User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Preliminary Operations
- Chapter 3 Optimization/Calibration
- Introduction to Optimization and Calibration
- Preparing the LMF
- Overview of Packet BTS files
- LMF Features and Installation Requirements
- LMF File Structure Overview
- LMF Home Directory
- NECF Filename Conventions and Directory Location
- LMF Installation and Update Procedures
- Copy BTS and CBSC CDF (or NECF) Files to the LMF Computer
- Creating a Named HyperTerminal Connection for MMI Communication
- Span Lines - Interface and Isolation
- LMF to BTS Connection
- Using the LMF
- Pinging the Processors
- Download the BTS
- CSM System Time - GPS & LFR/HSO Verification
- Test Equipment Set-up
- Test Set Calibration
- Background
- Calibration Procedures Included
- GPIB Addresses
- Selecting Test Equipment
- Manually Selecting Test Equipment in a Serial Connection Tab
- Automatically Selecting Test Equipment in the Serial Connection Tab
- Calibrating Test Equipment
- Calibrating Cables Overview
- Calibrating Test Cabling using Communications System Analyzer
- Calibrate Test Cabling Using Signal Generator & Spectrum Analyzer
- Setting Cable Loss Values
- Setting TX Coupler Loss Value
- Bay Level Offset Calibration
- Purpose of Bay Level Offset Calibration
- What is BLO Calibration?
- Component Verification During Calibration
- When to Calibrate BLOs
- BLO Calibration Data File
- Test Equipment Setup for RF Path Calibration
- Transmit (TX) Path Calibration Description
- TX Calibration and the LMF
- TX Calibration
- All Cal/Audit and TX Calibration Procedure
- Download BLO Procedure
- Calibration Audit Introduction
- TX Path Audit
- TX Audit Test
- Create CAL File
- RFDS Set-up and Calibration
- Alarms Testing
- Chapter 4 Automated Acceptance Test Procedures
BTS Equipment Identification68P64115A18–1
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T Lite BTS Optimization/ATP Software Release R2.16.1.x
DRAFT
1-17
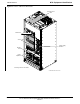
BTS Equipment Identification
Equipment Overview
The 1X SCt4812T–Lite BTS frame consists of a single cabinet
containing RF and power amplifier components. The BTS may be
powered powered by:
S 220 Vac (rectified internally to +27 Vdc)
S –48 Vdc (power converted internally to +27Vdc)
S +27 Vdc
Each frame can support up to two carriers in a 3–sector configuration.
Six–sector operation is not supported with any SC4812T Lite
configuration.
Figure 1-2 illustrates the external features of the BTS frame, the single
major component of the Motorola SC4812T Lite. The frame cabinet is
identical for starter and expansion frames except for the I/O interconnect
plate.
Frame Configurations
The SC4812T Lite is available in starter and expansion frame
configurations. Following are brief descriptions of each.
Starter frame configuration supports one or two carriers, each with
separate antenna sets. It can operate as a stand–alone BTS, or can be
modified in the field to the expansion frame configuration.
Expansion Frame configuration supports one or two carriers using 2:1
TX combiners and a single antenna set for the frame. It operates with an
SC4812T Lite starter frame which has its own antennas and different
carriers. Expansion frames share RX signals to provide diversity RX for
the opposite frame. Expansion frames allow equipping a single SC4812T
Lite site with up to four carriers.
Logical BTS
The BTS software implements the logical BTS capability. Previously, all
BTS frames co–located at a single site had to be identified in the
network with separate and distinct BTS ID numbers. In the Logical BTS
feature, all frames located at a single BTS site are identified with unique
Frame ID numbers (Frame ID Numbers 1, 101, 201, 301) under a single
(site) BTS ID number. A logical BTS can consist of up to four
SC 4812T frames.When the LMF is connected to frame 1 of a logical
BTS, you can access all devices in all of the frames that make up the
logical BTS. A logical BTS requires a CDF/NECF file that includes
equipage information for all of the logical BTS frames and their devices
and a CBSC file that includes channel data for all of the logical BTS
frames.