User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Preliminary Operations
- Chapter 3 Optimization/Calibration
- Introduction to Optimization and Calibration
- Preparing the LMF
- Overview of Packet BTS files
- LMF Features and Installation Requirements
- LMF File Structure Overview
- LMF Home Directory
- NECF Filename Conventions and Directory Location
- LMF Installation and Update Procedures
- Copy BTS and CBSC CDF (or NECF) Files to the LMF Computer
- Creating a Named HyperTerminal Connection for MMI Communication
- Span Lines - Interface and Isolation
- LMF to BTS Connection
- Using the LMF
- Pinging the Processors
- Download the BTS
- CSM System Time - GPS & LFR/HSO Verification
- Test Equipment Set-up
- Test Set Calibration
- Background
- Calibration Procedures Included
- GPIB Addresses
- Selecting Test Equipment
- Manually Selecting Test Equipment in a Serial Connection Tab
- Automatically Selecting Test Equipment in the Serial Connection Tab
- Calibrating Test Equipment
- Calibrating Cables Overview
- Calibrating Test Cabling using Communications System Analyzer
- Calibrate Test Cabling Using Signal Generator & Spectrum Analyzer
- Setting Cable Loss Values
- Setting TX Coupler Loss Value
- Bay Level Offset Calibration
- Purpose of Bay Level Offset Calibration
- What is BLO Calibration?
- Component Verification During Calibration
- When to Calibrate BLOs
- BLO Calibration Data File
- Test Equipment Setup for RF Path Calibration
- Transmit (TX) Path Calibration Description
- TX Calibration and the LMF
- TX Calibration
- All Cal/Audit and TX Calibration Procedure
- Download BLO Procedure
- Calibration Audit Introduction
- TX Path Audit
- TX Audit Test
- Create CAL File
- RFDS Set-up and Calibration
- Alarms Testing
- Chapter 4 Automated Acceptance Test Procedures
LMF to BTS Connection68P64115A18–1
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T Lite BTS Optimization/ATP Software Release R2.16.1.x
DRAFT
3-17
LMF to BTS Connection
Connect the LMF to the BTS
The LMF computer may be connected to the LAN A or B connector
located behind the frame lower air intake grill. Figure 3-3 below shows
the general location of these connectors. LAN A is considered the
primary LAN.
Table 3-5: Connecting the LMF to the BTS
n Step Action
1 To gain access to the LAN connectors, open the LAN cable access door, then pull apart the fabric
covering the BNC “T” connector and slide out the service tray, if desired (see Figure 3-3).
2 Connect the LMF computer to the LAN A (left–hand) BNC connector via PCMCIA Ethernet Adapter.
NOTE
Xircom Model PE3–10B2 or equivalent can also be used to interface the LMF Ethernet connection to
the BTS frame connected to the PC parallel port, powered by an external AC/DC transformer. In this
case, the BNC cable must not exceed 91 cm (3 ft) in length.
* IMPORTANT
The LAN shield is isolated from chassis ground. The LAN shield (exposed portion of BNC connector)
must not touch the chassis during optimization.
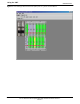
Figure 3-3: LMF Connection Detail
10BaseT/10Base2
Converter Connects
Directly to BNC T
LMF BNC “T” Connections on
left side of frame (Ethernet
“A” shown; Ethernet “B”
covered with hook–and–loop
fabric)
LMF Computer
Terminal with Mouse
PCMCIA Ethernet
Adpater & Ethernet
UTP Adapter
Universal Twisted
Pair (UTP) cable
(RJ11 connectors)
115 VAC Power
Connection
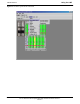
NOTE:
Open LAN CABLE ACCESS door.
Pull apart hook–and–loop fabric
and gain access to the LAN A or
LAN B LMF BNC connector.
ti-CDMA-WP-00232-v01-ildoc-ftw
SC 4812T LITE
3