User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Preliminary Operations
- Chapter 3 Optimization/Calibration
- Introduction to Optimization and Calibration
- Preparing the LMF
- Overview of Packet BTS files
- LMF Features and Installation Requirements
- LMF File Structure Overview
- LMF Home Directory
- NECF Filename Conventions and Directory Location
- LMF Installation and Update Procedures
- Copy BTS and CBSC CDF (or NECF) Files to the LMF Computer
- Creating a Named HyperTerminal Connection for MMI Communication
- Span Lines - Interface and Isolation
- LMF to BTS Connection
- Using the LMF
- Pinging the Processors
- Download the BTS
- CSM System Time - GPS & LFR/HSO Verification
- Test Equipment Set-up
- Test Set Calibration
- Background
- Calibration Procedures Included
- GPIB Addresses
- Selecting Test Equipment
- Manually Selecting Test Equipment in a Serial Connection Tab
- Automatically Selecting Test Equipment in the Serial Connection Tab
- Calibrating Test Equipment
- Calibrating Cables Overview
- Calibrating Test Cabling using Communications System Analyzer
- Calibrate Test Cabling Using Signal Generator & Spectrum Analyzer
- Setting Cable Loss Values
- Setting TX Coupler Loss Value
- Bay Level Offset Calibration
- Purpose of Bay Level Offset Calibration
- What is BLO Calibration?
- Component Verification During Calibration
- When to Calibrate BLOs
- BLO Calibration Data File
- Test Equipment Setup for RF Path Calibration
- Transmit (TX) Path Calibration Description
- TX Calibration and the LMF
- TX Calibration
- All Cal/Audit and TX Calibration Procedure
- Download BLO Procedure
- Calibration Audit Introduction
- TX Path Audit
- TX Audit Test
- Create CAL File
- RFDS Set-up and Calibration
- Alarms Testing
- Chapter 4 Automated Acceptance Test Procedures
BTS Equipment Identification
68P64115A18–1
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T Lite BTS Optimization/ATP Software Release R2.16.1.x
DRAFT
1-20
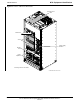
Internal Assemblies and FRUs
The BTS frame houses the fan modules, Small CDMA Channel
Processor (SCCP) shelf, RF Power Amplifier modules, PA trunking
modules, 2:1 combiners.
RF filtering includes: DRF – Duplexers with TX Filter, RX Filter, and
Diversity RX Filter and TRF – Non-Duplexed TX Filter, RX Filter, and
Diversity RX Filter.
Power system components include an AC Power Input/Filter, DC Filters,
+27 Vdc Power Distribution Assembly (PDA).
Figure 1-2 and Figure 1-3 show the location of the internal assemblies
and Field Replaceable Units (FRU). A brief description of each item is
found in the following paragraphs.
Figure 1-3: I/O Interconnect Plate
FRONT
SITE I/O
LAN
CONNECTIONS
GPS IN
HSO/LFR
RF FILTERING
POWER INPUT/
DC FILTER
ETHERNET ROUTER (IF USED;
OTHERWISE, FILLER PLATE)
EXP FILLER
PLATE
REAR
SPAN I/O
ti-CDMA-WP-00214-v01-ildoc-ftw
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ALARM
CONNECTORS
POWER INPUT/
AC FILTER
FILLER PLATE
DC Power Distribution Assembly (PDA)
Both rectifier output voltage and back–up battery voltage are routed to
the PDA (Figure 1-3) where they are combined into system DC bus
voltage. The PDA provides distribution of DC power and system DC
bus protection from the loads with MAIN BREAKER and the smaller
post–distribution circuit breakers. MAIN BREAKER permits removal of
all frame loading from the bus. The 13 post–distribution circuit breakers
permit removal of individual loads.