Datasheet
Table Of Contents
- Package Types
- Typical Application
- 1.0 Electrical Characteristics
- 2.0 Typical Performance Curves
- Figure 2-1: Input Offset Voltage
- Figure 2-2: Input Offset Voltage Drift
- Figure 2-3: Input Offset Voltage vs. Common Mode Input Voltage
- Figure 2-4: Input Offset Voltage vs. Common Mode Input Voltage
- Figure 2-5: Input Offset Voltage vs. Output Voltage
- Figure 2-6: Input Offset Voltage vs. Power Supply Voltage
- FIGURE 2-7: Input Noise Voltage Density vs. Frequency.
- FIGURE 2-8: Input Noise Voltage Density vs. Common Mode Input Voltage.
- FIGURE 2-9: CMRR, PSRR vs. Frequency.
- FIGURE 2-10: CMRR, PSRR vs. Ambient Temperature.
- FIGURE 2-11: Input Bias, Offset Currents vs. Ambient Temperature.
- FIGURE 2-12: Input Bias Current vs. Common Mode Input Voltage.
- FIGURE 2-13: Quiescent Current vs. Ambient Temperature.
- FIGURE 2-14: Quiescent Current vs. Common Mode Input Voltage.
- FIGURE 2-15: Quiescent Current vs. Common Mode Input Voltage.
- FIGURE 2-16: Quiescent Current vs. Power Supply Voltage.
- FIGURE 2-17: Open-Loop Gain, Phase vs. Frequency.
- FIGURE 2-18: DC Open-Loop Gain vs. Ambient Temperature.
- FIGURE 2-19: Gain Bandwidth Product, Phase Margin vs. Ambient Temperature.
- FIGURE 2-20: Gain Bandwidth Product, Phase Margin vs. Ambient Temperature.
- FIGURE 2-21: Output Short Circuit Current vs. Power Supply Voltage.
- FIGURE 2-22: Output Voltage Swing vs. Frequency.
- FIGURE 2-23: Output Voltage Headroom vs. Output Current.
- FIGURE 2-24: Output Voltage Headroom vs. Output Current.
- FIGURE 2-25: Output Voltage Headroom vs. Ambient Temperature.
- FIGURE 2-26: Output Voltage Headroom vs. Ambient Temperature.
- FIGURE 2-27: Slew Rate vs. Ambient Temperature.
- FIGURE 2-28: Small Signal Non-Inverting Pulse Response.
- FIGURE 2-29: Small Signal Inverting Pulse Response.
- FIGURE 2-30: Large Signal Non-Inverting Pulse Response.
- FIGURE 2-31: Large Signal Inverting Pulse Response.
- FIGURE 2-32: The MCP6491/2/4 Shows No Phase Reversal.
- FIGURE 2-33: Closed Loop Output Impedance vs. Frequency.
- FIGURE 2-34: Measured Input Current vs. Input Voltage (below VSS).
- FIGURE 2-35: Channel-to-Channel Separation vs. Frequency (MCP6492/4 only).
- 3.0 Pin Descriptions
- 4.0 Application Information
- 5.0 Design Aids
- 6.0 Packaging Information
- Appendix A: Revision History
- Product Identification System
- Trademarks
- Worldwide Sales and Service
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS20002321C-page 9
MCP6491/2/4
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, T
A
=+25°C, V
DD
= +2.4V to +5.5V, V
SS
= GND, V
CM
=V
DD
/2, V
OUT
V
DD
/2,
V
L
=V
DD
/2, R
L
=10kto V
L
and C
L
=20pF.
