Specifications
© 2008-2012 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70323E-page 43-105
Section 43. High-Speed PWM
High-Speed PWM
43
43.18.3 PWM – Interrupt Controller Interconnect
43.18.3.1 PWM INTERRUPTS
PWM Interrupts can be generated based on either a PWM fault, current-limit or trigger event.
This feature is useful when certain software needs to be executed every time such an event
occurs.
For example, the PWM Interrupt service routine may contain the fault handling routine that
should be executed after the PWM has been turned OFF. Tasks such as data logging, external
communication of the fault, or the fault recovery routine can be performed here.
The PWM interrupt may also be used for execution of the control algorithm, or update system
variables or control references.
43.18.3.2 ADC INTERRUPTS AND STAGGERING OF CPU LOAD
One of the unique advantages of using a digital signal controller for power conversion is the
ability to control multiple stages using a single controller. When multiple control loops are
executed on the same device, the execution of each loop must be carefully sequenced to avoid
any delays in processing the data from the ADC.
The PWM module provides a trigger divider option that can generate the ADC triggers every few
PWM cycles. In addition to this feature, the generation of the first trigger can be delayed to
stagger the control loops in the available CPU time.
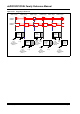
Figure 43-56 describes the sequence of control loop executions in a system where two power
converters are simultaneously controlled by a single dsPIC DSC.
As illustrated in Figure 43-56, the ADC pair interrupts are used for executing control algorithms
for each power converter stage. Each ADC pair conversion is triggered using the PWM triggers.
Each PWM trigger is generated every other PWM cycle by using the TRGDIV<3:0> bits
(TRGCONx<15:12>). Generation of the first trigger from PWM2 is delayed by one PWM cycle
using the TGSTRT<5:0> bits (TRGCONx<5:0>). With this configuration, the control loop
execution for each power converter is performed on alternate PWM cycles, thus effectively
utilizing the CPU bandwidth.