DIY Manual
16 | P a g e 10-543-1 REV A
DIY Manual
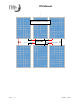
78V, 9A
702W*
To wire panels in series, is to connect one panel’s
positive wire to the next panel’s negative wire.
Positive-to-negative is a series connection, and the
individual panel volage adds.
Example: Voc = 39V; Isc = 9A. If the Voc is 39V, then
2 (in series) x 39V = 78V.
The PV string voltage is now 78V, as measured by a
multimeter via the string’s positive and negative
connections. And the string current remains the same
as for one panel (9A per panel, and 9A for the string).
To wire panels in parallel, is to connect one
panel’s positive wire to the next panel’s positive
wire. And the negative to negative.
Positive-to-positive, and negative-to-negative is
a parallel connection, and the individual panel
voltage remains the same, yet the current adds.
Example: Voc = 39V; Isc = 9A. The PV string
voltage is 39V and the array current is now 18A
(2 strings x 9A).
NOTE: This arrangement is now called a “PV
array.” This array is comprised of 2 strings.
Although each string only has 1 panel, this is still
a 2-string array.
39V, 18A
702W*
*NOTE: Wattage shown at 702W for both series and
parallel arrays shows the wattage stays the same
regardless of how the panels are wired. However, at
max Voc, the current is actually 0A. Conversely, at
max Isc, the voltage is 0V. Thus, the wattage is 0W
when these max theoretical values are used.
Series Connection
Parallel Connection