User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- N300 Wireless Router
- Contents
- 1. Hardware Setup
- 2. Connect to the Network and Access the Router
- 3. Specify Your Internet Settings
- 4. Networking
- View or Change WAN Settings
- Set Up a Default DMZ Server
- Change the Router’s Device Name
- Change the LAN TCP/IP Settings
- Specify the IP Addresses that the Router Assigns
- Disable the DHCP Server Feature in the Router
- Reserve LAN IP Addresses
- Use the WPS Wizard for WiFi Connections
- Specify Basic WiFi Settings
- Change the WiFi Security Option
- Set Up a Guest Network
- Control the Wireless Radio
- Set Up a Wireless Schedule
- Set up a Wireless Access List
- Specify WPS Settings
- Wireless Distribution System
- Static Routes
- View Devices Currently on the Network
- Improve Network Connections with Universal Plug and Play
- 5. Manage Your Network
- 6. Troubleshooting
- A. Supplemental Information
Specify Your Internet Settings
23
N300 Wireless Router
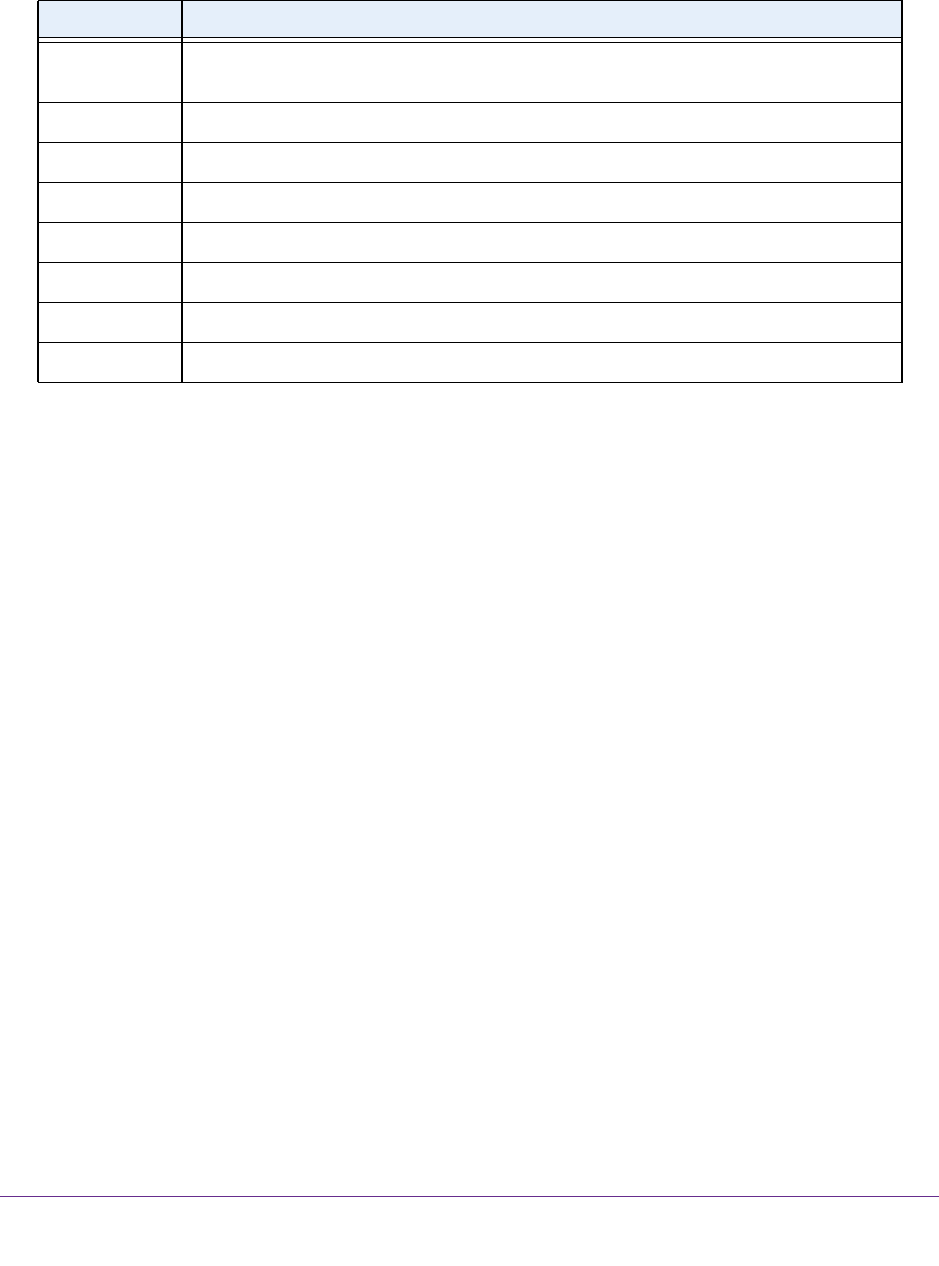
until the problem goes away. The following table describes common MTU sizes and
applications.
Table 3. Common MTU sizes
MTU Application
1500 The largest Ethernet packet size. This setting is typical for connections that do not use
PPPoE or VPN, and is the default value for NETGEAR routers, adapters, and switches.
1492 Used in PPPoE environments.
1472 Maximum size to use for pinging. (Larger packets are fragmented.)
1468 Used in some DHCP environments.
1460 Usable by AOL if you do not have large email attachments, for example.
1436 Used in PPTP environments or with VPN.
1400 Maximum size for AOL DSL.
576 Typical value to connect to dial-up ISPs.










