Datasheet
Table Of Contents
- High-Performance RISC CPU:
- Special Microcontroller Features:
- Low-Power Features:
- Peripheral Features:
- PIC16F631 Pin Diagram
- PIC16F677 Pin Diagram
- PIC16F685 Pin Diagram
- PIC16F687/689 Pin Diagram
- PIC16F690 Pin Diagram (PDIP, SOIC, SSOP)
- PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690 Pin Diagram (QFN)
- Most Current Data Sheet
- Errata
- Customer Notification System
- 1.0 Device Overview
- FIGURE 1-1: PIC16F631 Block Diagram
- FIGURE 1-2: PIC16F677 Block Diagram
- FIGURE 1-3: PIC16F685 Block Diagram
- FIGURE 1-4: PIC16F687/PIC16F689 Block Diagram
- FIGURE 1-5: PIC16F690 Block Diagram
- TABLE 1-1: Pinout Description - PIC16F631
- TABLE 1-2: Pinout Description - PIC16F677
- TABLE 1-3: Pinout Description - PIC16F685
- TABLE 1-4: Pinout Description - PIC16F687/PIC16F689
- TABLE 1-5: Pinout Description - PIC16F690
- 2.0 Memory Organization
- 2.1 Program Memory Organization
- 2.2 Data Memory Organization
- 2.2.1 General Purpose Register File
- 2.2.2 Special Function Registers
- FIGURE 2-4: PIC16F631 Special Function Registers
- FIGURE 2-5: PIC16F677 Special Function Registers
- FIGURE 2-6: PIC16F685 Special Function Registers
- FIGURE 2-7: PIC16F687/PIC16F689 Special Function Registers
- FIGURE 2-8: PIC16F690 Special Function Registers
- TABLE 2-1: PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690 Special Function Registers Summary Bank 0
- TABLE 2-2: PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690 Special Function Registers Summary Bank 1
- TABLE 2-3: PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690 Special Function Registers Summary Bank 2
- TABLE 2-4: PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690 Special Function Registers Summary Bank 3
- Register 2-1: STATUS: STATUS Register
- Register 2-2: OPTION_REG: Option Register
- Register 2-3: INTCON: Interrupt Control Register
- Register 2-4: PIE1: Peripheral Interrupt Enable Register 1
- Register 2-5: PIE2: Peripheral Interrupt Enable Register 2
- Register 2-6: PIR1: Peripheral Interrupt Request Register 1
- Register 2-7: PIR2: Peripheral Interrupt Request Register 2
- Register 2-8: PCON: Power Control Register
- 2.3 PCL and PCLATH
- 2.4 Indirect Addressing, INDF and FSR Registers
- 3.0 Oscillator Module (With Fail-Safe Clock Monitor)
- 4.0 I/O Ports
- 4.1 PORTA and the TRISA Registers
- 4.2 Additional Pin Functions
- 4.3 PORTB and TRISB Registers
- 4.4 Additional PORTB Pin Functions
- 4.5 PORTC and TRISC Registers
- 5.0 Timer0 Module
- 6.0 Timer1 Module with Gate Control
- 6.1 Timer1 Operation
- 6.2 Clock Source Selection
- 6.3 Timer1 Prescaler
- 6.4 Timer1 Oscillator
- 6.5 Timer1 Operation in Asynchronous Counter Mode
- 6.6 Timer1 Gate
- 6.7 Timer1 Interrupt
- 6.8 Timer1 Operation During Sleep
