User manual
USER MANUAL
m crob t
RRC-1258 MKII
mickes-reviderade- Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-PA5.docx
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
User manual
Rev. PA8 – 23 Jan 2011
136 of 146
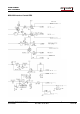
Network and Firewalls
One of the major obstacles when trying to remotely control something is the fact that the
Internet Service Provider (ISP) forces us to use dynamic IP addresses. We can never know,
from time to time, which IP address our modem / firewall / router has on its outside interface
(the IP address you will try to connect to). Most people use NAT routers that translates IP
addresses on the inside (your little LAN) to one common IP address on the outside using port
conversion.
To be able to stream audio and at the same time transfer CAT / CI-V commands or panel-to-
radio communications' we need to know which IP port numbers are used for each service.
There are some different techniques to fix this.
At the operator end (Control-RRC) there is normally OK just to use DHCP for the own IP-
settings. For the Sip contact parameter you enter the public fixed IP address or DynDNS-
name to the router at the radio site.
At the radio end (Radio-RRC) the router must be configured so that port 5060, 11000 and
12000 (default settings) is directed to the Radio-RRC which should have a static IP address.
The easy way to get connected is to set the RRC IP address as DMZ server in the router. This
makes it possible to connect to all services (SIP, audio and control) as well as the web and
telnet interfaces without further configuration. If you are using SIP based IP telephony you
need to change the port SIP port from 5060 to an other port not used by the IP-telephony
service in both RRC:s. If you run a web server at the radio site you need to change the
webserver port from 80 to something else, for example 8000. If you are using port forwarding
you have to configure the router in a way that every service forwards packets to the right
host on the inside.
When setting up the router check that there is No SIP ALG activated.
You will also need to register the Radio-RRC to DynDNS (www.dyndns.com) so you can use a
host name to connect to the Radio-RRC regardless of its dynamic IP address (which can
change without notice, but rarely does).
The following default IP ports are used (changeable)
port number
function
5060
SIP (change this port number in both ends if you are using SIP based IP-
telephony)
11000
RTP, audio
12000
DATA channel, control commands
80
WEB interface
23
Telnet Interface
SIP, RTP and DATA protocols are UDP-based, WEB and Telnet are TCP-based.