User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Preliminary Operations
- Chapter 3 Optimization/Calibration
- Introduction to Optimization and Calibration
- Preparing the LMF
- Overview of Packet BTS files
- LMF Features and Installation Requirements
- LMF File Structure Overview
- LMF Home Directory
- NECF Filename Conventions and Directory Location
- LMF Installation and Update Procedures
- Copy BTS and CBSC CDF (or NECF) Files to the LMF Computer
- Creating a Named HyperTerminal Connection for MMI Communication
- Span Lines - Interface and Isolation
- LMF to BTS Connection
- Using the LMF
- Pinging the Processors
- Download the BTS
- CSM System Time - GPS & LFR/HSO Verification
- Test Equipment Set-up
- Test Set Calibration
- Background
- Calibration Procedures Included
- GPIB Addresses
- Selecting Test Equipment
- Manually Selecting Test Equipment in a Serial Connection Tab
- Automatically Selecting Test Equipment in the Serial Connection Tab
- Calibrating Test Equipment
- Calibrating Cables Overview
- Calibrating Test Cabling using Communications System Analyzer
- Calibrate Test Cabling Using Signal Generator & Spectrum Analyzer
- Setting Cable Loss Values
- Setting TX Coupler Loss Value
- Bay Level Offset Calibration
- Purpose of Bay Level Offset Calibration
- What is BLO Calibration?
- Component Verification During Calibration
- When to Calibrate BLOs
- BLO Calibration Data File
- Test Equipment Setup for RF Path Calibration
- Transmit (TX) Path Calibration Description
- TX Calibration and the LMF
- TX Calibration
- All Cal/Audit and TX Calibration Procedure
- Download BLO Procedure
- Calibration Audit Introduction
- TX Path Audit
- TX Audit Test
- Create CAL File
- RFDS Set-up and Calibration
- Alarms Testing
- Chapter 4 Automated Acceptance Test Procedures
BTS Equipment Identification68P64115A18–1
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T Lite BTS Optimization/ATP Software Release R2.16.1.x
DRAFT
1-21
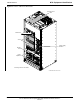
Filter/Combiner Shelf (Bandpass Filters or 2:1
Combiners)
The filter/combiner shelf (Figure 1-3) holds the transmit bandpass filters
or 2:1 combiners, depending on system configuration.
Span I/O Board
The span I/O board (Figure 1-3) provides the span line interface to the
SCCP backplane.
Small CDMA Channel Processor (SCCP) Shelf
The SCCP shelf has provisions for the following types and quantities of
modules (Figure 1-3 and Figure 1-4):
S Alarm Monitoring and Reporting (AMR) cards (2)
S Broad Band Transceiver, second generation or 1X, (BBX2 or
BBX–1X) cards, primary (6)
S BBX2 or BBX–1X card, redundant (1)
S CDMA Clock Distribution (CCD) cards (2)
S Clock Synchronization Manager (CSM) on two cards (one with GPS
receiver, if ordered)
S Combiner Input/Output (CIO) card (1)
S Fan modules (2)
S Filler panel (as required)
S Group Line Interface, second generation, (GLI2) cards (2)
S High Stability Oscillator (HSO)/Low Frequency Receiver (LFR) card
(Optional) (1)
S Multi–coupler Preselector Cards (MPC) (2 per starter frame; 1 per
companion frame)
S Expansion Multi–coupler Preselector Card (EMPC) (1 per companion
frame)
S Multi–Channel CDMA (MCC8E, MCC24E, or MCC–1X) cards (4)
S Power supply cards (2)
S Switch card (1)