User manual
Table Of Contents
- CHAPTER 1
- CHAPTER 2
- mikroC PRO for PIC32
- Environment
- Main Menu Options
- File
- Edit
- View
- Project
- Build
- Run
- Tools
- Help
- mikroC PRO for PIC32 IDE
- Code Editor
- Code Explorer
- Project Manager
- Project Settings
- Library Manager
- Routine List
- Statistics
- Messages Window
- Quick Converter
- Macro Editor
- Image Preview
- Toolbars
- Customizing IDE Layout
- Options
- Integrated Tools
- Active Comments
- Export Project
- Jump To Interrupt
- Regular Expressions
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- CHAPTER 3
- CHAPTER 4
- CHAPTER 5
- CHAPTER 6
- CHAPTER 7
- CHAPTER 8
- mikroC PRO for PIC32 Language Reference
- Lexical Elements Overview
- Whitespace
- Comments
- Tokens
- Constants
- Integer Constants
- Floating Point Constants
- Character Constants
- String Constants
- Enumeration Constants
- Pointer Constants
- Constant Expressions
- Keywords
- Identifiers
- Punctuators
- Concepts
- Objects
- Scope and Visibility
- Name Spaces
- Duration
- Types
- Fundamental Types
- Arithmetic Types
- Enumerations
- Void Type
- Derived Types
- Arrays
- Pointers
- Pointer Arithmetic
- Structures
- Working with Structures
- Structure Member Access
- Unions
- Bit Fields
- Types Conversions
- Standard Conversions
- Explicit Types Conversions (Typecasting)
- Declarations
- Linkage
- Storage Classes
- Type Qualifiers
- Typedef Specifier
- asm Declaration
- Initialization
- Functions
- Function Calls and Argument Conversions
- Ellipsis (‘...’) Operator
- Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Logical Operators
- Conditional Operator ? :
- Assignment Operators
- Unary Operators
- Sizeof Operator
- Expressions
- Comma Expressions
- Statements
- Labeled Statements
- Expression Statements
- Selection Statements
- If Statement
- Switch Statement
- Iteration Statements (Loops)
- Do Statement
- For Statement
- Jump Statements
- Break and Continue Statements
- Goto Statement
- Return Statement
- Compound Statements (Blocks)
- Preprocessor
- Preprocessor Directives
- Macros
- File Inclusion
- Preprocessor Operators
- Conditional Compilation
- CHAPTER 9
- mikroC PRO for PIC32 Libraries
- Hardware Libraries
- Standard ANSI C Libraries
- Miscellaneous Libraries
- Hardware Libraries
- ADC Library
- CANSPI Library
- Library Dependency Tree
- External dependencies of CANSPI Library
- Library Routines
- CANSPISetOperationMode
- CANSPIGetOperationMode
- CANSPIInitialize
- CANSPISetBaudRate
- CANSPISetMask
- CANSPISetFilter
- CANSPIRead
- CANSPIWrite
- CANSPI Constants
- CANSPI_OP_MODE Constants
- CANSPI_CONFIG_FLAGS Constants
- CANSPI_TX_MSG_FLAGS Constants
- CANSPI_RX_MSG_FLAGS Constants
- CANSPI_MASK Constants
- CANSPI_FILTER Constants
- Library Example
- HW Connection
- Compact Flash Library
- Library Dependency Tree
- External dependencies of Compact Flash Library
- Library Routines
- Cf_Init
- Cf_Detect
- Cf_Enable
- Cf_Disable
- Cf_Read_Init
- Cf_Read_Byte
- Cf_Write_Init
- Cf_Write_Byte
- Cf_Read_Sector
- Cf_Write_Sector
- Cf_Fat_Init
- Cf_Fat_QuickFormat
- Cf_Fat_Assign
- Cf_Fat_Reset
- Cf_Fat_Read
- Cf_Fat_Rewrite
- Cf_Fat_Append
- Cf_Fat_Delete
- Cf_Fat_Write
- Cf_Fat_Set_File_Date
- Cf_Fat_Get_File_Date
- Cf_Fat_Get_File_Date_Modified
- Cf_Fat_Get_File_Size
- Cf_Fat_Get_Swap_File
- Library Example
- HW Connection
- Epson S1D13700 Graphic Lcd Library
- External dependencies of the Epson S1D13700 Graphic Lcd Library
