Service Manual
GSM-204-323
Transmit blocks overview
31st Oct 01
Technical Description: Horizon
macro
outdoor
68P02902W02-A
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Tech. 5–31
Transmit blocks overview
Introduction to
transmit blocks
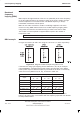
Transmit (Tx) blocks are located in three positions in the basket above the
CTUs. There are four types of transmit (Tx) blocks, three of which are available
as 850, 900, 1800 or 1900 variants, and one dual band variant (for use with
900 MHz or 1800 MHz BTSs only).
CAUTION
Unused Tx block locations must be covered with a
blanking plate for correct air flow and EMC shielding.
TDF (850, 900, 1800 or 1900) = Twin Duplexed Filter.
Dual band TDF (900/1800) = Dual band twin duplexed filter.
DCF (850, 900, 1800 or 1900) = Duplexed Combining bandpass Filter.
DDF (850, 900, 1800 or 1900) = Dual-stage Duplexed combining Filter.
These Tx blocks are cooled by airflow from underneath. The DDF has fins,
whereas the TDF, dual band TDF and DCF do not.
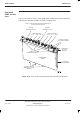
Tx blocks are attached to the top surface of the top panel using two M6 screws.
Three types of plate can be located in the basket, one as blanking plate and two
to interface CTU Tx cables:
Blanking plate. This ensures proper airflow and EMC shielding for an
unused basket Tx Block location.
Feedthrough plate. This converts two SMA connectors to two N-type
connectors, used for connecting Tx cables to DDFs.
Hybrid Combining Unit (HCU). This combines two SMA connectors to
one N-type, enabling two additional CTUs to be connected to a DDF.
The plates are attached to the base of the top panel basket using six M4
screws.
Screw retention
in Tx block
locations
The plates are attached to the base of the top panel basket using six M4
screws.
Tx blocks are attached to the top surface of the top panel using two M6 screws.
To ensure correct EMC shielding and general containment, it is important to
ensure that all Tx block/plate screw locations have a screw in place and
tightened to correct torque.