User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Front Cover
- Manual number
- Table of Contents
- Positioning of This Manual
- Related Manuals
- Generic Names and Abbreviations Used in Manuals
- 1. Outline
- 2. Function List
- 2.1 Type Conversion Functions
- 2.2 Standard Functions Of One Numeric Variable
- 2.3 Standard Arithmetic Functions
- 2.4 Standard Bit Shift Functions
- 2.5 Standard Bitwise Boolean Functions
- 2.6 Standard Selection Functions
- 2.7 Standard Comparison Functions
- 2.8 Standard Character String Functions
- 2.9 Functions Of Time Data Types
- 2.10 Standard Function Blocks
- 3. Function Construction
- 4. How to Read Explanation of Functions
- 5. Applied Functions
- 5.1 Type Conversion Functions
- 5.1.1 BOOL_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.2 BOOL_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.3 BOOL_TO_STR(_E)
- 5.1.4 BOOL_TO_WORD(_E)
- 5.1.5 BOOL_TO_DWORD(_E)
- 5.1.6 BOOL_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.7 INT_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.8 DINT_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.9 INT_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.10 DINT_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.11 INT_TO_REAL(_E)
- 5.1.12 DINT_TO_REAL(_E)
- 5.1.13 INT_TO_STR(_E)
- 5.1.14 DINT_TO_STR(_E)
- 5.1.15 INT_TO_WORD(_E)
- 5.1.16 DINT_TO_WORD(_E)
- 5.1.17 INT_TO_DWORD(_E)
- 5.1.18 DINT_TO_DWORD(_E)
- 5.1.19 INT_TO_BCD(_E)
- 5.1.20 DINT_TO_BCD(_E)
- 5.1.21 INT_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.22 DINT_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.23 REAL_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.24 REAL_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.25 REAL_TO_STR(_E)
- 5.1.26 WORD_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.27 DWORD_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.28 WORD_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.29 WORD_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.30 DWORD_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.31 DWORD_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.32 WORD_TO_DWORD(_E)
- 5.1.33 DWORD_TO_WORD(_E)
- 5.1.34 WORD_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.35 DWORD_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.36 STR_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.37 STR_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.38 STR_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.39 STR_TO_REAL(_E)
- 5.1.40 STR_TO_TIME(_E)
- 5.1.41 BCD_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.42 BCD_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.43 TIME_TO_BOOL(_E)
- 5.1.44 TIME_TO_INT(_E)
- 5.1.45 TIME_TO_DINT(_E)
- 5.1.46 TIME_TO_STR(_E)
- 5.1.47 TIME_TO_WORD(_E)
- 5.1.48 TIME_TO_DWORD(_E)
- 5.2 Standard Functions Of One Numeric Variable
- 5.3 Standard Arithmetic Functions
- 5.4 Standard Bit Shift Functions
- 5.5 Standard Bitwise Boolean Functions
- 5.6 Standard Selection Functions
- 5.7 Standard Comparison Functions
- 5.8 Standard Character String Functions
- 5.9 Functions Of Time Data Types
- 5.1 Type Conversion Functions
- 6. Standard Function Blocks
- Appendix A: Correspondence between Devices and Addresses
- Warranty
- Revision History
- Back Cover
5.6 Standard Selection Functions
164
FXCPU Structured Programming Manual
(Application Functions)
5.6.2 MAXIMUM(_E)
Outline
This function searches the maximum value among data, and outputs the maximum value.
