User Manual
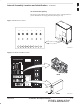
Internal Assembly Location and Identification – continued
PRELIMINARY
SC 4812ETL BTS Optimization/ATP
08/15/2000
1-20
Punch Block
The Punch Block is the interface between the cabinet and the T1/E1 span
lines, the Customer I/O, alarms, multi–cabinet timing (RGPS and
RHSO), and Pilot Beacon control (optional).
Span I/O Board
The Span I/O Board provides the interface for the span lines from the
CSU to the SCCP backplane (see Figure 1-3).
RF Diagnostic Subsystem (RFDS)
The RFDS provides the capability for remotely monitoring the status of
the SC4812ETL RF transmit and receive paths (Figure 1-6).
Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger provides cooling to the cabinet RF compartment.
The fan speed of the heat exchanger adjusts automatically with
temperature. The heat exchanger is located in the cabinet main door.
SC4812ETL Interface Board (ETIB) and LPA Control (LPAC)
Board
The ETIB is an interconnect module with status LEDs, MMI receptacles,
and secondary surge protection for the LPA modules. The LPAC board
provides the interface for LPA connections (See Figure 1-3).
SC4812ETL Trunking Modules
The trunking modules contain a complex, passive RF network that
allows RF signals to share the resources of a bank of four LPAs. They
also provides DC power and digital interconnect (See Figure 1-3).
Batteries
The batteries provide +24Vdc backup to the cabinet should AC power be
lost. The cabinet can accommodate a total of 12 12V batteries,
configured in six series–connected strings of two batteries each. The
time duration of backup provided depends on system configuration (See
Figure 1-3).
Battery Heaters
The battery heater pads warm the batteries to provide improved
cold–weather performance. A separate heater pad is required for each
battery string, and is located between each battery string and its
respective support shelf. The number of heaters is dependent on system
configuration (See Figure 1-3).
Rectifiers
The rectifiers convert AC power supplied to the cabinet to +27Vdc to
power the cabinet and maintain the charge of the backup batteries (See
Figure 1-3).
1