The different fault codes can be found in the table below.
The fault codes, their causes and correcting actions are presented in the table below. The
shadowed faults are A faults only. The faults written in white on black background may appear as
both A and F fault.
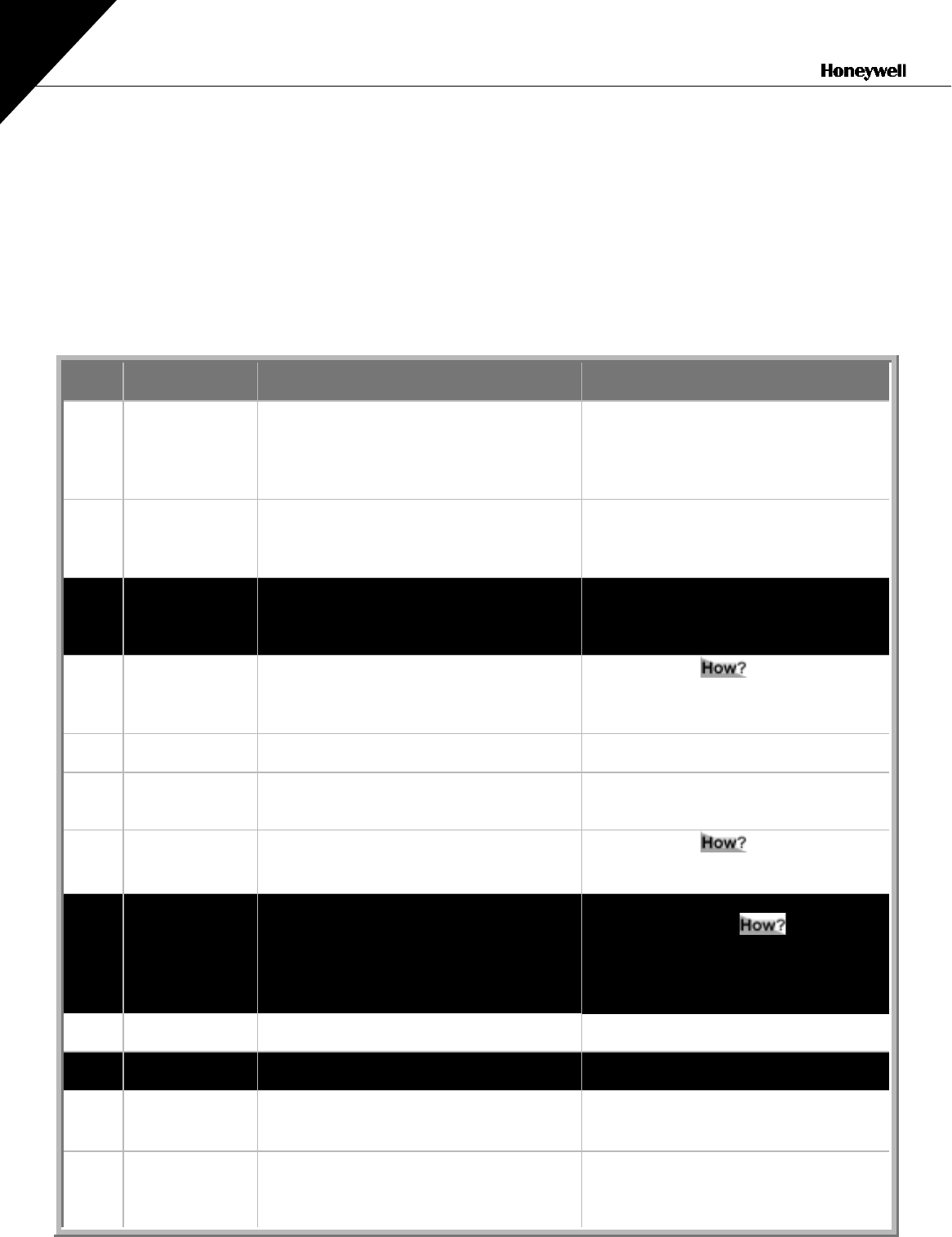
Fault
code
Fault Possible cause Correcting measures
1
Overcurrent Frequency converter has detected too
high a current (>4*I
n
) in the motor cable:
−
sudden heavy load increase
−
short circuit in motor cables
−
unsuitable motor
Check loading.
Check motor size.
Check cables.
2
Overvoltage The DC-link voltage has exceeded the
limits defined in Table 4-1.
−
too short a deceleration time
−
high overvoltage spikes in utility
Make the deceleration time longer.
3
Earth fault Current measurement has detected that
the sum of motor phase current is not
zero.
−
insulation failure in cables or motor
Check motor cables and motor.
5
Charging switch The charging switch is open, when the
START command has been given.
−
faulty operation
−
component failure
Reset the fault
and restart.
Should the fault re-occur, contact your
nearest distributor.
6
Emergency
stop
Stop signal has been given from the
option board.
7
Saturation trip Very high overload
Defective component
Cannot be reset from the keypad.
Switch off power. If this does not help
contact your nearest distributor.
8
System fault The frequency converter troubleshooting
system is unable to locate the fault.
Reset the fault
and restart.
Should the fault re-occur, contact your
nearest distributor,
9
Undervoltage DC-link voltage is under the voltage limits
defined in.
−
most probable cause: too low a
supply voltage
−
frequency converter internal fault
In case of temporary supply voltage
break reset the fault and restart
the frequency converter. Check the
supply voltage. If it is adequate, an
internal failure has occurred.
Contact your nearest distributor..
10
Input line
supervision
Input line phase is missing. Check supply voltage and cable.
11
Output phase
supervision
Current measurement has detected that
there is no current in one motor phase.
Check motor cable and motor.
12
Brake chopper
supervision
−
no brake resistor installed
−
brake resistor is broken
−
brake chopper failure
Check brake resistor.
If the resistor is ok, the chopper is faulty.
Contactyour nearest distributor.
13
Frequency
converter
under-
temperature
Heatsink temperature is under –10
°
C