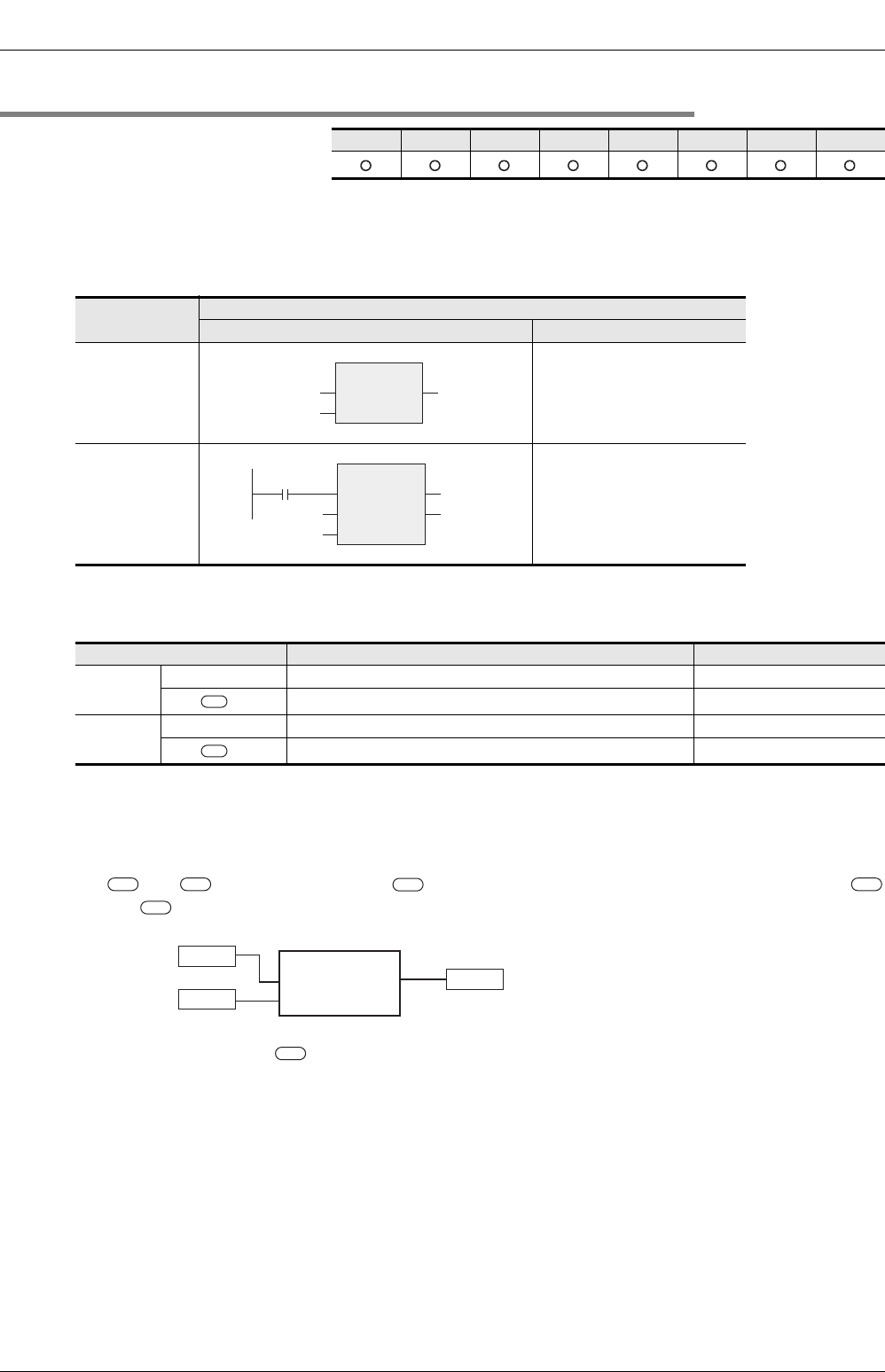
1. Format
*1. Output variable
2. Set data
In explanation of functions, I/O variables inside ( ) are described.
Explanation of function and operation
1) This function outputs the maximum value among ANY_SIMPLE type data stored in devices specified in
and to a device specified in using the data type of data stored in devices specified in
and .
Example: When the data type is word [signed]
2) The number of pins in can be changed.
Cautions
1) Use the function having "_E" in its name to connect a bus.
2) When handling 32-bit data in structured programs, you cannot specify 16-bit devices directly, different
from simple projects. Use labels when handling 32-bit data.
You can specify 32-bit counters directly, however, because they are 32-bit devices.
Use global labels when specifying labels.
FX3U(C) FX3G FX2N(C) FX1N(C) FX1S
FX
U
/FX
2C
FX0N FX0(S)
Function name
Expression in each language
Structured ladder ST
MAXIMUM
MAXIMUM(_IN,_IN);
Example:
D20:=
MAXIMUM(D0,D10);
MAXIMUM_E
MAXIMUM_E(EN,_IN,_IN,Output
label);
Example:
MAXIMUM_E(X000,D0,D10,D20);
Variable Description Data type
Input
variable
EN Execution condition Bit
_IN ( …)
Compared data, or word device which stores such data ANY_SIMPLE
Output
variable
ENO Execution status Bit
*1 ( )
Word device which will store the maximum value ANY_SIMPLE
MAXIMUM
*1
D20D0 _IN
_IND10
MAXIMUM_E
EN ENO
*1
D20
X000
D0
_IN
_IND10
s1
d
s1
s2
d
s1
s2
MAXIMUM
_IN
_IN
1234
5678
5678
Word [signed] data
Word [signed] data
Word [signed] data
s










