Manual
7-12 Advanced Programming
Multipass Patterns
A multipass pattern is a pattern that reuses one set of fiducials to repeat the same pattern at one or more
locations on the workpiece. This is a helpful feature when an application requires multiple dispenses or
requires a "seal run" after adhesion. One big advantage of multipass patterns is that once the substrate
height has been found and the fiducials defined, the information is reused for all of the passes, which can
greatly increase throughput.
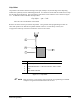
For example, the workpiece shown in Figure 7-9 contains eight identical rectangle-shaped chips:
Figure 7-9 Multipass Workpiece
Assume you want to perform the following dispensing functions:
• Perform a height sense on each chip.
• Dispense an L-shaped weight control line.
• Dispense an L-shaped seal pass.
It is much faster to perform all the height sense operations, dispense the first fluid and then come back
and dispense the sealant for each chip than to perform all three operations on a chip before moving to the
next chip.
There are several commands associated with multipass patterns:
• Loop Block
• Pass Block
• Multipass Timer commands
Loop Block and Pass Block commands are accessed from the
Pattern drop-down menu. Multipass
Timer commands are accessed from the Timer drop-down menu.
Loop Block Command
Loop Block commands define the number of passes for multipass patterns. When you define a loop,
FmNT inserts
Loop Pass: from 1 to X (X represents the total number of passes) and Next Loop:
commands into your program.
Pass Block Command
Pass Block commands are used to setup multipass patterns. When you create a multipass Pattern, FmNT
inserts a
Start Pass and End Pass command into your program. The number of Start Pass/End Pass sets
should equal the number of passes you wish to setup. The dispensing commands for each pass are
inserted between the Start and End Pass commands.