- 6.9 ECCP Capture/Compare Time Base
- 6.10 ECCP Special Event Trigger
- 6.11 Comparator Synchronization
- 6.12 Timer1 Control Register
- 7.0 Timer2 Module
- 8.0 Comparator Module
- 8.1 Comparator Overview
- 8.2 Comparator Control
- 8.3 Comparator Response Time
- 8.4 Comparator Interrupt Operation
- 8.5 Operation During Sleep
- 8.6 Effects of a Reset
- 8.7 Analog Input Connection Considerations
- 8.8 Additional Comparator Features
- 8.9 Comparator SR Latch
- 8.10 Comparator Voltage Reference
- 9.0 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Module
- FIGURE 9-1: ADC Block Diagram
- 9.1 ADC Configuration
- 9.2 ADC Operation
- 9.2.1 Starting A Conversion
- 9.2.2 Completion of a Conversion
- 9.2.3 Terminating a conversion
- 9.2.4 ADC Operation During Sleep
- 9.2.5 SPecial Event Trigger
- 9.2.6 A/D Conversion Procedure
- 9.2.7 ADC Register Definitions
- Register 9-1: ADCON0: A/D Control Register 0
- Register 9-2: ADCON1: A/D Control Register 1
- Register 9-3: ADRESH: ADC Result Register High (ADRESH) ADFM = 0
- Register 9-4: ADRESL: ADC Result Register Low (ADRESL) ADFM = 0
- Register 9-5: ADRESH: ADC Result Register High (ADRESH) ADFM = 1
- Register 9-6: ADRESL: ADC Result Register Low (ADRESL) ADFM = 1
- 9.3 A/D Acquisition Requirements
- 10.0 Data EEPROM and Flash Program Memory Control
- 10.1 EEADR and EEADRH Registers
- 10.2 Write Verify
- 10.3 Protection Against Spurious Write
- 10.4 Data EEPROM Operation During Code-Protect
- 11.0 Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Module
- TABLE 11-1: ECCP Mode - Timer Resources Required
- Register 11-1: CCP1CON: Enhanced CCP1 Control Register
- 11.1 Capture Mode
- 11.2 Compare Mode
- 11.3 PWM Mode
- 11.4 PWM (Enhanced Mode)
- FIGURE 11-5: Example Simplified Block Diagram of the Enhanced PWM Mode
- TABLE 11-4: example Pin Assignments for Various PWM Enhanced Modes
- FIGURE 11-6: Example PWM (enhanced Mode) Output Relationships (Active-High State)
- FIGURE 11-7: Example Enhanced PWM Output Relationships (Active-Low State)
- 11.4.1 Half-Bridge Mode
- 11.4.2 Full-Bridge Mode
- 11.4.3 Start-up Considerations
- 11.4.4 Enhanced PWM Auto-shutdown mode
- 11.4.5 Auto-Restart Mode
- 11.4.6 Programmable Dead-Band Delay mode
- 11.4.7 Pulse Steering Mode
- Register 11-4: PSTRCON: Pulse Steering Control Register(1)
- FIGURE 11-19: Simplified Steering Block Diagram
- FIGURE 11-20: Example of Steering Event at End of Instruction (STRSYNC = 0)
- FIGURE 11-21: Example of Steering Event at Beginning of Instruction (STRSYNC = 1)
- TABLE 11-5: Summary of Registers Associated with Capture, Compare and PWM
- 12.0 Enhanced Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (EUSART)
- FIGURE 12-1: EUSART Transmit Block Diagram
- FIGURE 12-2: EUSART Receive Block Diagram
- 12.1 EUSART Asynchronous Mode
