Datasheet
Table Of Contents
- Features
- 1. Pin Configurations
- 2. Overview
- 3. Resources
- 4. Data Retention
- 5. About Code Examples
- 6. Capacitive touch sensing
- 7. AVR CPU Core
- 8. AVR Memories
- 9. System Clock and Clock Options
- 10. Power Management and Sleep Modes
- 11. System Control and Reset
- 12. Interrupts
- 13. I/O Ports
- 13.1 Overview
- 13.2 Ports as General Digital I/O
- 13.3 Alternate Port Functions
- 13.4 Register Description
- 13.4.1 SFIOR – Special Function I/O Register
- 13.4.2 PORTA – Port A Data Register
- 13.4.3 DDRA – Port A Data Direction Register
- 13.4.4 PINA – Port A Input Pins Address
- 13.4.5 PORTB – Port B Data Register
- 13.4.6 DDRB – Port B Data Direction Register
- 13.4.7 PINB – Port B Input Pins Address
- 13.4.8 PORTC – Port C Data Register
- 13.4.9 DDRC – Port C Data Direction Register
- 13.4.10 PINC – Port C Input Pins Address
- 13.4.11 PORTD – Port D Data Register
- 13.4.12 DDRD – Port D Data Direction Register
- 13.4.13 PIND – Port D Input Pins Address
- 14. External Interrupts
- 15. 8-bit Timer/Counter0 with PWM
- 16. Timer/Counter0 and Timer/Counter1 Prescalers
- 17. 16-bit Timer/Counter1
- 17.1 Features
- 17.2 Overview
- 17.3 Accessing 16-bit Registers
- 17.4 Timer/Counter Clock Sources
- 17.5 Counter Unit
- 17.6 Input Capture Unit
- 17.7 Compare Match Output Unit
- 17.8 Modes of Operation
- 17.9 Timer/Counter Timing Diagrams
- 17.10 Register Description
- 17.10.1 TCCR1A – Timer/Counter1 Control Register A
- 17.10.2 TCCR1B – Timer/Counter1 Control Register B
- 17.10.3 TCNT1H and TCNT1L – Timer/Counter1
- 17.10.4 OCR1AH and OCR1AL – Output Compare Register 1 A
- 17.10.5 OCR1BH and OCR1BL – Output Compare Register 1 B
- 17.10.6 ICR1H and ICR1L – Input Capture Register 1
- 17.10.7 TIMSK – Timer/Counter Interrupt Mask Register(1)
- 17.10.8 TIFR – Timer/Counter Interrupt Flag Register
- 18. 8-bit Timer/Counter2 with PWM and Asynchronous Operation
- 18.1 Features
- 18.2 Overview
- 18.3 Timer/Counter Clock Sources
- 18.4 Counter Unit
- 18.5 Output Compare Unit
- 18.6 Compare Match Output Unit
- 18.7 Modes of Operation
- 18.8 Timer/Counter Timing Diagrams
- 18.9 Asynchronous Operation of the Timer/Counter
- 18.10 Timer/Counter Prescaler
- 18.11 Register Description
- 18.11.1 TCCR2 – Timer/Counter Control Register
- 18.11.2 TCNT2 – Timer/Counter Register
- 18.11.3 OCR2 – Output Compare Register
- 18.11.4 ‘ASSR – Asynchronous Status Register
- 18.11.5 TIMSK – Timer/Counter Interrupt Mask Register
- 18.11.6 TIFR – Timer/Counter Interrupt Flag Register
- 18.11.7 SFIOR – Special Function IO Register
- 19. SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface
- 20. USART
- 20.1 Features
- 20.2 Overview
- 20.3 Clock Generation
- 20.4 Frame Formats
- 20.5 USART Initialization
- 20.6 Data Transmission – The USART Transmitter
- 20.7 Data Reception – The USART Receiver
- 20.8 Asynchronous Data Reception
- 20.9 Multi-processor Communication Mode
- 20.10 Accessing UBRRH/ UCSRC Registers
- 20.11 Register Description
- 20.12 Examples of Baud Rate Setting
- 21. Two-wire Serial Interface
- 22. Analog Comparator
- 23. Analog to Digital Converter
- 24. JTAG Interface and On-chip Debug System
- 25. IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Boundary-scan
- 26. Boot Loader Support – Read-While-Write Self-Programming
- 26.1 Features
- 26.2 Overview
- 26.3 Application and Boot Loader Flash Sections
- 26.4 Read-While-Write and no Read-While-Write Flash Sections
- 26.5 Boot Loader Lock Bits
- 26.6 Entering the Boot Loader Program
- 26.7 Addressing the Flash during Self-Programming
- 26.8 Self-Programming the Flash
- 26.8.1 Performing Page Erase by SPM
- 26.8.2 Filling the Temporary Buffer (Page Loading)
