- NetComm Modem Router User Guide
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Overview
- NB5 Package Contents Note
- Minimum System Requirements
- Front Indicators
- Back Panel
- Resetting Factory Defaults
- Do I need a Micro filter?
- Default Settings
- Quick Start Guide
- Connecting your NB5 ADSL Modem via ETHERNET
- Connecting your NB5 ADSL Modem via USB
- Setting up your ADSL Router
- Log into your ADSL Router
- Quick Start Menu
- Connecting your ADSL Router
- Step 1: Connecting the ADSL Router to Your Computer/Notebook
- Step 1.1 Connecting to the Ethernet/USB
- Step 1.2 Connecting to the ADSL Line
- Step 1.3 Connecting to the Power Outlet
- Step 1.4 Powering On
- Step 2: Configuring Your Ethernet Network Card / Installing Your USB Device
- 2.1 Configuring Your Ethernet Network Card
- 2.2 Installing the USB Device Driver
- Step 3: Configuring Your Internet Browser
- Step 4: Connecting to the Internet
- Firewall Configuration
- Introduction to Firewalls
- Network Address Translation and Port Mapping
- Dedicated Firewalls
- Advanced Configuration of your ADSL Router
- Log into your ADSL Router
- Advanced Configuration of your ADSL Router-Login Settings
- Advanced Menus
- Introduction to Setup and Advanced Menus
- Configuring the ADSL Connection
- The Setup Menu
- WAN Setup
- PPPoE Connection
- PPPoA Connection Setup
- DHCP Connection Setup
- Static Connection Setup
- Bridged Connection Setup
- CLIP [Classical IP over ATM] Connection Setup
- LAN Setup
- DHCP Configuration
- Management IP
- The Advanced Menu
- UPnP
- SNMP
- IP QoS
- LAN Clients
- MAC Filter Control
- Enable/Disable MAC Filtering
- Create MAC Filter Rules
- Edit or Delete MAC Filter Rules
- Hidden MAC Filter Rules
- Multicasting
- Static Routing
- Dynamic Routing
- Port Forwarding
- Access Control
- IP Filters
- DMZ Configuration
- Tools Menu
- System Commands
- User Management
- Update Firmware
- Ping Test
- Modem Test
- Reboot
- Log Out
- Status Menu
- Network Statistics
- Connection Status
- DHCP Clients
- Modem Status
- Product Information
- System Log
- Appendix A: Troubleshooting
- The ADSL Router is not functional
- I can't connect to the ADSL Router.
- The DSL Link LED continues to blink but does not go solid
- The DSL Link LED is always off
- Appendix B: ADSL Router terms
- What is a firewall?
- What is NAT?
- What is a DMZ?
- What is a Gateway?
- Appendix C: Features
- ADSL/ATM Support
- Encapsulation Support
- Network Support
- Management Support
- Security Support
- External Connectors:
- Appendix D: Cable Connections
- RJ-45 Network Ports
- Twisted pair cables
- Straight and crossover cable configuration
- RJ11 connector and cable
- 605 to RJ-11 adapter
- USB cable
- 9 Pin (RS-232 ) Serial Cable
- Appendix E: Registering your NetComm Product
- Contact Information
- Legal & Regulatory Information
- Product Warranty
YML717 Rev1 NetComm NB5 Ethernet/USB Modem Router
www.netcomm.com.au 51
If the total number of network nodes is greater than the range of available IP addresses, the DHCP
server will run out of DHCP addresses, and some users will not get access to network resources. If
this happens you can either (1) increase the Ending IP address (to the limit of 255) or (2) reduce the
Lease Time. (see below)
Caution: If you change the Start IP or End IP values, ensure the values are still within
the same subnet as the Routers' IP address. In other words, if the Routers'
IP address is 192.168.1.1 (default) and you change the DHCP Start/End IP
addresses to be 192.128.1.2/192.128.1.100, you will not be able to
communicate with the ADSL Router if your PC has DHCP enabled.
DHCP Lease Time
The Lease Time is the amount of time a network user will be allowed connection to the ADSL
Router with their current dynamic IP address. The amount of time is in units of minutes; the default
value is 3600 minutes (60 hours). In a situation where a number of casual users need to be connected
for relatively short periods this default value is frequently set at a lower value.
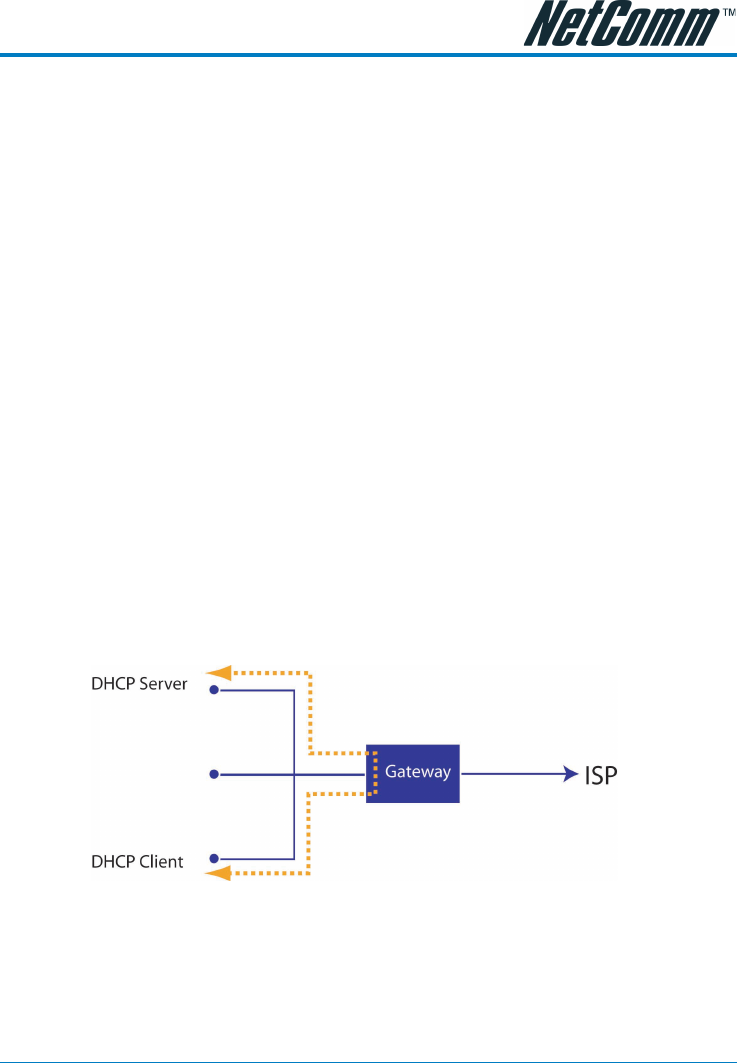
DHCP Relay
DHCP relay allows requests and responses between a DHCP client and DHCP server to traverse the
Router between the LAN and WAN subnets. The DHCP relay is positioned on the LAN (DCHP
client) side. This will allow LAN DHCP clients to be assigned DHCP information (IP Address,
Subnet Mask and Default Gateway) from a DHCP server on the WAN (usually at the ISP).
Enable/Disable DHCP










