User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Foreword
- FCC Requirements
- General Safety
- Revision History
- Patent Notification
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Preliminary Operations
- Chapter 3 Optimization/Calibration
- Optimization/Calibration - Introduction
- Isolate Span Lines/Connect LMF
- Preparing the LMF
- Using CDMA LMF
- Download the BTS
- CSM System Time/GPS and LFR/HSO Verification
- Test Equipment Set-up
- Test Set Calibration
- Bay Level Offset Calibration
- RFDS Set-up and Calibration
- BTS Redundancy/Alarm Testing
- BTS Alarms Testing
- Preliminary Operations: Overview
- Pre-Power-up Tests
- Initial Power-up Tests
- Chapter 4 Automated Acceptance Test Procedure
- Automated Acceptance Test Procedures - All-inclusive TX & RX
- TX Output Acceptance Tests: Introduction
- TX Spectral Purity Transmit Mask Acceptance Test
- TX Waveform Quality (rho) Acceptance Test
- TX Pilot Time Offset Acceptance Test
- TX Code Domain Power/Noise Floor Acceptance Test
- RX Frame Error Rate (FER) Acceptance Test
- Generate an ATP Report
- Chapter 5 Prepare to Leave the Site
- Chapter 6 Basic Troubleshooting
- Basic Troubleshooting Overview
- Troubleshooting: Installation
- Troubleshooting: Download
- Troubleshooting: Calibration
- Troubleshooting: Transmit ATP
- Troubleshooting: Receive ATP
- Troubleshooting: CSM Check-list
- C-CCP Backplane Troubleshooting
- Module Front Panel LED Indicators and Connectors
- Basic Troubleshooting - Span Control Link
- Appendix A Data Sheets
- Appendix B PN Offset/I & Q Offset Register Programming Information
- Appendix C FRU Optimization/ATP Test Matrix
- Appendix D BBX Gain Set Point vs. BTS Output
- Appendix E CDMA Operating Frequency
- Appendix F PCS Interface Setup for Manual Testing
- Appendix G VSWR
- Appendix H Download ROM Code
- Appendix I In-Service Calibration
- Appendix J GPIB Addresses
- Introduction
- HP437 Power Meter GPIB Address
- Gigatronics 8541C Power Meter GPIB Address
- Motorola CyberTest GPIB Address
- HP8935 Test Set GPIB Address
- Setting HP8921A and HP83236A/B GPIB Address
- Advantest R3465 GPIB Address
- RS232 GPIB Interface Box
- Advantest R3267 Spectrum Analyzer GPIB Address
- Agilent E4406A Transmitter Tester GPIB Address
- Index
BTS Equipment Identification
68P09255A61-4
Aug 2002
1X SC 4812T BTS Optimization/ATP Software Release 2.16.1.x
FIELD TRIAL
1-16
BTS Equipment Identification
Equipment Overview
The Motorola SC 4812T BTS can consist of the following equipment
frames:
At least one BTS starter frame
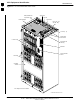
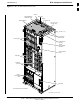
- +27 V BTS (see Figure 1-2)
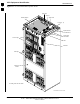
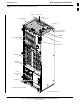
- -48 V BTS (see Figure 1-3)
Ancillary equipment frame (or wall mounted equipment)
Expansion frames
- +27 V BTS (see Figure 1-4)
- -48 V BTS (see Figure 1-5)
Ancillary Equipment Frame Identification
NOTE
Equipment listed below can be wall mounted or mounted in a
standard 19 inch frame. The description assumes that all
equipment is mounted in a frame for clarity.
If equipped with the RFDS option, the RFDS and directional couplers
are the interface between the site antennas and the BTS or Modem
frame. The RFDS equipment includes:
Directional couplers
Site receive bandpass/bandreject filters
RFDS
Logical BTS
The BTS software implements the logical BTS capability. Previously, all
BTS frames co-located at a single site had to be identified in the
network with separate and distinct BTS ID numbers. In the Logical BTS
feature, all frames located at a single BTS site are identified with unique
Frame ID numbers (Frame ID Numbers 1, 101, 201, 301) under a single
(site) BTS ID number. A logical BTS can consist of up to four
SC 4812T frames.When the LMF is connected to frame 1 of a logical
BTS, you can access all devices in all of the frames that make up the
logical BTS. A logical BTS requires a CDF file that includes equipage
information for all of the logical BTS frames and their devices and a
CBSC file that includes channel data for all of the logical BTS fames.
1