User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- Target audience
- Prerequisites
- Notation
- Product overview
- Product features
- Package contents
- Physical dimensions
- LED indicators
- Ethernet port LED indicators
- Interfaces
- Mounting options
- DIN rail mounting bracket
- Wall mounted via DIN rail bracket
- DIN rail mount
- Pole mount using DIN rail bracket
- Desk mount
- Powering the router
- Installing the router
- Data Connection
- Connect on demand
- SIM Management
- Operator settings
- SIM security settings
- LAN
- Wireless settings
- Ethernet LAN/WAN
- WAN failover
- Routing
- VPN
- Dynamic DNS
- Network time (NTP)
- Data stream manager
- PADD
- SNMP
- TR-069
- GPS
- USSD
- IO configuration
- SMS messaging
- Diagnostics
- Sending an SMS Diagnostic Command
- Log
- System configuration
- Administration
- Watchdogs
- Power management
- USB-OTG
- Storage
- Reboot
- Restoring factory default settings
- Accessing recovery mode
- Status
- Log
- Application Installer
- Settings
- Reboot
- Overview
- Accessing USB/SD card storage devices
- Host and Device mode
34
NetComm Wireless 4G WiFi M2M Router
www.netcommwireless.com
UM-00009
DHCP
The DHCP page is used to adjust the settings used by the router’s built in DHCP Server which assigns IP addresses to locally
connected devices.
DHCP relay configuration
In advanced networks configurations where the NTC-140W Series router should not be responsible for DHCP assignment, but
instead an existing DHCP server is located on the Wireless WAN or LAN connections, the clients behind the NTC-140W Series
router are able to communicate with the DHCP server when DHCP relay is enabled. This enables the NTC-140W Series router to
accept client broadcast messages and to forward them onto another subnet.
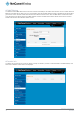
To configure the router to act as a DHCP relay agent click the DHCP relay toggle key to turn it ON and enter the DHCP server
address into the DHCP server address field. DHCP relay is disabled by default.
Figure 39 – DHCP relay configuration
DHCP configuration
You can manually set the start and end address range to be used to automatically assign addresses within, the lease time of the
assigned address, the default domain name suffix, primary and secondary DNS server, the primary and secondary WINS server, as
well as the advanced DHCP settings such as NTP, TFTP and Option 150/Option 160 (VoIP options).
Figure 40 - DHCP configuration