User's Guide Part 2
PureWave Quantum 6600 User Guide v2.1
Page 104
Client Profiles are assigned to individual Subscriber CPE’s and within each client profile there is the
ability to throttle throughput, and organize types of traffic into specific connection types. The use of
ARQ/HARQ is also contained within this system.
The Subscriber CPE Client Profile contains a Service Flow for both the uplink and the downlink directions.
The Service Flow is created from the following components:
The direction of flow of traffic
The specific Quality of Service (QoS) type, e.g. Best Effort (BE) or Unsolicited Grant Service
(UGS) etc that is to be applied.
ARQ and/or HARQ definitions. These are the error recovery mechanisms.
Packet Classifiers. This will classify on a packet by packet basis depending on the defined
classification criteria. For example, the conditions under which the packet is to be
transported and/or which Service flow it is to be assigned.
A Client Profile is a set a Service Flows that correspond to a specific Service Level Agreement assigned
to a customer. Each Client Profile supports up to 16 service flows and each service flow is uni-
directional. A set of service flows includes an Uplink and a Downlink direction.
Tip
When designing Client Profiles, it is important to understand how the
throughout rating mechanism works. In the event of contradicting parameters
being set, the system will allocate to a Subscriber CPE the lower of the
parameters. For example, assume a conflict between the Client Profile setting
the maximum uplink rate of 2Mbps and the QoS Profile setting the maximum
sustained rate to 1Mbps. In this example, the system will limit the uplink rate to
1Mbps.
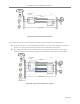
Figure 101 demonstrates a typical "Best Effort" type of Client Profile. Consider a packet that is flowing in
the downlink direction (i.e. Base Station to Subscriber CPE). The same concept applies in the uplink
direction.
A packet flow from the network and into the Base Station. It is destined for the Subscriber CPE.
The packet is then processed by the Classifiers rules that have been defined. In this example
these are the Downlink Packet Classifier.
If the packet is subject to the Classifier rule then it is processed and classified as defined by that
rule. Packets that are not subject to the rule are then identified as a Non Classified Packet.
The Non Classified Packets are then passed out of the Base Station and are now subject to the
relevant Service Flow definitions. In this example this would be Best Effort.