User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance Reference Manual
- Contents
- About This Manual
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Using the Setup Wizard to Provision the STM in Your Network
- Choosing a Deployment Scenario
- Understanding the Steps for Initial Connection
- Logging In to the STM
- Using the Setup Wizard to Perform the Initial Configuration
- Setup Wizard Step 1 of 10: Introduction
- Setup Wizard Step 2 of 11: Networking Settings
- Setup Wizard Step 3 of 11: Time Zone
- Setup Wizard Step 4 of 11: Email Security
- Setup Wizard Step 5 of 11: Web Security
- Setup Wizard Step 6 of 11: Email Notification Server Settings
- Setup Wizard Step 7 of 11: Update Settings
- Setup Wizard Step 8 of 11: HTTP Proxy Settings
- Setup Wizard Step 9 of 11: Web Categories
- Setup Wizard Step 10 of 11: Configuration Summary
- Setup Wizard Step 11 of 11: Restarting the System
- Verifying Proper Installation
- Registering the STM with NETGEAR
- What to Do Next
- Chapter 3 Performing Network and System Management
- Configuring Network Settings
- Configuring Session Limits and Timeouts
- Configuring the HTTP Proxy Settings
- About Users with Administrative and Guest Privileges
- Configuring Remote Management Access
- Using an SNMP Manager
- Managing the Configuration File
- Updating the Software
- Configuring Date and Time Service
- Managing Digital Certificates
- Managing the Quarantine Settings
- Performance Management
- Chapter 4 Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans
- About Content Filtering and Scans
- Configuring E-mail Protection
- Configuring Web and Services Protection
- Configuring Application Control
- Setting Scanning Exclusions and Web Access Exceptions
- Chapter 5 Managing Users, Groups, and Authentication
- About Users, Groups, and Domains
- Configuring Groups
- Configuring User Accounts
- Configuring Authentication
- Global User Settings
- Viewing and Logging Out Active Users
- Chapter 6 Monitoring System Access and Performance
- Chapter 7 Troubleshooting and Using Online Support
- Appendix A Default Settings and Technical Specifications
- Appendix B Related Documents
- Index
ProSecure Web/Email Security Threat Management (STM) Appliance Reference Manual
Content Filtering and Optimizing Scans 4-39
v1.0, September 2009
3. Complete the fields and select the checkboxes as explained in Table 4-13.
4. Click Apply to save your settings.
Specifying Trusted Hosts
You can specify trusted hosts for which the STM bypasses HTTPS traffic scanning and security
certificate authentication. The security certificate is sent directly to the client for authentication,
which means that the user does not receive a security alert for trusted hosts. For more information
about security alerts, see “Managing Digital Certificates” on page 3-25.
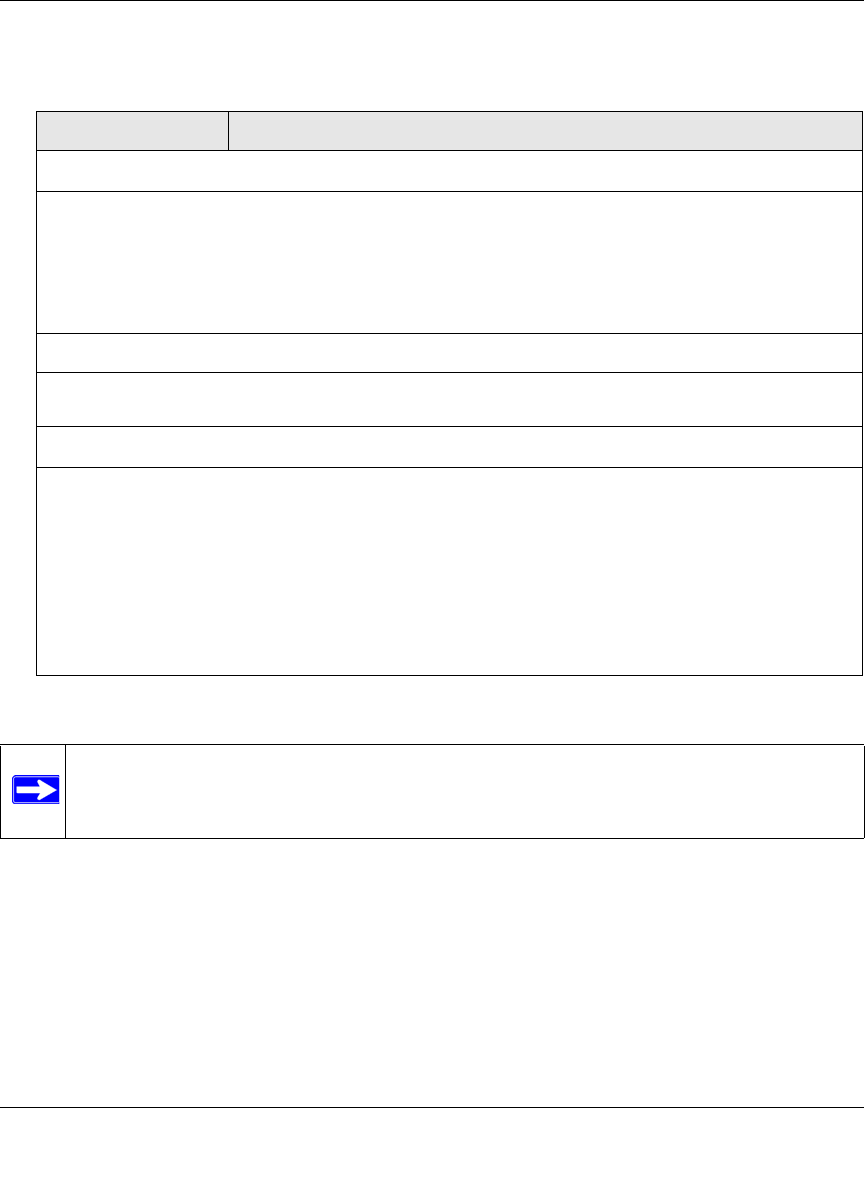
Table 4-13. HTTPS Settings
Setting Description
HTTP Tunneling
Select this checkbox to allow scanning of HTTPS connections through an HTTP proxy, which is
disabled by default. Traffic from trusted hosts is not scanned (see “Specifying Trusted Hosts” on
page 4-39).
Note: For HTTPS scanning to occur properly, you must add the HTTP proxy server port in the Ports to
Scan field for the HTTPS service on the Services screen (see “Configuring the HTTP Proxy Settings”
on page 3-7).
HTTPS 3rd Party Website Certificate Handling
Select this checkbox to allow a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connection with a valid certificate that is
not signed by a trusted certificate authority (CA). The default setting is to allow such as a connection.
Show This Message When an SSL Connection Attempt Fails
By default, a rejected SSL connection is replaced with the following text, which you can customize:
The SSL connection cannot be established.|
URL: %URL%
REASON: %REASON% ”
Note: The text is displayed on the HTTPS Settings screen with HTML tags. Click Preview to open a
screen that displays the notification text in HTML format.
Note: Make sure that you keep the %URL% and %REASON% meta words in the text to enable the
STM to insert the proper URL information and the reason of the rejection.
Note: For information about certificates that are used for SSL connections and HTTPS
traffic, see “Managing Digital Certificates” on page 3-25.