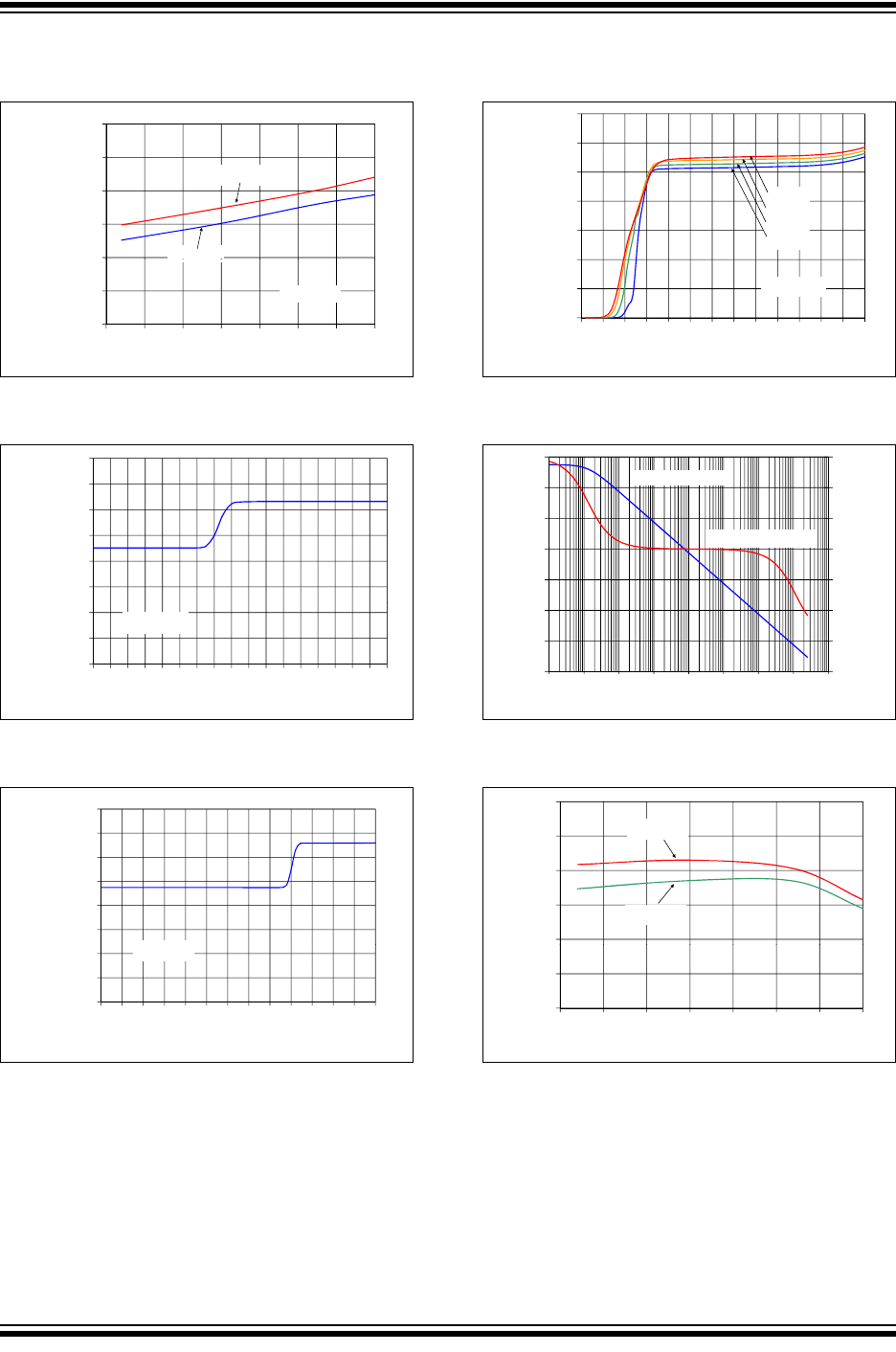
FIGURE 2-13: Quiescent Current vs.
Ambient Temperature.
FIGURE 2-14: Quiescent Current vs.
Common Mode Input Voltage.
FIGURE 2-15: Quiescent Current vs.
Common Mode Input Voltage.
FIGURE 2-16: Quiescent Current vs.
Power Supply Voltage.
FIGURE 2-17: Open-Loop Gain, Phase vs.
Frequency.
FIGURE 2-18: DC Open-Loop Gain vs.
Ambient Temperature.
500
525
550
575
600
Q
uiescent Current
(µA/Amplifier)
V
DD
= 5.5V
V
DD
= 2.4
V
450
475
500
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Q
Ambient Temperature (°C)
DD
V
CM
= V
DD
/4
450
500
550
600
650
700
Quiescent Current
(µA/Amplifier)
300
350
400
-0.5
-0.3
-0.1
0.1
0.3
0.5
0.7
0.9
1.1
1.3
1.5
1.7
1.9
2.1
2.3
2.5
2.7
2.9
Common Mode Input Voltage (V)
V
DD
= 2.4V
450
500
550
600
650
700
Quiescent Current
(µA/Amplifier)
V
V
300
350
400
-0.5
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
5.5
6.0
Common Mode Input Voltage (V)
V
DD
= 5.5
V
200
300
400
500
600
700
Q
uiescent Current
(µA/Amplifier)
+125°C
+85°C
+25°C
-40°C
0
100
200
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
5.5
6.0
6.5
Q
Power Supply Voltage (V)
V
CM
= V
DD
/4
-
150
-120
-90
-60
-30
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
e
n-Loop Phase (°)
e
n-Loop Gain (dB)
Open-Loop Gain
Open-Loop Phase
-210
-180
150
-20
0
20
1.0E+00 1.0E+01 1.0E+02 1.0E+03 1.0E+04 1.0E+05 1.0E+06 1.0E+07 1.0E+08
Op
e
Op
e
Frequency (Hz)
1 10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
110
120
130
140
150
pen-Loop Gain (dB)
V
DD
= 2.4V
V
DD
= 5.5V
90
100
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
DC O
Temperature (°C)










