User's Manual Part 2
Bay Level Offset Calibration
DRAFT
SCt4812T CDMA BTS Optimization/ATP
Mar 2001
3-64
Introduction to Bay Level
Offset Calibration
Calibration compensates for normal equipment variations within the
BTS and assures maximum measurement accuracy.
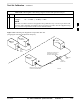
RF Path Bay Level Offset
Calibration
Calibration identifies the accumulated gain in every transmit path (BBX
slot) at the BTS site and stores that value in a BLO database calibration
table in the LMF. The BLOs are subsequently downloaded to each BBX.
For starter frames, each receive path starts at a BTS RX antenna port and
terminates at a backplane BBX slot. Each transmit path starts at a BBX
backplane slot, travels through the LPA, and terminates at a BTS TX
antenna port.
For expansion frames each receive path starts at the BTS RX port of the
cell site starter frame, travels through the frame-to-frame expansion
cable, and terminates at a backplane BBX slot of the expansion frame.
The transmit path starts at a BBX backplane slot of the expansion frame,
travels though the LPA, and terminates at a BTS TX antenna port of the
same expansion frame.
Calibration identifies the accumulated gain in every transmit path (BBX
slot) at the BTS site and stores that value in a BLO database. Each
transmit path starts at a C–CCP shelf backplane BBX slot, travels
through the LPA, and ends at a BTS TX antenna port. When the TX path
calibration is performed, the RX path BLO is automatically set to the
default value.
At omni sites, BBX slots 1 and 13 (redundant) are tested. At sector sites,
BBX slots 1 through 12, and 13 (redundant) are tested. Only those slots
(sectors) actually equipped in the current CDF are tested, regardless of
physical BBX board installation in the slot.
When to Calibrate BLOs
Calibration of BLOs is required:
After initial BTS installation
Once each year
After replacing any of the following components or associated
interconnecting RF cabling:
– BBX board
– C–CCP shelf
– CIO card
– CIO to LPA backplane RF cable
– LPA backplane
– LPA
. . . continued on next page
3