User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Front Cover
- Manual number
- Table of Contents
- Positioning of This Manual
- Related Manuals
- Generic Names and Abbreviations Used in Manuals
- 1. Outline
- 2. Function List
- 2.1 Type Conversion Functions
- 2.2 Standard Functions Of One Numeric Variable
- 2.3 Standard Arithmetic Functions
- 2.4 Standard Bit Shift Functions
- 2.5 Standard Bitwise Boolean Functions
- 2.6 Standard Selection Functions
- 2.7 Standard Comparison Functions
- 2.8 Standard Character String Functions
- 2.9 Functions Of Time Data Types
- 2.10 Standard Function Blocks
- 3. Function Construction
- 4. How to Read Explanation of Functions
- 5. Applied Functions
- 5.1 Type Conversion Functions
- 5.1.1 BOOL_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.2 BOOL_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.3 BOOL_TO_STR(_E)
- 5.1.4 BOOL_TO_WORD(_E)
- 5.1.5 BOOL_TO_DWORD(_E)
- 5.1.6 BOOL_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.7 INT_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.8 DINT_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.9 INT_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.10 DINT_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.11 INT_TO_REAL(_E)
- 5.1.12 DINT_TO_REAL(_E)
- 5.1.13 INT_TO_STR(_E)
- 5.1.14 DINT_TO_STR(_E)
- 5.1.15 INT_TO_WORD(_E)
- 5.1.16 DINT_TO_WORD(_E)
- 5.1.17 INT_TO_DWORD(_E)
- 5.1.18 DINT_TO_DWORD(_E)
- 5.1.19 INT_TO_BCD(_E)
- 5.1.20 DINT_TO_BCD(_E)
- 5.1.21 INT_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.22 DINT_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.23 REAL_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.24 REAL_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.25 REAL_TO_STR(_E)
- 5.1.26 WORD_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.27 DWORD_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.28 WORD_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.29 WORD_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.30 DWORD_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.31 DWORD_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.32 WORD_TO_DWORD(_E)
- 5.1.33 DWORD_TO_WORD(_E)
- 5.1.34 WORD_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.35 DWORD_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.36 STR_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.37 STR_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.38 STR_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.39 STR_TO_REAL(_E)