- Library Routines
- S1D13700_Init
- S1D13700_Write_Command
- S1D13700_Write_Parameter
- S1D13700_Read_Parameter
- S1D13700_Fill
- S1D13700_GrFill
- S1D13700_TxtFill
- S1D13700_Display_GrLayer
- S1D13700_Display_TxtLayer
- S1D13700_Set_Cursor
- S1D13700_Display_Cursor
- S1D13700_Write_Char
- S1D13700_Write_Text
- S1D13700_Dot
- S1D13700_Line
- S1D13700_H_Line
- S1D13700_V_Line
- S1D13700_Rectangle
- S1D13700_Box
- S1D13700_Rectangle_Round_Edges
- S1D13700_Rectangle_Round_Edges_Fill
- S1D13700_Circle
- S1D13700_Circle_Fill
- S1D13700_Image
- S1D13700_PartialImage
- Flash Memory Library
- Graphic Lcd Library
- Library Dependency Tree
- External dependencies of Graphic Lcd Library
- Glcd_Init
- Glcd_Set_Side
- Glcd_Set_X
- Glcd_Set_Page
- Glcd_Read_Data
- Glcd_Write_Data
- Glcd_Fill
- Glcd_Dot
- Glcd_Line
- Glcd_V_Line
- Glcd_H_Line
- Glcd_Rectangle
- Glcd_Rectangle_Round_Edges
- Glcd_Rectangle_Round_Edges_Fill
- Glcd_Box
- Glcd_Circle
- Glcd_Circle_Fill
- Glcd_Set_Font
- Glcd_Write_Char
- Glcd_Write_Text
- Glcd_Image
- Glcd_PartialImage
- I²C Library
- Keypad Library
- Lcd Library
- Manchester Code Library
- Memory Manager Library
- Multi Media Card Library
- Secure Digital Card
- Secure Digital High Capacity Card
- Library Dependency Tree
- External dependencies of MMC Library
- Library Routines
- Mmc_Init
- Mmc_Read_Sector
- Mmc_Write_Sector
- Mmc_Read_Cid
- Mmc_Read_Csd
- Mmc_Fat_Init
- Mmc_Fat_QuickFormat
- Mmc_Fat_Assign
- Mmc_Fat_Reset
- Mmc_Fat_Read
- Mmc_Fat_Rewrite
- Mmc_Fat_Append
- Mmc_Fat_Delete
- Mmc_Fat_Write
- Mmc_Fat_Set_File_Date
- Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Date
- Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Date_Modified
- Mmc_Fat_Get_File_Size
- Mmc_Fat_Get_Swap_File
- Library Example
- HW Connection
- OneWire Library
- Port Expander Library
- Library Dependency Tree
- External dependencies of Port Expander Library
- Library Routines
- Expander_Init
- Expander_Init_Advanced
- Expander_Read_Byte
- Expander_Write_Byte
- Expander_Read_PortA
- Expander_Read_PortB
- Expander_Read_PortAB
- Expander_Write_PortA
- Expander_Write_PortB
- Expander_Write_PortAB
- Expander_Set_DirectionPortA
- Expander_Set_DirectionPortB
- Expander_Set_DirectionPortAB
- Expander_Set_PullUpsPortA
- Expander_Set_PullUpsPortB
- Expander_Set_PullUpsPortAB
- Library Example
- HW Connection
- PS/2 Library
- PWM Library
- RS-485 Library
- Software I²C Library
- Software SPI Library
- Software UART Library
- Sound Library
- SPI Library
- SPI Ethernet Library
- Library Dependency Tree
- External dependencies of SPI Ethernet Library
- Library Routines
- SPI_Ethernet_Init
- SPI_Ethernet_Enable
- SPI_Ethernet_Disable
- SPI_Ethernet_doPacket
- SPI_Ethernet_putByte
- SPI_Ethernet_putBytes
- SPI_Ethernet_putConstBytes
- SPI_Ethernet_putString
- SPI_Ethernet_putConstString
- SPI_Ethernet_getByte
- SPI_Ethernet_getBytes
- SPI_Ethernet_UserTCP
- SPI_Ethernet_UserUDP
- SPI_Ethernet_getIpAddress
- Ethernet_getGwIpAddress
- SPI_Ethernet_getDnsIpAddress
- SPI_Ethernet_getIpMask
- SPI_Ethernet_confNetwork
- SPI_Ethernet_arpResolve
- SPI_Ethernet_sendUDP
- SPI_Ethernet_dnsResolve
- SPI_Ethernet_initDHCP
- SPI_Ethernet_doDHCPLeaseTime
- SPI_Ethernet_renewDHCP
- Library Example
- HW Connection
- SPI Ethernet ENC24J600 Library
- Library Dependency Tree
- External dependencies of SPI Ethernet ENC24J600 Library
- Library Routines