- 26.8.3 Performing a Page Write
- 26.8.4 Using the SPM Interrupt
- 26.8.5 Consideration while Updating BLS
- 26.8.6 Prevent Reading the RWW Section during Self-Programming
- 26.8.7 Setting the Boot Loader Lock Bits by SPM
- 26.8.8 EEPROM Write Prevents Writing to SPMCR
- 26.8.9 Reading the Fuse and Lock Bits from Software
- 26.8.10 Preventing Flash Corruption
- 26.8.11 Programming Time for Flash when using SPM
- 26.8.12 Simple Assembly Code Example for a Boot Loader
- 26.8.13 Boot Loader Parameters
- 26.9 Register Description
- 27. Memory Programming
- 27.1 Program And Data Memory Lock Bits
- 27.2 Fuse Bits
- 27.3 Signature Bytes
- 27.4 Calibration Byte
- 27.5 Page Size
- 27.6 Parallel Programming Parameters, Pin Mapping, and Commands
- 27.7 Parallel Programming
- 27.7.1 Enter Programming Mode
- 27.7.2 Considerations for Efficient Programming
- 27.7.3 Chip Erase
- 27.7.4 Programming the Flash
- 27.7.5 Programming the EEPROM
- 27.7.6 Reading the Flash
- 27.7.7 Reading the EEPROM
- 27.7.8 Programming the Fuse Low Bits
- 27.7.9 Programming the Fuse High Bits
- 27.7.10 Programming the Lock Bits
- 27.7.11 Reading the Fuse and Lock Bits
- 27.7.12 Reading the Signature Bytes
- 27.7.13 Reading the Calibration Byte
- 27.7.14 Parallel Programming Characteristics
- 27.8 SPI Serial Downloading
- 27.9 SPI Serial Programming Pin Mapping
- 27.10 Programming via the JTAG Interface
- 27.10.1 Programming Specific JTAG Instructions
- 27.10.2 AVR_RESET ($C)
- 27.10.3 PROG_ENABLE ($4)
- 27.10.4 PROG_COMMANDS ($5)
- 27.10.5 PROG_PAGELOAD ($6)
- 27.10.6 PROG_PAGEREAD ($7)
- 27.10.7 Data Registers
- 27.10.8 Reset Register
- 27.10.9 Programming Enable Register
- 27.10.10 Programming Command Register
- 27.10.11 Virtual Flash Page Load Register
- 27.10.12 Virtual Flash Page Read Register
- 27.10.13 Programming Algorithm
- 27.10.14 Entering Programming Mode
- 27.10.15 Leaving Programming Mode
- 27.10.16 Performing Chip Erase
- 27.10.17 Programming the Flash
- 27.10.18 Reading the Flash
- 27.10.19 Programming the EEPROM
- 27.10.20 Reading the EEPROM
- 27.10.21 Programming the Fuses
- 27.10.22 Programming the Lock Bits
- 27.10.23 Reading the Fuses and Lock Bits
- 27.10.24 Reading the Signature Bytes
- 27.10.25 Reading the Calibration Byte
- 28. Electrical Characteristics
- 29. Typical Characteristics
- 29.1 Active Supply Current
- 29.2 Idle Supply Current
- 29.3 Power-down Supply Current
- 29.4 Power-save Supply Current
- 29.5 Standby Supply Current
- 29.6 Pin Pull-up
- 29.7 Pin Driver Strength
- 29.8 Pin Thresholds and Hysteresis
- 29.9 BOD Thresholds and Analog Comparator Offset
- 29.10 Internal Oscillator Speed
- 29.11 Current Consumption of Peripheral Units
- 29.12 Current Consumption in Reset and Reset Pulsewidth
- 30. Register Summary
- 31. Instruction Set Summary
- 32. Ordering Information
- 33. Packaging Information
- 34. Errata
- 35. Datasheet Revision History
- Table of Contents
202
ATmega32A [DATASHEET]
Atmel-8155D-AVR-ATmega32A-Datasheet_02/2014
23.7.3 Offset Compensation Schemes
The gain stage has a built-in offset cancellation circuitry that nulls the offset of differential measurements as much
as possible. The remaining offset in the analog path can be measured directly by selecting the same channel for
both differential inputs. This offset residue can be then subtracted in software from the measurement results. Using
this kind of software based offset correction, offset on any channel can be reduced below one LSB.
23.7.4 ADC Accuracy Definitions
An n-bit single-ended ADC converts a voltage linearly between GND and V
REF
in 2
n
steps (LSBs). The lowest code
is read as 0, and the highest code is read as 2
n
-1.
