User`s manual
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Getting Started
- 3. Initial IP Address Configuration
- 4. Introducing Serial Port Operation Modes
- 5. Introducing OnCell Central and Ethernet Operation Modes
- 6. Using the Web Console
- 7. Cellular Network Settings
- 8. Configuring Serial Port Operation Modes
- 9. Configuring the Cellular-Enabling Ethernet Device
- 10. Configuring OnCell Central Management Software
- 11. Additional Serial Port Settings
- 12. System Management Settings
- 13. Software Installation/Configuration
- A. Pinouts and Cable Wiring
- B. RFC2217
- C. Dynamic Domain Name Server
- D. Well Known Port Numbers
- E. Auto IP Report Protocol
- F. GSM Alphabet
- G. Default Settings
OnCell G3111/G3151/G3211/G3251 Series User’s Manual Serial Port Operation Modes
4-3
Device Control Applications
The OnCell G3111/G3151/G3211/G3251 offers the following modes for device control applications:
Real COM, Reverse Real COM, and RFC2217 modes.
Real COM Modes
The OnCell G3111/G3151/G3211/G3251 comes bundled with Moxa drivers for Windows
98/ME/NT/ 2000/XP/2003/2008/Vista systems and TTY drivers for Linux and Unix systems. (For
Windows systems, this option is only supported for Windows 2000, XP x86/x64, 2003 x86/x64,
Vista x86/x64, and 2008 x86/x64.)
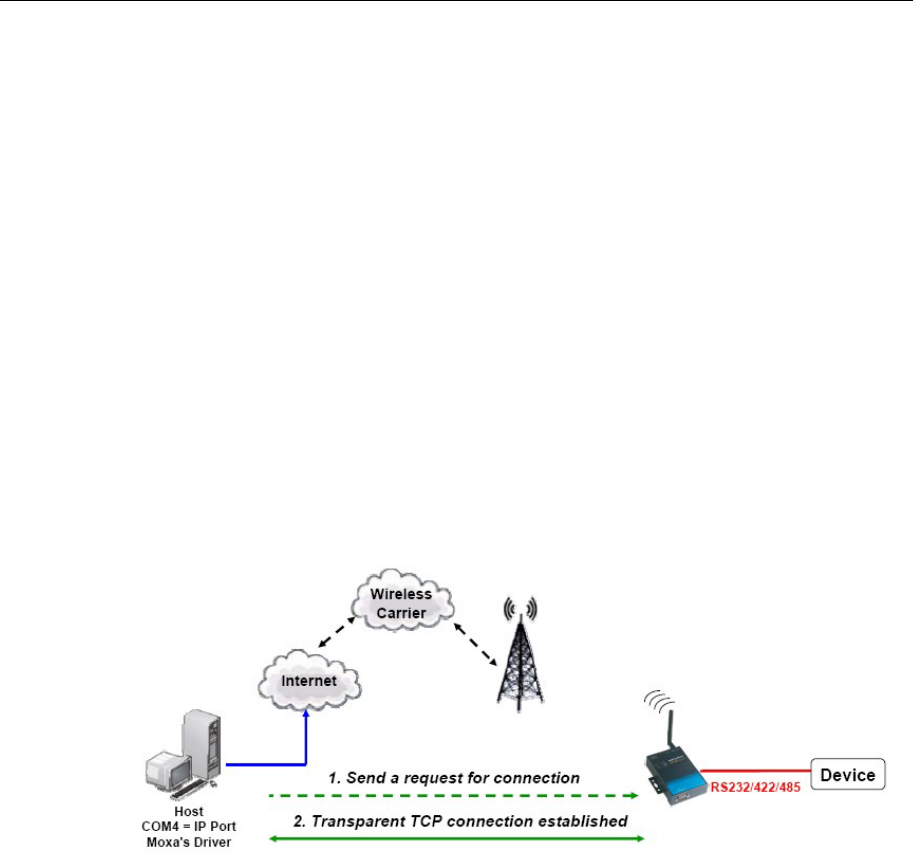
In Real COM mode, the bundled drivers are able to establish a transparent connection between a
host and a serial device by mapping the serial port on the OnCell G3111/G3151/G3211/G3251 to a
local COM/TTY port on the host computer. Real COM mode supports up to 2 simultaneous
connections that enable 2 hosts to simultaneously collect data from the same serial device.
One of the major conveniences of using Real COM mode is that it allows you to use software that
was written for pure serial communication applications. The OnCell COM driver intercepts data
sent to the host’s COM port, packs it into a TCP/IP packet, and then redirects it through the host’s
Ethernet card to the Internet. At the other end of the connection, the OnCell
G3111/G3151/G3211/G3251 accepts the IP frame from the cellular network, unpacks the TCP/IP
packet, and then transparently sends the data through the serial port to the attached serial device.