User`s manual
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Getting Started
- 3. Initial IP Address Configuration
- 4. Introducing Serial Port Operation Modes
- 5. Introducing OnCell Central and Ethernet Operation Modes
- 6. Using the Web Console
- 7. Cellular Network Settings
- 8. Configuring Serial Port Operation Modes
- 9. Configuring the Cellular-Enabling Ethernet Device
- 10. Configuring OnCell Central Management Software
- 11. Additional Serial Port Settings
- 12. System Management Settings
- 13. Software Installation/Configuration
- A. Pinouts and Cable Wiring
- B. RFC2217
- C. Dynamic Domain Name Server
- D. Well Known Port Numbers
- E. Auto IP Report Protocol
- F. GSM Alphabet
- G. Default Settings
OnCell G3111/G3151/G3211/G3251 Series User’s Manual Serial Port Operation Modes
9-2
Host to OnCell via Cellular
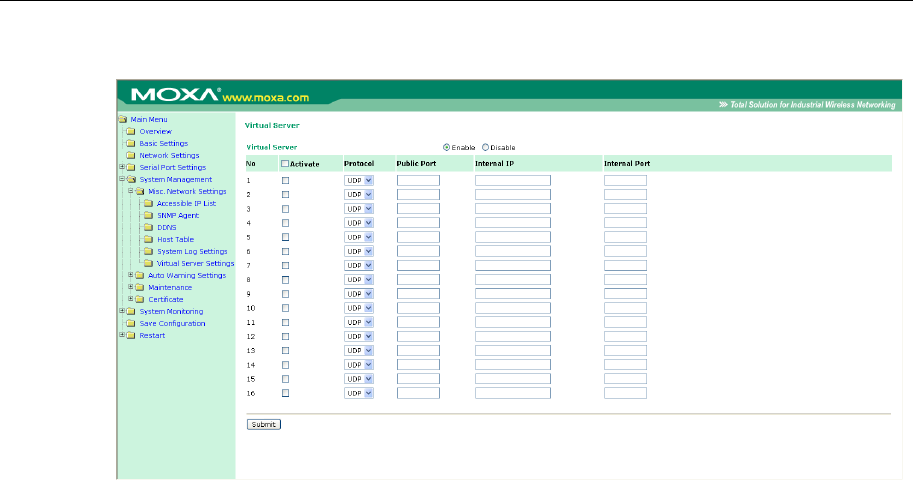
Virtual Server Settings (default=Disable): This function allows remote users to access the Host or
FTP services via a public IP address, and automatically redirects them to local servers in the LAN
(Local Area Network).
The OnCell firewall feature filters out unrecognized packets to protect your LAN network when
computers networked with the OnCell are hidden from public view. If you wish, you can make
some of the LAN computers accessible from the Internet by enabling Virtual Server. Depending on
the requested service, the OnCell redirects the external service request to the appropriate server
within the LAN network.
The OnCell is also capable of port-redirection, meaning incoming traffic to a particular port may
be redirected to a different port on the server computer.
Public Port: The public port is the port seen from the Internet side. Public ports cannot be set to
ports used by OP modes (950, 966, 4001, …)
Internal IP: Enter the IP address of the host on your local network that you want to link the
incoming service to.
Internal Port: The internal port is the port being used by the application on the host within your
local network.