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_Init
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_Enable
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_Disable
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_doPacket
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_putByte
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_putBytes
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_putConstBytes
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_putString
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_putConstString
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_getByte
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_getBytes
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_UserTCP
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_UserUDP
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_getIpAddress
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_getGwIpAddress
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_getDnsIpAddress
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_getIpMask
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_confNetwork
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_arpResolve
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_sendUDP
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_dnsResolve
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_initDHCP
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_doDHCPLeaseTime
- SPI_Ethernet_24j600_renewDHCP
- SPI Graphic Lcd Library
- Library Dependency Tree
- External dependencies of SPI Lcd Library
- Library Routines
- SPI_Glcd_Init
- SPI_Glcd_Set_Side
- SPI_Glcd_Set_Page
- SPI_Glcd_Set_X
- SPI_Glcd_Read_Data
- SPI_Glcd_Write_Data
- SPI_Glcd_Fill
- SPI_Glcd_Dot
- SPI_Glcd_Line
- SPI_Glcd_V_Line
- SPI_Glcd_H_Line
- SPI_Glcd_Rectangle
- SPI_Glcd_Rectangle_Round_Edges
- SPI_Glcd_Rectangle_Round_Edges_Fill
- SPI_Glcd_Box
- SPI_Glcd_Circle
- SPI_Glcd_Circle_FIll
- SPI_Glcd_Set_Font
- SPI_Glcd_Write_Char
- SPI_Glcd_Write_Text
- SPI_Glcd_Image
- SPI_Glcd_PartialImage
- Library Example
- HW Connection
- SPI Lcd Library
- SPI Lcd8 (8-bit interface) Library
- SPI T6963C Graphic Lcd Library
- Library Dependency Tree
- External dependencies of SPI T6963C Graphic Lcd Library
- Library Routines
- SPI_T6963C_config
- SPI_T6963C_writeData
- SPI_T6963C_writeCommand
- SPI_T6963C_setPtr
- SPI_T6963C_waitReady
- SPI_T6963C_fill
- SPI_T6963C_dot
- SPI_T6963C_write_char
- SPI_T6963C_write_text
- SPI_T6963C_line
- SPI_T6963C_rectangle
- SPI_T6963C_rectangle_round_edges
- SPI_T6963C_rectangle_round_edges_fill
- SPI_T6963C_box
- SPI_T6963C_circle
- SPI_T6963C_circle_fill
- SPI_T6963C_image
- SPI_T6963C_PartialImage
- SPI_T6963C_sprite
- SPI_T6963C_set_cursor
- SPI_T6963C_clearBit
- SPI_T6963C_setBit
- SPI_T6963C_negBit
- SPI_T6963C_displayGrPanel
- SPI_T6963C_displayTxtPanel
- SPI_T6963C_setGrPanel
- SPI_T6963C_setTxtPanel
- SPI_T6963C_panelFill
- SPI_T6963C_grFill
- SPI_T6963C_txtFill
- SPI_T6963C_cursor_height
- SPI_T6963C_graphics
- SPI_T6963C_text
- SPI_T6963C_cursor
- SPI_T6963C_cursor_blink
- Library Example
- HW Connection
- T6963C Graphic Lcd Library
- Library Dependency Tree
- External dependencies of T6963C Graphic Lcd Library
- Library Routines
- T6963C_init
- T6963C_writeData
- T6963C_writeCommand
- T6963C_setPtr
- T6963C_waitReady
- T6963C_fill
- T6963C_dot
- T6963C_write_char
- T6963C_write_text