- 5.1.40 STR_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.41 BCD_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.42 BCD_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.43 TIME_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.44 TIME_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.45 TIME_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.46 TIME_TO_STR(_E)
- 5.1.47 TIME_TO_WORD(_E)
- 5.1.48 TIME_TO_DWORD(_E)
- 5.2 Standard Functions Of One Numeric Variable
- 5.3 Standard Arithmetic Functions
- 5.4 Standard Bit Shift Functions
- 5.5 Standard Bitwise Boolean Functions
- 5.6 Standard Selection Functions
- 5.7 Standard Comparison Functions
- 5.8 Standard Character String Functions
- 5.9 Functions Of Time Data Types
- 5.1 Type Conversion Functions
- 6. Standard Function Blocks
- Appendix A: Correspondence between Devices and Addresses
- Warranty
- Revision History
- Back Cover
1 Outline
1.3 Cautions on Creation of Fundamental Programs
18
FXCPU Structured Programming Manual
(Application Functions)
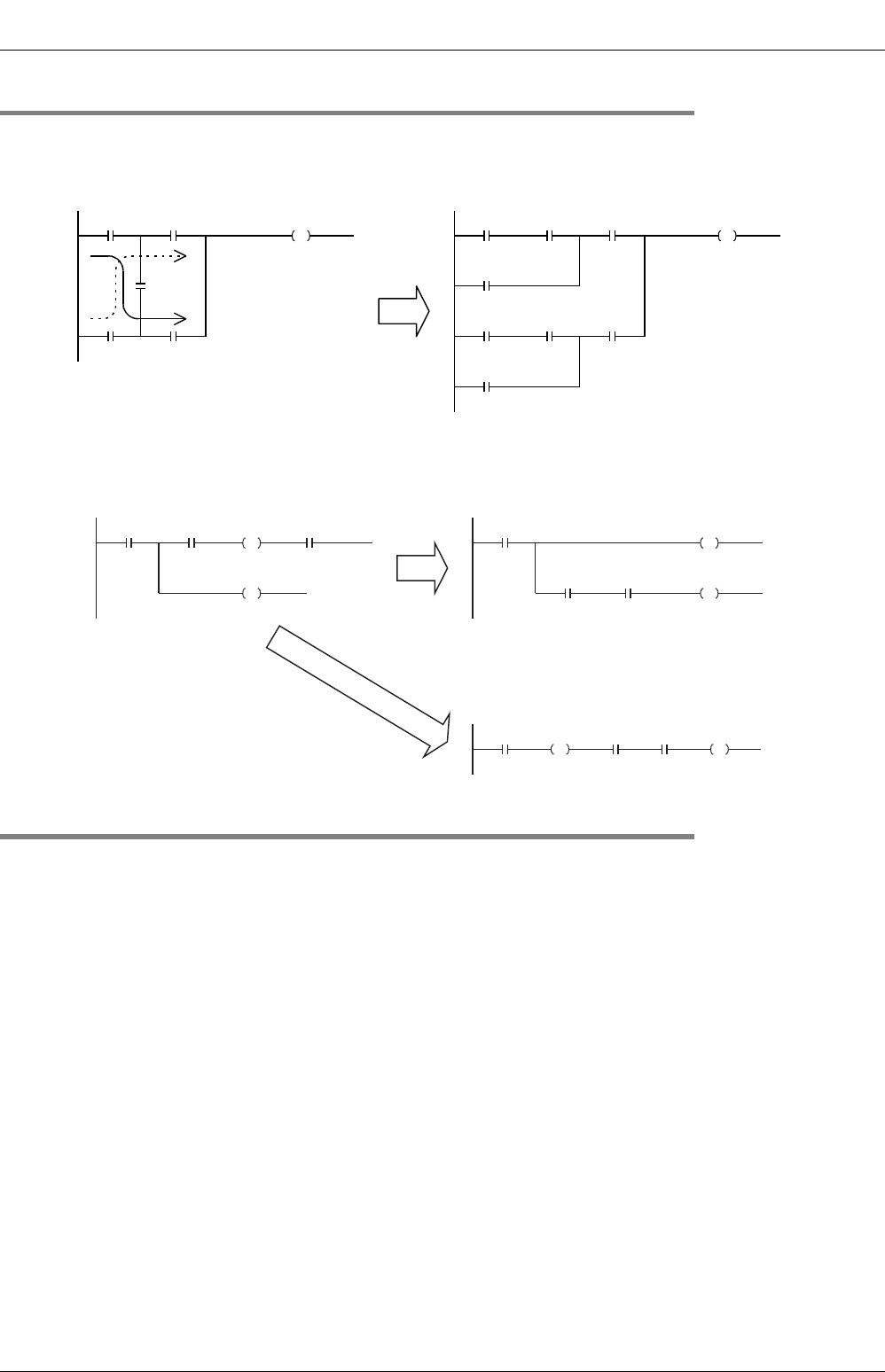
1.3.3 Circuits not available in structured ladder programs and countermeasures
1. Bridge circuit
A circuit in which the current flows in both directions should be changed as shown in the right figure (so that a
circuit without D and a circuit without B are connected in parallel).
2. Coil connection position
• You can program a contact on the right side of a coil. In this case, make sure to program a coil (including a
function or function block) at the end of the circuit.
1.3.4 Handling of general flags
The following flags are valid in general sequence instructions:
(Examples)
M8020:Zero flag M8021:Borrow flag M8022:Carry flag
M8029:Instruction execution complete flag M8090:Block comparison signal
*1
M8328:Instruction non-execution flag
*1
M8329:Instruction execution abnormal complete flag
*2
M8304:Zero flag
*1
M8306:Carry flag
*1
*1. Supported only in FX3U/FX3UC PLCs.
*2. Supported only in FX
3U/FX3UC/FX3G PLCs.
Each of these flags turns ON or OFF every time the PLC executes a corresponding instruction. These flags
do not turn ON or OFF when the PLC does not execute a corresponding instruction or when an error occurs.
Because these flags are related to many sequence instructions, their ON/OFF status changes every time the
PLC executes each corresponding instruction.
Refer to examples in the next page, and program a flag contact just under the target sequence instruction.
A B
C
E
D
C E
A
B
A E
C
D
F F
Or
A B D A
B D
C
E
CE
AB
E
D
C










