User manual
Table Of Contents
- Chapter 1. Overview
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Highlights
- 1.3 PICDEM™ Lab Development Kit Contents
- 1.4 PICDEM™ Lab Development Board Construction and Layout
- 1.5 Target Power
- 1.6 Connecting the PICkit™ 2 Programmer/Debugger
- 1.7 Solderless Prototyping Area Strip Configuration
- Chapter 2. Getting Started
- 2.1 Introduction
- 2.2 Prerequisites
- 2.3 The Software Control Loop
- 2.4 MPLAB® IDE Download Instructions
- 2.5 Installing the Included Lab Files
- Chapter 3. General Purpose Input/Output Labs
- 3.1 Introduction
- 3.2 General Purpose Input/Output Labs
- 3.3 GPIO Output Labs
- 3.3.1 Reference Documentation
- 3.3.2 Equipment Required for GPIO Output Labs
- 3.3.3 PICDEM Lab Development Board Setup for GPIO Output Labs
- Figure 3-1: PICDEM Lab Schematic for GPIO Output Labs
- 3.3.4 Lab 1: Light LEDs
- Figure 3-2: MAIN() Software Control Loop Flowchart for Lab 1
- Figure 3-3: Step One
- Figure 3-4: Step Two
- Figure 3-5: Step Three
- Figure 3-6: Step Four
- Figure 3-7: Summary
- Figure 3-8: Project Window
- Figure 3-9: PICkit 2 PROGRAMMER/DEBUGGER TOOLBAR
- Figure 3-10: Lab 1 LED Output
- 3.3.5 Lab 2: Flash LEDs (Delay Loop)
- Figure 3-11: Main() Software Control Loop Flowchart for Lab 2
- Figure 3-12: Timing() Delay Routine Flowchart for Lab 2
- 3.3.6 Lab 3: Simple Delays Using Timer0
- Equation 3-1: TMR0 Overflow Period using FOSC/4
- Equation 3-2: TMR0 Overflow Period when including the Prescaler
- Equation 3-3: Calculating a TMR0 PreLoad Value to generate a 10mS Overflow Period
- Figure 3-13: Delay_10mS() using Timer0
- Equation 3-4: Maximum TMR0 Overflow Period
- Figure 3-14: Delay_1S() using Timer0
- 3.3.7 Lab 4: Rotate LEDs
- Figure 3-15: Main() Software Control Loop Flowchart for Lab 4
- Figure 3-16: Decide() Flowchart for Lab 4
- Figure 3-17: Results of Do_Output()
- 3.4 GPIO Input Labs
- 3.4.1 Reference Documentation
- 3.4.2 Equipment Required for GPIO Input Labs
- 3.4.3 PICDEM Lab Development Board Setup for GPIO Input Labs
- Figure 3-18: PICDEM Lab Schematic for GPIO Input Labs
- 3.4.4 Lab 5: Adding a Push Button
- Figure 3-19: Main() Software Control Loop Flowchart for Lab 5
- Figure 3-20: Get_Inputs() Software Flowchart for Lab 5
- Figure 3-21: Delay_5mS() Software Flowchart for Lab 5
- Figure 3-22: Decide() Software FlowChart for Lab 5
- 3.4.5 Lab 6: Push Button Interrupt
- Figure 3-23: Main() Software Control Loop Flowchart for GPIO Lab 6
- Figure 3-24: pb_pressISR() for Lab 6 Showing Switch Debounce
- 3.4.6 Lab 7: Push Button Interrupt-on-Change
- Figure 3-25: pb_pressisr Flowchart for Lab 7
- 3.4.7 Lab 8: Using Weak Pull-Ups
- Chapter 4. Comparator Peripheral Labs
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Comparator Labs
- 4.2.1 Reference Documentation
- 4.2.2 Comparator Labs
- 4.2.3 Equipment Required
- 4.2.4 Lab 1: Simple Compare
- Figure 4-1: Schematic for Comparator Lab 1
- Figure 4-2: Main() software Control Loop Flowchart for Comparator Lab 1
- 4.2.5 Lab 2: Using the Comparator Voltage Reference
- Equation 4-1: CVref Output Voltage
- Equation 4-2: Calculating a 2.5V Internal Reference (Low-Range Method)
- Figure 4-3: Schematic for Comparator Lab 2
- 4.2.6 Lab 3: Higher Resolution Sensor Readings Using a Single Comparator
- Figure 4-4: Basic Relaxation Oscillator Circuit
- Figure 4-5: Schematic for Comparator Lab 3
- Figure 4-6: Main() software Control Loop Flowchart for Comparator Lab 3
- Figure 4-7: TMR0_ISR Flowchart for Comparator Lab 3
- Chapter 5. Analog-to-Digital Converter Peripheral Labs
- 5.1 Introduction
- 5.2 ADC Labs
- Figure 5-1: Schematic for ADC Lab 1
- Figure 5-2: Main() software Control Loop Flowchart for Comparator Lab 1
- Figure 5-3: Main() software Control Loop Flowchart for Comparator Lab 1
- Figure 5-4: ADC Result Bit Significance
- Figure 5-5: Schematic for ADC Lab 2
- Figure 5-6: Main() software Control Loop Flowchart for ADC Lab 2
- Appendix A. Schematic
- Worldwide Sales
PICDEM
TM
Lab Development Board User’s Guide
DS41369A-page 68 © 2009 Microchip Technology Inc.