- T6963C_line
- T6963C_rectangle
- T6963C_rectangle_round_edges
- T6963C_rectangle_round_edges_fill
- T6963C_box
- T6963C_circle
- T6963C_circle_fill
- T6963C_image
- T6963C_PartialImage
- T6963C_sprite
- T6963C_set_cursor
- T6963C_clearBit
- T6963C_setBit
- T6963C_negBit
- T6963C_displayGrPanel
- T6963C_displayTxtPanel
- T6963C_setGrPanel
- T6963C_setTxtPanel
- T6963C_panelFill
- T6963C_grFill
- T6963C_txtFill
- T6963C_cursor_height
- T6963C_graphics
- T6963C_text
- T6963C_cursor
- T6963C_cursor_blink
- Library Example
- HW Connection
- TFT Library
- External dependencies of TFT Library
- Library Routines
- TFT_Init
- TFT_Set_Index
- TFT_Write_Command
- TFT_Write_Data
- TFT_Set_Active
- TFT_Set_Font
- TFT_Write_Char
- TFT_Write_Text
- TFT_Fill_Screen
- TFT_Dot
- TFT_Set_Pen
- TFT_Set_Brush
- TFT_Line
- TFT_H_Line
- TFT_V_Line
- TFT_Rectangle
- TFT_Rectangle_Round_Edges
- TFT_Circle
- TFT_Image
- TFT_Partial_Image
- TFT_Image_Jpeg
- TFT_RGBToColor16bit
- TFT_Color16bitToRGB
- HW Connection
- Touch Panel Library
- Touch Panel TFT Library
- UART Library
- USB Library
- Standard ANSI C Libraries
- ANSI C Ctype Library
- ANSI C Math Library
- ANSI C Stdlib Library
- ANSI C String Library
- Miscellaneous Libraries
- Button Library
- Conversions Library
- PrintOut Library
- Setjmp Library
- Sprint Library
- Time Library
- Trigonometry Library
- CHAPTER 10
- Tutorials
- Managing Project
- New Project
- New Project
- Customizing Projects
- Add/Remove Files from Project
- Source Files
- Edit Project
- Source Files
- Clean Project Folder
- Compilation
- Creating New Library
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I use your compilers and programmer on Windows Vista (Windows 7) ?
- I am getting “Access is denied” error in Vista, how to solve this problem ?
- What are differences between mikroC PRO, mikroPascal PRO and mikroC PRO compilers ? Why do they have different prices ?
- Why do your PIC compilers don’t support 12F508 and some similar chips ?
- What are limitations of demo versions of mikroElektronika’s compilers ?
- Why do I still get demo limit error when I purchased and installed license key ?
- I have bought license for the older version, do I have to pay license for the new version of the compiler ?
- Do your compilers work on Windows Vista (Windows 7) ?
- What does this function/procedure/routine do ?
- I try to compile one of the provided examples and nothing happens, what is the problem?
- Can I get your library sources ? I need to provide all sources with my project.
- Can I use code I developed in your compilers in commercial purposes ? Are there some limitations ?
- Why does an example provided with your compilers doesn’t work ?
- Your example works if I use the same MCU you did, but how to make it work for another MCU ?
- I need this project finished, can you help me ?
- Do you have some discount on your compilers/development systems for students/professors ?
- I have a question about your compilers which is not listed here. Where can I find an answer ?
198
mikoC PRO for PIC32
MikroElektronika
Floating-point Types
The types oat and double, together with the long double variant, are considered to be oating-point types. The
mikroC PRO for PIC32’s implementation of an ANSI Standard considers all three to be the same type.
Floating point in the mikroC PRO for PIC32 is implemented using the Microchip AN575 32-bit format (IEEE 754
compliant).