- 12.2 Clock Accuracy with Asynchronous Operation
- 12.3 EUSART Baud Rate Generator (BRG)
- 12.4 EUSART Synchronous Mode
- 12.5 EUSART Operation During Sleep
- 13.0 SSP Module Overview
- 13.1 SPI Mode
- 13.2 Operation
- 13.3 Enabling SPI I/O
- 13.4 Typical Connection
- 13.5 Master Mode
- 13.6 Slave Mode
- 13.7 Slave Select Synchronization
- 13.8 Sleep Operation
- 13.9 Effects of a Reset
- 13.10 Bus Mode Compatibility
- 13.11 SSP I2C Operation
- 13.12 Slave Mode
- 13.13 Master Mode
- 13.14 Multi-Master Mode
- 14.0 Special Features of the CPU
- 14.1 Configuration Bits
- 14.2 Reset
- FIGURE 14-1: Simplified Block Diagram of On-chip Reset Circuit
- 14.2.1 Power-on Reset (POR)
- 14.2.2 MCLR
- 14.2.3 Power-up Timer (PWRT)
- 14.2.4 Brown-out Reset (BOR)
- 14.2.5 Time-out Sequence
- 14.2.6 Power Control (PCON) Register
- TABLE 14-1: Time-out in Various Situations
- TABLE 14-2: Status/PCON Bits and Their Significance
- TABLE 14-3: Summary of Registers Associated with Brown-out
- FIGURE 14-4: Time-out Sequence On Power-up (Delayed MCLR): Case 1
- FIGURE 14-5: Time-out Sequence On Power-up (Delayed MCLR): Case 2
- FIGURE 14-6: Time-out Sequence on Power-up (MCLR with Vdd)
- TABLE 14-4: Initialization Condition for Register
- TABLE 14-5: Initialization Condition for Special Registers
- 14.3 Interrupts
- 14.4 Context Saving During Interrupts
- 14.5 Watchdog Timer (WDT)
- 14.6 Power-Down Mode (Sleep)
- 14.7 Code Protection
- 14.8 ID Locations
- 14.9 In-Circuit Serial Programming
- 15.0 Instruction Set Summary
- 16.0 Development Support
- 16.1 MPLAB Integrated Development Environment Software
- 16.2 MPASM Assembler
- 16.3 MPLAB C18 and MPLAB C30 C Compilers
- 16.4 MPLINK Object Linker/ MPLIB Object Librarian
- 16.5 MPLAB ASM30 Assembler, Linker and Librarian
- 16.6 MPLAB SIM Software Simulator
- 16.7 MPLAB ICE 2000 High-Performance In-Circuit Emulator
- 16.8 MPLAB REAL ICE In-Circuit Emulator System
- 16.9 MPLAB ICD 2 In-Circuit Debugger
- 16.10 MPLAB PM3 Device Programmer
- 16.11 PICSTART Plus Development Programmer
- 16.12 PICkit 2 Development Programmer
- 16.13 Demonstration, Development and Evaluation Boards
- 17.0 Electrical Specifications
- Absolute Maximum Ratings(†)
- 17.1 DC Characteristics: PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690-I (Industrial) PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690-E (Extended)
- 17.2 DC Characteristics: PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690-I (Industrial) PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690-E (Extended)
- 17.3 DC Characteristics: PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690-E (Extended)
- 17.4 DC Characteristics: PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690-I (Industrial) PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690-E (Extended)
