Specifications
• The machines in your AD tree must be well maintained. This is not always the case in many larger
organizations. Machines need to be deleted and placed into appropriate containers in AD for ePolicy
Orchestrator to properly mirror your AD structure.
• You must have the proper credentials, have the admin$ share enabled, and there must be no local
firewall blocking the netbios ports on the destination client for the push from ePolicy Orchestrator
to work properly.
• The target machine must be turned on. Just because the machine exists in Active Directory does
not mean it is turned on and active on your network. During the push from the McAfee ePO server
if the machine is not connected to the network then the push fails.
Agent deployment from the McAfee ePO server works well as long you have a well maintained AD
structure. If not, you will end up with excessive shells or placeholders in your System Tree. These
shells are machines that have been imported from your AD server but have never received a McAfee
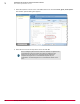
Agent. The following figure is an example of shell machines without agents installed.
Shell machine appear in the previous figure with no date in the Last
Communication column.
Make sure your environment is properly covered with McAfee Agents to avoid these shell machines.
These shell machines:
• Leave your System Tree cluttered and unorganized
• Should be deleted on a regular basis using an ePolicy Orchestrator server task, if needed
• Skew your reports and queries because they are only placeholders for machines, not machines that
are actively talking to the McAfee ePO server
You can filter out these shells in your reports but it is much better to
make sure your environment is properly covered with McAfee Agents.
Deploy the agent using third-party tools
You can deploy the McAfee agent using a third-party tool that you already use for patches and new
product deployments.
McAfee Agent
Deploying agents
6
McAfee
®
ePolicy Orchestrator
®
4.0 and 4.5 Best Practices Guide
47