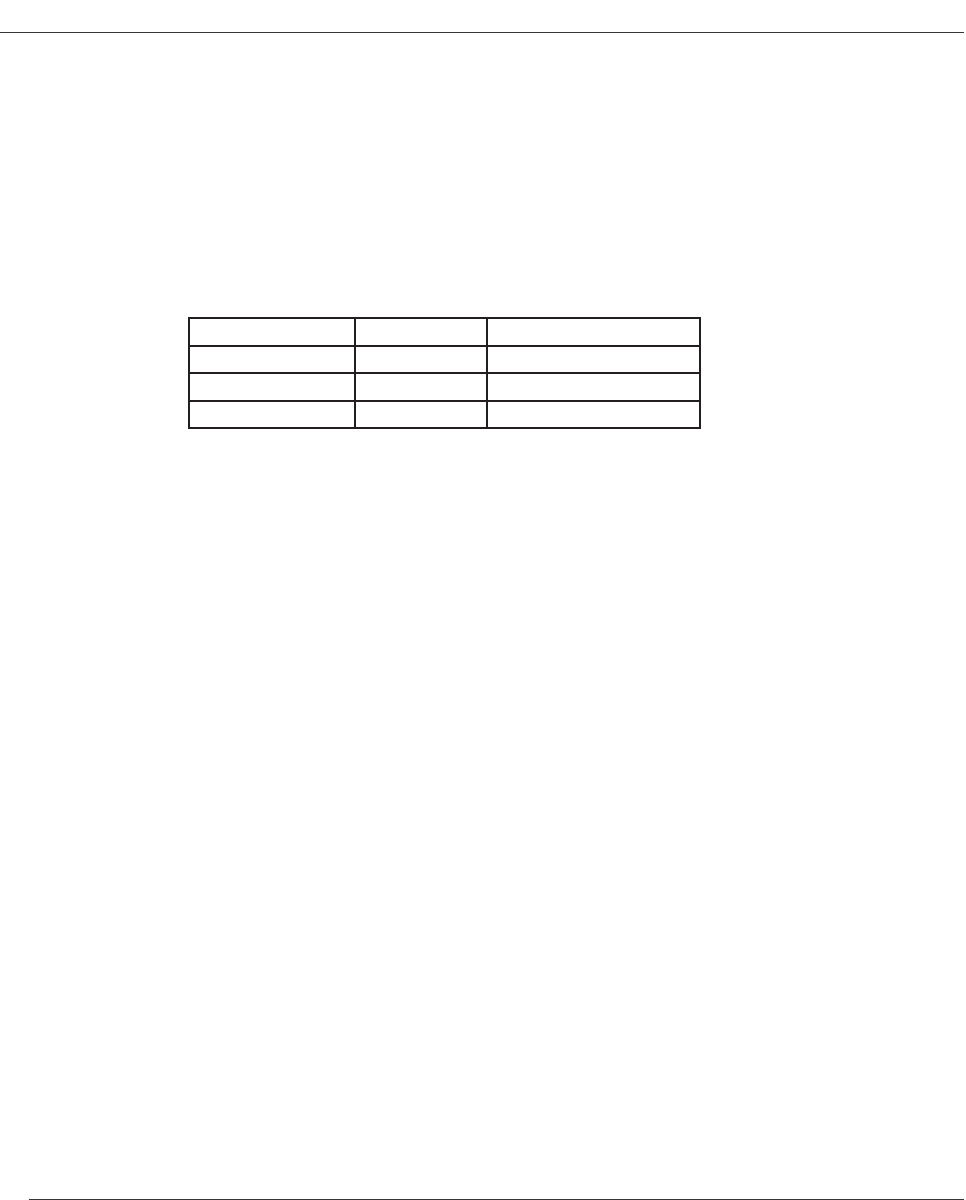
An overview of the oating-point types is shown in the table below:
Type Size in bytes Range
oat
4 -1.5 * 10
45
.. +3.4 * 10
38
double
4 -1.5 * 10
45
.. +3.4 * 10
38
long double
4 -1.5 * 10
45
.. +3.4 * 10
38
Enumerations
An enumeration data type is used for representing an abstract, discreet set of values with appropriate symbolic
names.
Enumeration Declaration
Enumeration is declared like this:
enum tag {enumeration-list};
Here, tag is an optional name of the enumeration; enumeration-list is a comma-delimited list of discreet values,
enumerators (or enumeration constants). Each enumerator is assigned a xed integral value. In the absence of explicit
initializers, the rst enumerator is set to zero, and the value of each succeeding enumerator is set to a value of its
predecessor increased by one.
Variables of the enum type are declared the same as variables of any other type. For example, the following
declaration:
enum colors { black, red, green, blue, violet, white } c;
establishes a unique integral type, enum colors, variable c of this type, and set of enumerators with constant integer
values (black = 0, red = 1, ...). In the mikroC PRO for PIC32, a variable of an enumerated type can be assigned any
value of the type int – no type checking beyond that is enforced. That is:
c = red; // OK
c = 1; // Also OK, means the same