- 17.5 Thermal Considerations
- 17.6 Timing Parameter Symbology
- 17.7 AC Characteristics: PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690 (Industrial, Extended)
- FIGURE 17-4: Clock Timing
- TABLE 17-1: Clock Oscillator Timing Requirements
- TABLE 17-2: Oscillator Parameters
- FIGURE 17-5: CLKOUT and I/O Timing
- TABLE 17-3: CLKOUT and I/O Timing Parameters
- FIGURE 17-6: Reset, Watchdog Timer, Oscillator Start-up Timer and Power-up Timer Timing
- FIGURE 17-7: Brown-out Reset Timing and Characteristics
- TABLE 17-4: Reset, Watchdog Timer, Oscillator Start-up Timer, Power-up Timer and Brown-out Reset Parameters
- FIGURE 17-8: Timer0 and Timer1 External Clock Timings
- TABLE 17-5: Timer0 and Timer1 External Clock Requirements
- FIGURE 17-9: Capture/Compare/PWM Timings (ECCP)
- TABLE 17-6: Capture/Compare/PWM Requirements (ECCP)
- TABLE 17-7: Comparator Specifications
- TABLE 17-8: Comparator Voltage Reference (CVref) Specifications
- TABLE 17-9: Voltage (VR) Reference Specifications
- FIGURE 17-10: EUSART Synchronous Transmission (Master/Slave) Timing
- TABLE 17-10: EUSART Synchronous Transmission Requirements
- FIGURE 17-11: EUSART Synchronous Receive (Master/Slave) Timing
- TABLE 17-11: EUSART Synchronous Receive Requirements
- FIGURE 17-12: SPI Master Mode Timing (CKE = 0, SMP = 0)
- FIGURE 17-13: SPI Master Mode Timing (CKE = 1, SMP = 1)
- FIGURE 17-14: SPI Slave Mode Timing (CKE = 0)
- FIGURE 17-15: SPI Slave Mode Timing (CKE = 1)
- TABLE 17-12: SPI Mode requirements
- FIGURE 17-16: I2C™ Bus Start/Stop Bits Timing
- TABLE 17-13: I2C™ Bus Start/Stop Bits Requirements
- FIGURE 17-17: I2C™ Bus Data Timing
- TABLE 17-14: I2C™ Bus Data Requirements
- TABLE 17-15: A/D Converter (ADC) Characteristics:
- FIGURE 17-18: A/D Conversion Timing (Normal Mode)
- TABLE 17-16: A/D Conversion Requirements
- FIGURE 17-19: A/D Conversion Timing (Sleep Mode)
- 18.0 DC and AC Characteristics Graphs and Tables
- FIGURE 18-1: Typical Idd vs. Fosc Over Vdd (EC Mode)
- FIGURE 18-2: Maximum Idd vs. Fosc Over Vdd (EC Mode)
- FIGURE 18-3: Typical Idd vs. Fosc Over Vdd (HS Mode)
- FIGURE 18-4: Maximum Idd vs. Fosc Over Vdd (HS Mode)
- FIGURE 18-5: Typical Idd vs. Vdd Over Fosc (XT Mode)
- FIGURE 18-6: Maximum Idd vs. Vdd Over Fosc (XT Mode)
- FIGURE 18-7: Idd vs. Vdd (LP Mode)
- FIGURE 18-8: Typical Idd vs. Vdd Over Fosc (EXTRC Mode)
- FIGURE 18-9: Maximum Idd vs. Vdd Over Fosc (EXTRC Mode)
- FIGURE 18-10: Idd vs. Vdd Over Fosc (LFINTOSC Mode, 31 kHz)
- FIGURE 18-11: Typical Idd vs. Fosc Over Vdd (HFINTOSC Mode)
- FIGURE 18-12: Maximum Idd vs. Fosc Over Vdd (HFINTOSC Mode)
- FIGURE 18-13: Typical Ipd vs. Vdd (Sleep Mode, all Peripherals Disabled)
- FIGURE 18-14: Maximum Ipd vs. Vdd (Sleep Mode, all Peripherals Disabled)
