Install Instructions
20
103876-08 - 1/19
CL Installation & Service Manual
b. Evaluate the Existing Steam System.
The single most important factor in
determining the expected life cycle of a
steam boiler, is the amount of fresh water
added to the boiler during operation. Fresh
water brings minerals and oxygen into
the boiler. These contaminants greatly
accelerate corrosion of the cast iron boiler
sections.
i. Assure that all system radiators, piping
and vents are absolutely leak tight.
• When a steam boiler is installed in an
existing system, ALL air vents should
be replaced at the same time. This
assures that the new boiler will not be
compromised by existing system
leaks.
• If the system contains hidden supply
or return piping (hidden behind walls,
buried in concrete, etc.) pressure
test this piping to assure there are no
leaks.
ii. Repair any leaks in the system.
iii. Install accurate water meter on the fresh
water supply to the boiler.
NOTICE DO NOT use softened water in steam
boilers. Accelerated boiler corrosion will
result. Tie in fresh water supply to the boiler
upstream of a water softener.
4. Oxygen Contamination:
a. There are many possible causes of oxygen
contamination such as:
i. Addition of excessive make-up water as
a result of system leaks.
ii. Absorption through open tanks and
fittings.
iii. Oxygen permeable materials in the
distribution system.
b. In order to insure long product life, oxygen
sources should be eliminated. This can
be accomplished by taking the following
measures:
i. Repairing system leaks to eliminate the
need for addition of make-up water.
ii. Eliminating open tanks from the system.
iii. Eliminating and/or repairing fittings
which allow oxygen absorption.
iv. Use of non-permeable materials in the
distribution system.
v. Isolating the boiler from the system
water by installing a heat exchanger.
See Section VII, Paragraph B, Step 3 for
additional details.
Boiler
Series
Rating (Gal/Min) Pressure Drop (PSI)
Steam Water Steam Water
CL3-091 2.25 2.75 2.3 3.9
CL3-105 2.25 3.00 2.3 4.7
CL3-140 2.50 3.25 3.1 5.6
CL4-126 2.50 3.25 3.1 5.6
CL4-175 2.75 3.75 3.9 7.2
CL4-210 3.00 4.00 4.7 8.0
CL5-168 2.75 3.50 3.9 6.4
CL5-245 3.25 4.25 5.6 8.8
CL5-280 3.50 4.75 6.4 9.6
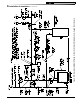
Table 4: Tankless Heater Data
Figure 15: Schematic Tankless Heater Piping
CAUTION
Oxygen contamination of
the boiler water will cause corrosion of iron
and steel boiler components, and can lead to
boiler failure. New Yorker's Standard Warranty
does not cover problems caused by oxygen
contamination of boiler water or scale (lime)
build-up caused by frequent addition of water.
J. CONNECT TANKLESS HEATER PIPING AS
SHOWN IN Figure 15. See Table 4 for Tankless
Heater Ratings.
The following guidelines should be followed when
piping the tankless heater:
1. Flow Regulation — If flow through the heater is
greater than its rating, the supply of adequate
hot water may not be able to keep up with
the demand. For this reason a flow regulator
matching the heater rating should be installed
in the cold water line to the heater. The flow
regulator should preferably be located below
the inlet to the heater and a minimum of 3’
3 Installation Instructions (continued)