DIY Manual
18 | P a g e 10-543-1 REV A
DIY Manual
PV Panel Design – Factors and Considerations
Determining how many panels to buy, which panels to buy, how to wire them up, how many in
series, how many in parallel, how many combiner boxes are needed … all those considerations
must be simultaneously considered along with, “Which charge controller do I need?” and “How
many charge controllers?” and “What is the voltage of my battery bank?” That is why this
section on PV Design is important, to explain how to tie together all these disparate factors into
one final PV solution!
EXAMPLE:
• PV wattage needed – 8000W
• Batt bank voltage – 48V
• PV module Voc – 42Voc
• PV module Isc – 9.2A
• PV module wattage – 340W
In this example, we assume you found a good deal on these 340W panels, you bought a bunch
of them, and now you need to figure out the PV array. This approach is backwards, but
commonplace, hence this example.
The correct flow in designing a solar system is as follows:
1. Conduct load analysis;
2. Size battery bank;
3. Determine quantity of PV wattage to re-charge the batt bank; and
4. Select charge controller and determine PV array configuration concurrently.
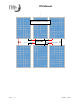
A combination of series/parallel is the most common manner to configure PV arrays when
using a charge controller, such as the Classic or KID.
Example PV specs: Voc = 39V; Isc = 9A; Wattage = 250W
This array has the following specifications:
• String voltage - 117Voc (3 x 39V)
• String current - 9A
• Array voltage - 117Voc
• Array current - 18A (2 x 9A)
• Array wattage – 1500W (6 x 250W)