- FIGURE 18-15: Comparator Ipd vs. Vdd (Both Comparators Enabled)
- FIGURE 18-16: BOR Ipd VS. Vdd Over Temperature
- FIGURE 18-17: Typical WDT Ipd VS. Vdd Over Temperature
- FIGURE 18-18: Maximum WDT Ipd VS. Vdd Over Temperature
- FIGURE 18-19: WDT Period VS. Vdd Over Temperature
- FIGURE 18-20: WDT Period VS. Temperature Over Vdd (5.0V)
- FIGURE 18-21: CVref Ipd VS. Vdd Over Temperature (High Range)
- FIGURE 18-22: CVref Ipd VS. Vdd Over Temperature (Low Range)
- FIGURE 18-23: Typical VP6 Reference Ipd vs. Vdd (25 C)
- FIGURE 18-24: Maximum VP6 Reference Ipd vs. Vdd Over Temperature
- FIGURE 18-25: T1OSC Ipd vs. Vdd Over Temperature (32 kHz)
- FIGURE 18-26: Vol VS. Iol Over Temperature (Vdd = 3.0V)
- FIGURE 18-27: Vol VS. Iol Over Temperature (Vdd = 5.0V)
- FIGURE 18-28: Voh VS. Ioh Over Temperature (Vdd = 3.0V)
- FIGURE 18-29: Voh VS. Ioh Over Temperature (Vdd = 5.0V)
- FIGURE 18-30: TTL Input Threshold Vin VS. Vdd Over Temperature
- FIGURE 18-31: Schmitt Trigger Input Threshold Vin VS. Vdd Over Temperature
- FIGURE 18-32: Comparator Response Time (Rising Edge)
- FIGURE 18-33: Comparator Response Time (Falling Edge)
- FIGURE 18-34: LFINTOSC Frequency vs. Vdd Over Temperature (31 kHz)
- FIGURE 18-35: ADC Clock Period vs. Vdd Over Temperature
- FIGURE 18-36: Typical HFINTOSC Start-Up Times vs. Vdd Over Temperature
- FIGURE 18-37: Maximum HFINTOSC Start-Up Times vs. Vdd Over Temperature
- FIGURE 18-38: Minimum HFINTOSC Start-Up Times vs. Vdd Over Temperature
- FIGURE 18-39: Typical HFINTOSC Frequency Change vs. Vdd (25 C)
- FIGURE 18-40: Typical HFINTOSC Frequency Change Over Device Vdd (85 C)
- FIGURE 18-41: Typical HFINTOSC Frequency Change vs. Vdd (125 C)
- FIGURE 18-42: Typical HFINTOSC Frequency Change vs. Vdd (-40 C)
- FIGURE 18-43: Typical VP6 Reference Voltage vs. Vdd (25 C)
- FIGURE 18-44: Typical VP6 Reference Voltage Over Temperature (3V)
- FIGURE 18-45: Typical VP6 Reference Voltage Over Temperature (5V)
- FIGURE 18-46: Typical VP6 Reference Voltage Distribution (3V, 25 C)
- FIGURE 18-47: Typical VP6 Reference Voltage Distribution (3V, 85 C)
- FIGURE 18-48: Typical VP6 Reference Voltage Distribution (3V, 125 C)
- FIGURE 18-49: Typical VP6 Reference Voltage Distribution (3V, -40 C)
- FIGURE 18-50: Typical VP6 Reference Voltage Distribution (5V, 25 C)
- FIGURE 18-51: Typical VP6 Reference Voltage Distribution (5V, 85 C)
- FIGURE 18-52: Typical VP6 Reference Voltage Distribution (5V, 125 C)
- FIGURE 18-53: Typical VP6 Reference Voltage Distribution (5V, -40 C)
- 19.0 Packaging Information
- Appendix A: Data Sheet Revision History
- Appendix B: Migrating from other PIC® Devices
- INDEX
- The Microchip Web Site
- Customer Change Notification Service
- Customer Support
- Reader Response
- Product Identification System
- Worldwide Sales
PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690
DS41262E-page 34 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
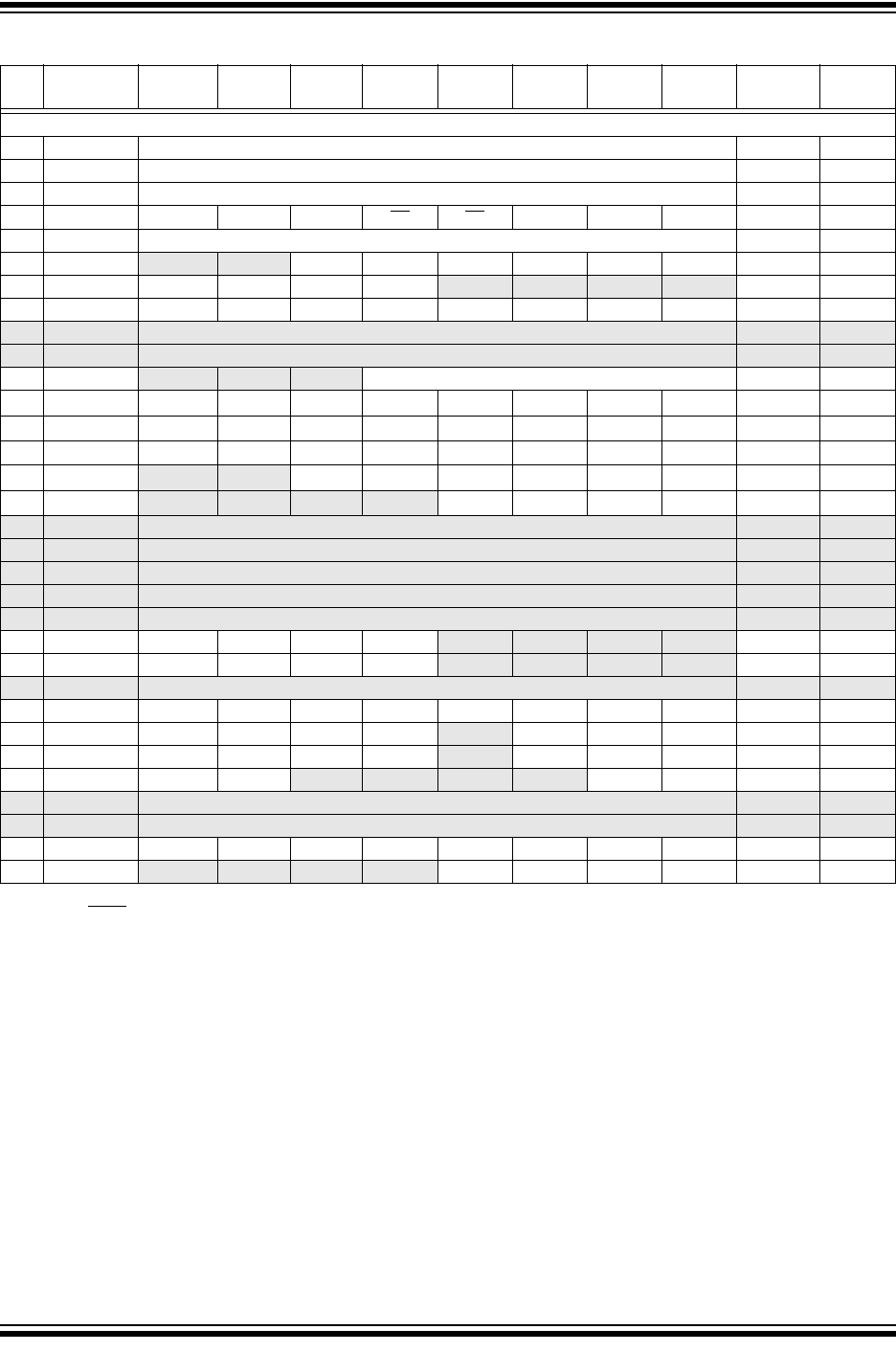
TABLE 2-3: PIC16F631/677/685/687/689/690 SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTERS SUMMARY BANK 2
Addr Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Value on
POR, BOR
Page
Bank 2
100h INDF Addressing this location uses contents of FSR to address data memory (not a physical register) xxxx xxxx 44,205
101h TMR0 Timer0 Module Register xxxx xxxx 81,205
102h PCL Program Counter’s (PC) Least Significant Byte 0000 0000 44,205
103h STATUS IRP RP1 RP0 TO
PD ZDCC0001 1xxx 36,205
104h FSR Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer xxxx xxxx 44,205
105h PORTA
(4)
— — RA5 RA4 RA3 RA2 RA1 RA0 --xx xxxx 59,205
106h PORTB
(4)
RB7 RB6 RB5 RB4 — — — — xxxx ---- 69,205
107h PORTC
(4)
RC7 RC6 RC5 RC4 RC3 RC2 RC1 RC0 xxxx xxxx 76,205
108h — Unimplemented — —
109h — Unimplemented — —
10Ah PCLATH
— — — Write Buffer for the upper 5 bits of the Program Counter ---0 0000 44,205
10Bh INTCON GIE PEIE T0IE INTE RABIE T0IF INTF RABIF
(1)
0000 000x 38,205
10Ch
EEDAT EEDAT7 EEDAT6 EEDAT5 EEDAT4 EEDAT3 EEDAT2 EEDAT1 EEDAT0 0000 0000 120,206
10Dh
EEADR EEADR7
(3)
EEADR6 EEADR5 EEADR4 EEADR3 EEADR2 EEADR1 EEADR0 0000 0000 120,206
10Eh EEDATH
(2)
— —
EEDATH5 EEDATH4 EEDATH3 EEDATH2 EEDATH1 EEDATH0
--00 0000 120,206
10Fh EEADRH
(2)
— — — —
EEADRH3 EEADRH2 EEADRH1 EEADRH0
---- 0000 120,206
110h — Unimplemented — —
111h — Unimplemented — —
112h — Unimplemented — —
113h — Unimplemented — —
114h — Unimplemented — —
115h WPUB WPUB7 WPUB6 WPUB5 WPUB4
— — — — 1111 ---- 70,206
116h IOCB IOCB7 IOCB6 IOCB5 IOCB4
— — — — 0000 ---- 70,206
117h — Unimplemented — —
118h VRCON C1VREN C2VREN VRR VP6EN VR3 VR2 VR1 VR0 0000 0000 105,206
119h CM1CON0 C1ON C1OUT
C1OE C1POL — C1R C1CH1 C1CH0 0000 -000 98,206
11Ah CM2CON0 C2ON C2OUT
C2OE C2POL — C2R C2CH1 C2CH0 0000 -000 99,206
11Bh CM2CON1 MC1OUT MC2OUT
— — — — T1GSS C2SYNC 00-- --10 101,206
11Ch — Unimplemented — —
11Dh — Unimplemented — —
11Eh ANSEL ANS7 ANS6 ANS5 ANS4 ANS3
(3)
ANS2
(3)
ANS1 ANS0 1111 1111 61,206
11Fh ANSELH
(3)
— — — — ANS11 ANS10 ANS9 ANS8 ---- 1111 11 5,206
Legend: – = Unimplemented locations read as ‘0’, u = unchanged, x = unknown, q = value depends on condition, shaded = unimplemented
Note 1: MCLR
and WDT Reset does not affect the previous value data latch. The RABIF bit will be cleared upon Reset but will set again if the
mismatch exists.
2: PIC16F685/PIC16F689/PIC16F690 only.
3: PIC16F677/PIC16F685/PIC16F687/PIC16F689/PIC16F690 only.
4: Port pins with analog functions controlled by the ANSEL and ANSELH registers will read ‘0’ immediately after a Reset even though the
data latches are either undefined (POR) or unchanged (other Resets).