4.2.6 Lab 3: Higher Resolution Sensor Readings Using a Single
Comparator
4.2.6.1 NEW REGISTERS USED IN THIS LAB
To configure the peripherals used in this lab, the following registers are used:
1. Timer1 Control Register: T1CON (Register 6-1 in Section 6 of the PIC16F690
data sheet)
- This register is used to control Timer1 and select various features of the
module. In this lab the register will be used to enable Timer1 and select the
clock source.
4.2.6.2 OVERVIEW
This lab expands on concepts discussed in the previous comparator lab by
implementing intelligence to create a higher resolution temperature sensor
measurement application. The comparator will be configured to operate as a simple
relaxation oscillator with the addition of a few external components. The internal
voltage reference will still be used to provide the non-inverting reference only this time
the 0.6V fixed voltage reference feature will be implemented.
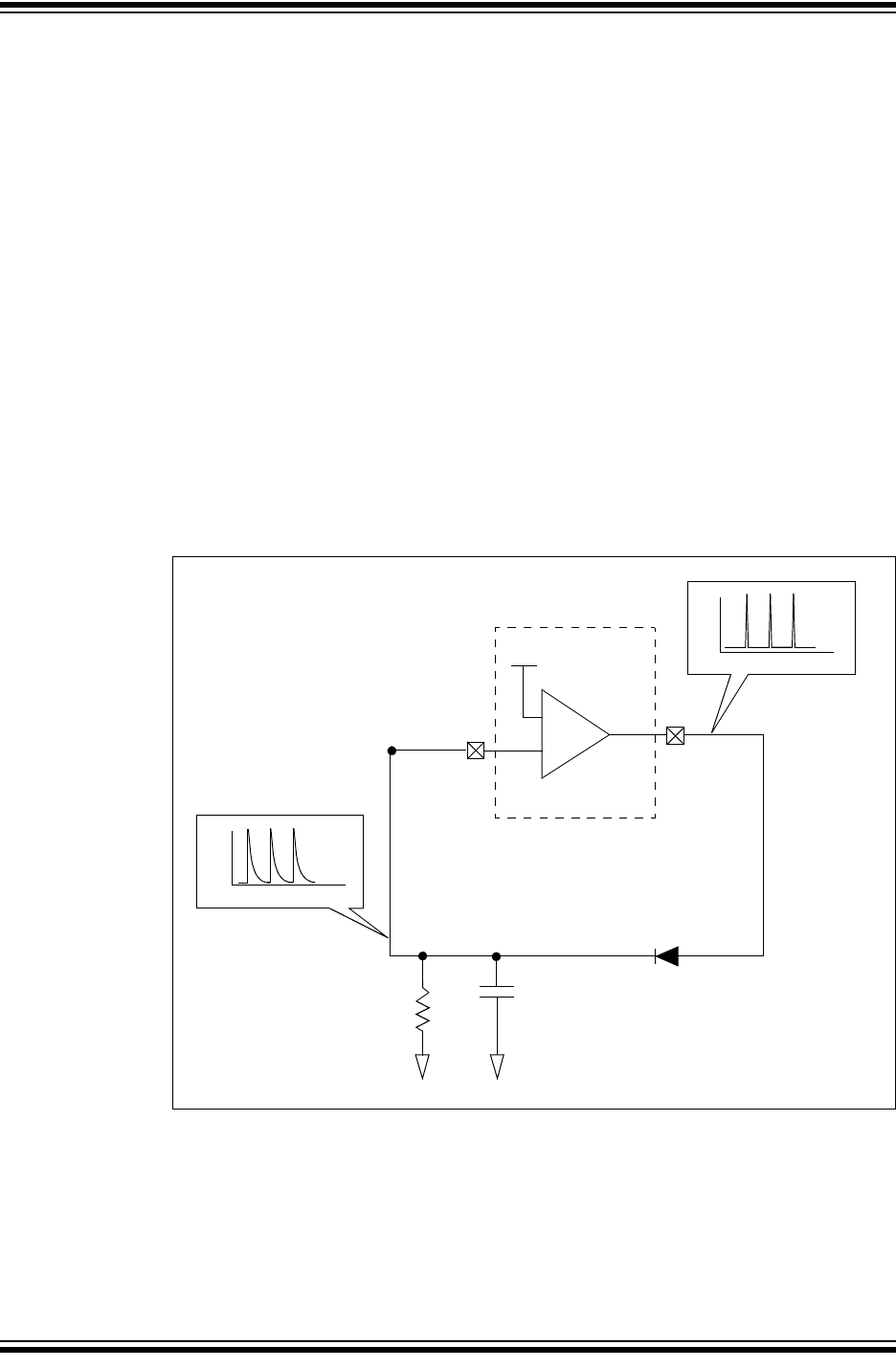
The basic oscillator circuit is shown in Figure 4-4.
FIGURE 4-4: BASIC RELAXATION OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT
Referring to Figure 4-4, at start-up, the capacitor connected to the inverting reference
of Comparator 1 is completely discharged. Therefore, the voltage present on the invert-
ing reference is 0V which is less than the 0.6V fixed voltage reference on the
non-inverting reference and Comparator 1’s output goes high. This rapidly charges the
capacitor through the diode (D1) to a level approximately equal to V
DD. Once the Com-
parator detects that the inverting reference input is greater than the 0.6V fixed voltage
reference, the output transitions low. The charge across the capacitor then discharges
slowly across the resistor R1. Once the capacitor charge drops below the 0.6V fixed
+
_
0.6V
V
SS
C
1
V
SS
PIC16F690
V
t
V
t
C1OUT
C12IN0-
D1
R
1










