Datasheet
Table Of Contents
- Features
- Description
- Block Diagram
- SFR Mapping
- Pin Configurations
- Oscillators
- Enhanced Features
- Dual Data Pointer Register DPTR
- Expanded RAM (XRAM)
- Reset
- Power Monitor
- Timer 2
- Programmable Counter Array PCA
- Serial I/O Port
- Interrupt System
- Power Management
- Keyboard Interface
- 2-wire Interface (TWI)
- Serial Port Interface (SPI)
- Hardware Watchdog Timer
- ONCE(TM) Mode (ON Chip Emulation)
- Power-off Flag
- EEPROM Data Memory
- Reduced EMI Mode
- Flash Memory
- Electrical Characteristics
- Absolute Maximum Ratings
- DC Parameters
- AC Parameters
- Explanation of the AC Symbols
- External Program Memory Characteristics
- External Program Memory Read Cycle
- External Data Memory Characteristics
- External Data Memory Write Cycle
- External Data Memory Read Cycle
- Serial Port Timing - Shift Register Mode
- Shift Register Timing Waveforms
- External Clock Drive Waveforms
- AC Testing Input/Output Waveforms
- Float Waveforms
- Clock Waveforms
- Ordering Information
- Packaging Information
- Table of Contents
28
AT89C51ID2
4289C–8051–11/05
Expanded RAM
(XRAM)
The AT89C51ID2 provides additional Bytes of random access memory (RAM) space for
increased data parameter handling and high level language usage.
AT89C51ID2 devices have expanded RAM in external data space configurable up to
1792bytes (see Table 24.).
The AT89C51ID2 has internal data memory that is mapped into four separate
segments.
The four segments are:
1. The Lower 128 bytes of RAM (addresses 00h to 7Fh) are directly and indirectly
addressable.
2. The Upper 128 bytes of RAM (addresses 80h to FFh) are indirectly addressable
only.
3. The Special Function Registers, SFRs, (addresses 80h to FFh) are directly
addressable only.
4. The expanded RAM bytes are indirectly accessed by MOVX instructions, and
with the EXTRAM bit cleared in the AUXR register (see Table 24).
The lower 128 bytes can be accessed by either direct or indirect addressing. The Upper
128 bytes can be accessed by indirect addressing only. The Upper 128 bytes occupy
the same address space as the SFR. That means they have the same address, but are
physically separate from SFR space.
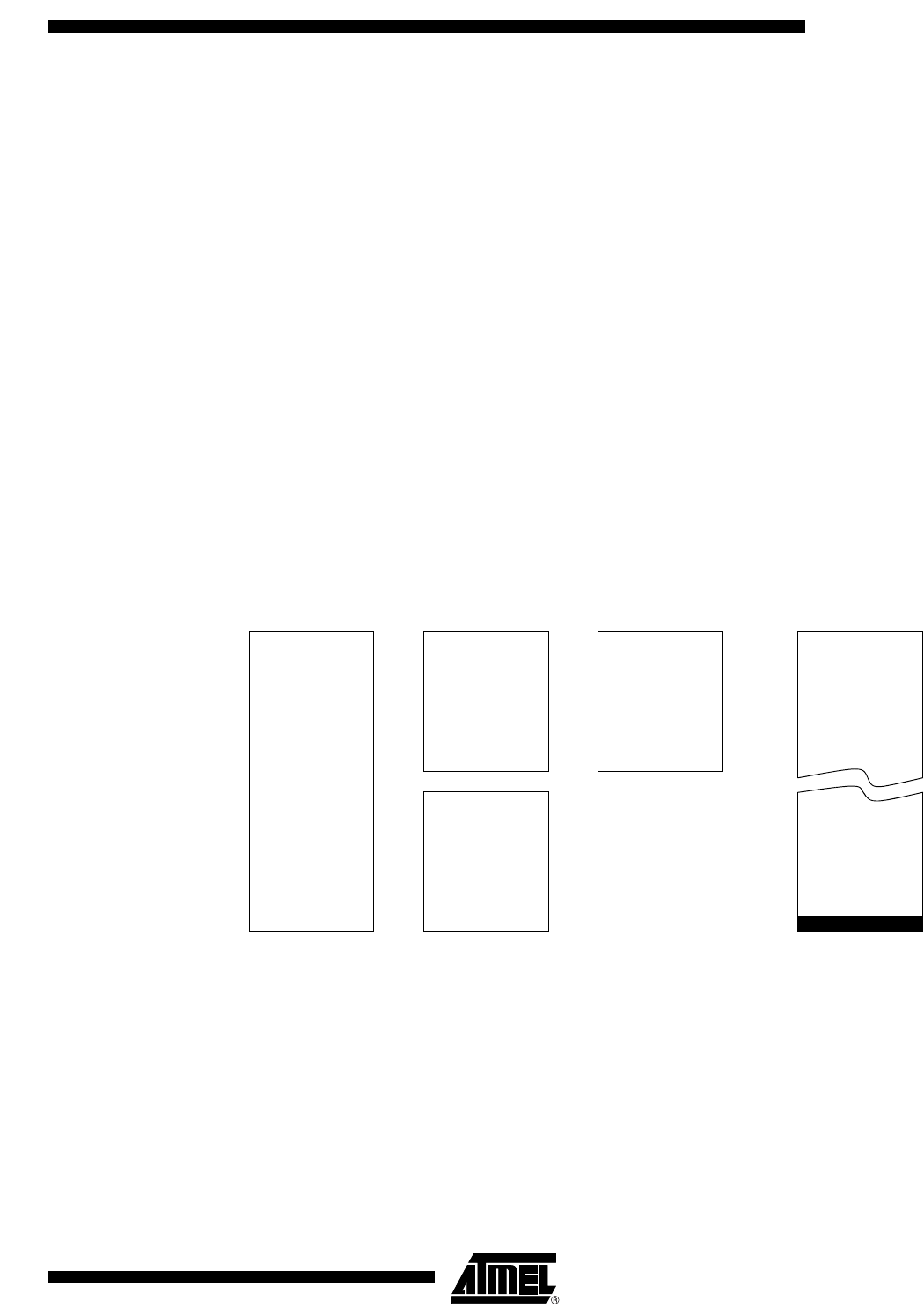
Figure 6. Internal and External Data Memory Address
When an instruction accesses an internal location above address 7Fh, the CPU knows
whether the access is to the upper 128 bytes of data RAM or to SFR space by the
addressing mode used in the instruction.
• Instructions that use direct addressing access SFR space. For example: MOV
0A0H, # data, accesses the SFR at location 0A0h (which is P2).
• Instructions that use indirect addressing access the Upper 128 bytes of data RAM.
For example: MOV @R0, # data where R0 contains 0A0h, accesses the data byte
at address 0A0h, rather than P2 (whose address is 0A0h).
• The XRAM bytes can be accessed by indirect addressing, with EXTRAM bit cleared
and MOVX instructions. This part of memory which is physically located on-chip,
logically occupies the first bytes of external data memory. The bits XRS0 and XRS1
are used to hide a part of the available XRAM as explained in Table 24. This can be
XRAM
Upper
128 bytes
Internal
Ram
Lower
128 bytes
Internal
Ram
Special
Function
Register
80h 80h
00
0FFh to 6FFh
0FFh
00
0FFh
External
Data
Memory
0000
00FFh up to 06FFh
0FFFFh
indirect accesses
direct accesses
direct or indirect
accesses
7Fh










