Specifications
4.2 Audio objects and principles 45
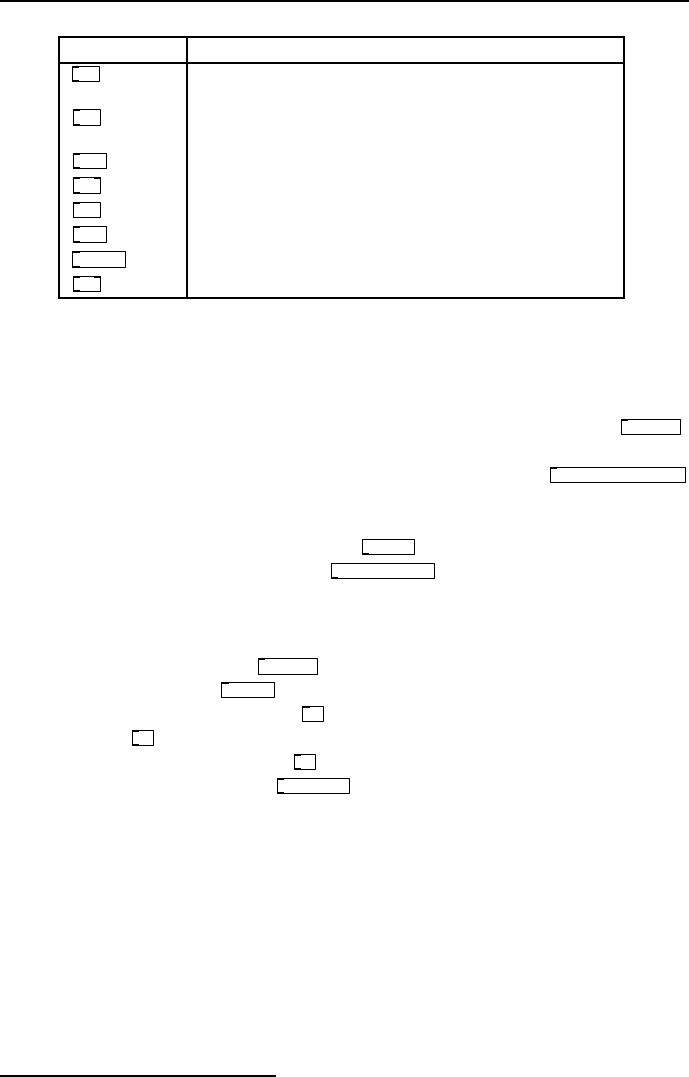
Object Function
cos~
Signal version of cosine function. Domain: −1.0 to +
1.0. Note the input domain is “rotation normalised”
sin~
Not intrinsic but defined in terms of signal cosine by
subtracting 0.25 from the input.
atan~
* Signal version of arctangent with normalised range.
log~
Signal version of natural log.
abs~
* Signal version of abs.
sqrt~
A square root for signals.
q8_sqrt~
A fast square root with less accuracy.
pow~
Signal version of power function.
fig 4.9: List of trig and higher math operators
Audio delay objects
Delaying an audio sig nal requires us to create a memory buffer using
delwrite~
.
Two arguments must be supplied at creation time, a unique name for the mem-
ory buffer and a maximum size in milliseconds. For example,
delwrite~ mydelay 500
creates a named delay buffer “mydelay” of size 500ms. This object can now
be used to write audio data to the delay buffer through its left inlet. Getting
delayed signals back from a buffer nee ds
delread~
. The only argument needed is
the name of a buffer to re ad from, so
delread~ mydelay
will listen to the contents of
mydelay. The delay time is set by a second argument, or by the left inlet. It
can r ange from zer o to the maximum buffer size. Setting a delay time larger
than the buffer results in a delay o f the maximum size . It is not pos sible to
alter the maximum size of a
delwrite~
buffer once created. But it is possible to
change the delay time of
delread~
for chorus a nd other effects. This often results
in clicks and pops
1
so we have a
vd~
variable-delay object. Instead of moving
the read point
vd~
changes the rate it reads the buffer, so we get tape echo and
Doppler shift type effects. Using
vd~
is as easy as before, c reate an object that
reads from a named buffer like
vd~ mydelay
. The left inlet (or argument following
the name) sets the delay time.
1
Hearing clicks when moving a delay read point is norm al , not a bug. There is no reason
to assume that wavforms will align nicely once we jump to a new location in the buffer. An
advanced solution crossfades between m ore than one buffer.