Several parameters describe the deviation from the ideal behavior:
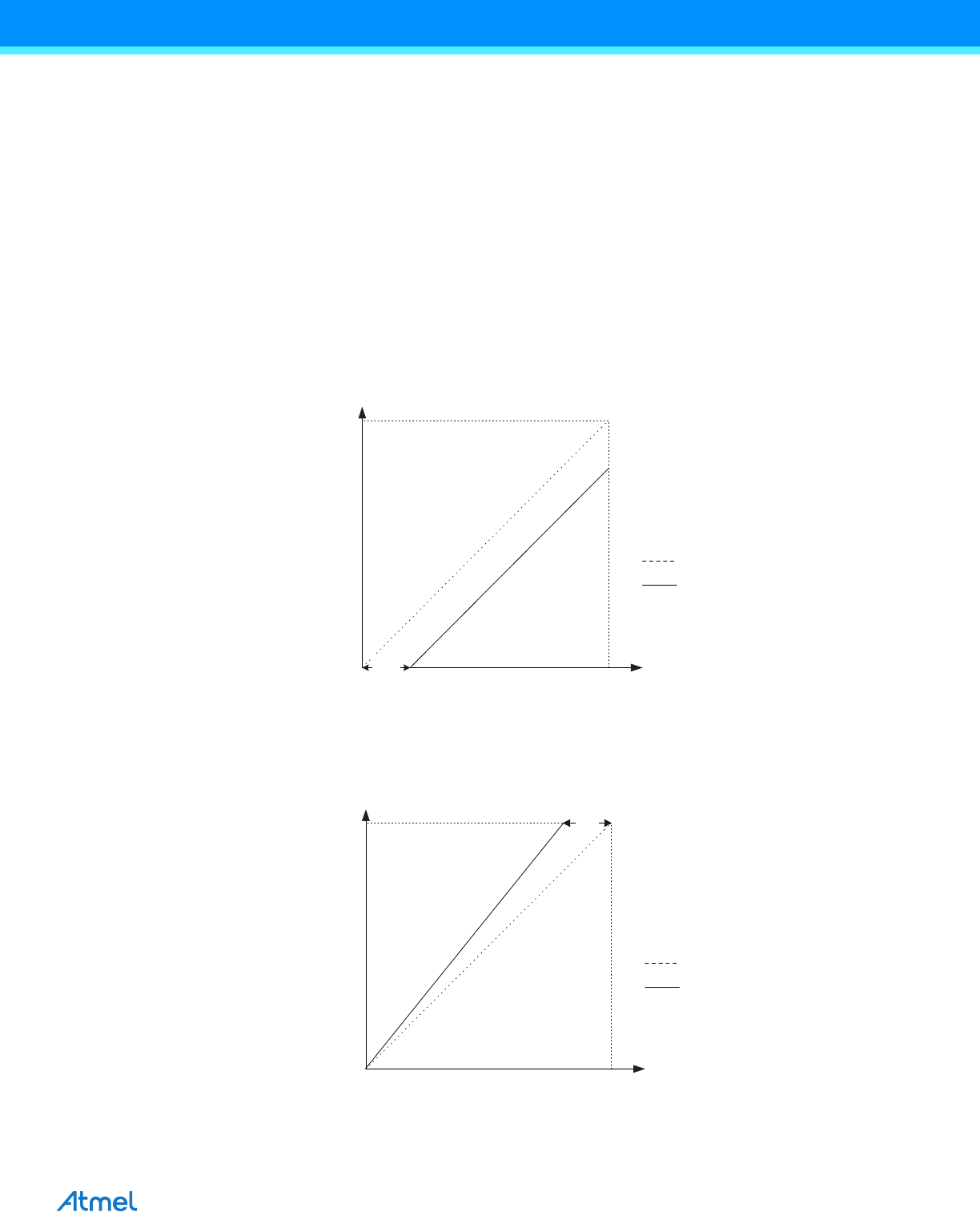
• Offset: The deviation of the first transition (0x000 to 0x001) compared to the ideal transition (at 0.5 LSB). Ideal
value: 0 LSB.
Figure 23-10. Offset Error
• Gain Error: After adjusting for offset, the Gain Error is found as the deviation of the last transition (0x3FE to
0x3FF) compared to the ideal transition (at 1.5 LSB below maximum). Ideal value: 0 LSB
Figure 23-11. Gain Error
• Integral Non-linearity (INL): After adjusting for offset and gain error, the INL is the maximum deviation of an
actual transition compared to an ideal transition for any code. Ideal value: 0 LSB.
Output Code
V
REF
Input Voltage
Ideal ADC
Actual ADC
Offset
Error
Output Code
V
REF
Input Voltage
Ideal ADC
Actual ADC
Gain
Error










