Datasheet
2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS22331A-page 165
MCP19111
27.4.7 CLOCK STRETCHING
Clock stretching occurs when a device on the bus holds
the SCL line low, effectively pausing communication.
The slave may stretch the clock to allow more time to
handle data or prepare a response for the master
device. A master device is not concerned with
stretching, as anytime it is active on the bus and not
transferring data it is stretching. Any stretching done by
a slave is invisible to the master software and handled
by the hardware that generates SCL.
The CKP bit of the SSPCON1 register is used to control
stretching in software. Any time the CKP bit is cleared,
the module will wait for the SCL line to go low and then
hold it. Setting CKP will release SCL and allow more
communication.
27.4.7.1 Normal Clock Stretching
Following an ACK, if the R/W bit of the SSPSTAT is
set, causing a read request, the slave hardware will
clear CKP. This allows the slave time to update
SSPBUF with data to transfer to the master. If the SEN
bit of SSPCON2 is set, the slave hardware will always
stretch the clock after the ACK
sequence. Once the
slave is ready; CKP is set by software and
communication resumes.
27.4.7.2 10-bit Addressing Mode
In 10-bit Addressing mode, when the UA bit is set, the
clock is always stretched. This is the only time the SCL
is stretched without CKP being cleared. SCL is
released immediately after a write to SSPADDx.
27.4.7.3 Byte NACKing
When AHEN bit of SSPCON3 is set; CKP is cleared by
the hardware after the 8
th
falling edge of SCL for a
received matching address byte. When DHEN bit of
SSPCON3 is set; CKP is cleared after the 8
th
falling
edge of SCL for received data.
Stretching after the 8
th
falling edge of SCL allows the
slave to look at the received address or data and
decide if it wants to ACK the received data.
27.4.8 CLOCK SYNCHRONIZATION AND
THE CKP BIT
Any time the CKP bit is cleared, the module will wait for
the SCL line to go low and then hold it. However,
clearing the CKP bit will not assert the SCL output low
until the SCL output is already sampled low. Therefore,
the CKP bit will not assert the SCL line until an external
I
2
C master device has already asserted the SCL line.
The SCL output will remain low until the CKP bit is set
and all other devices on the I
2
C bus have released
SCL. This ensures that a write to the CKP bit will not
violate the minimum high time requirement for SCL
(see Figure 27-15).
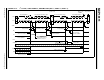
FIGURE 27-15: CLOCK SYNCHRONIZATION TIMING
Note 1: The BF bit has no effect on if the clock will
be stretched or not. This is different than
previous versions of the module that
would not stretch the clock or clear CKP,
if SSPBUF was read before the 9
th
falling
edge of SCL.
2: Previous versions of the module did not
stretch the clock for a transmission if
SSPBUF was loaded before the 9
th
falling
edge of SCL. It is now always cleared for
read requests.
Note: Previous versions of the module did not
stretch the clock if the second address byte
did not match.
SDA
SCL
DX ‚ – 1DX
WR
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
SSPCON1
CKP
Master device
releases clock
Master device
asserts clock