Users Guide: Network Microcontroller Supplement User Manual
High-Speed Microcontroller User’s
Guide: Network Microcontroller
Supplement
ASYNCHRONOUS TCP/IP MAINTENANCE FUNCTIONS
The default timer-interrupt handler (WOS_tick) periodically calls the default task scheduler (WOS_IOPoll). This WOS_IOPoll routine
automatically calls certain asynchronous TCP/IP stack-maintenance functions and then calls the User_IOPoll redirect function. The
User_IOPoll hook provides a simple means for the user to extend the task scheduler if he/she desires. Since WOS_IOPoll is already
designed to handle the necessary TCP/IP maintenance function and can easily be supplemented with user-specific task-scheduler
code, it is the preferred method for ensuring proper and timely execution of the specified TCP/IP maintenance tasks. Therefore, only
high-level descriptions are given for the functions called by WOS_IOPoll.
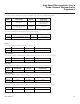
MAINTENANCE FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
1) IP_ProcessReceiveQueues Drive all the protocol receive queues. Checks the ARP
, TCP, UDP, and ICMP
r
eceive queues for messages that need to be processed. Processing the receive
packet may involve passing the message to a higher level protocol handler or
building a response queuing the response for transmission.
2) IP_ProcessOutput Drive all the protocol transmit queues. Checks all active connections to deter
mine whether output is needed in the form of data, acknowledge, or both.
3) IP6_ProcessReceiveQueues Drive all the IPv6 protocol receive queues
4) IP6_ProcessOutput Drive all the IPv6 protocol transmit queues
5) TCP_RetryTop Run TCP retr
y process. Searches connections for unacknowledged segments.
Any found with expired retry timers are retransmitted.
6) ETH_ProcessOutput Age all entries in the ARP cache
7) IGMP_GroupMaintenance Let IGMP output run. Checks all groups to see if IGMP repor
t messages need to
be generated.
OTHER FUNCTIONS/POINTERS
eth_processinterrupt—default Ethernet interrupt handler. The Ethernet interrupt handler unloads packets from the Ethernet hardware
buffer and enqueues them into the appropriate TCP/IP protocol queues.
arp_generaterequest—generates ARP request
MAC_ID—pointer to MAC ID, stored Big Endian
entercritsection—enter critical section. This function increments the variable wos_crit_count located in direct data memory at
address 68h.
leavecritsection—leave critical section. This function decrements the variable wos_crit_count located in direct data memor
y at
address 68h.
WOS_tick—default timer interrupt handler. A flow diagram for this interrupt handler is provided in Figure 23-1.
BLOB—pointer to the start address of xdata memory ignored by NetBoot. The BLOB memory space, by default, occupies at least 4kB
of contiguous memor
y, ending at address (BOOT_MEMBEGIN - 1). Since this memory is not touched by the DS80C400 Silicon
Software, it is well suited for user xdata.
RAMTOP—reserved for use by Maxim.
BOOT_MEMBEGIN—pointer to starting addr
ess of network stack buffers and heap memory. The user may define this star
ting address
as an input parameter to the rom_init function call or may allow a default assignment to be made by rom_init. The default starting
addr
ess for heap memory is the second 256-byte page boundary (i.e., 00xx00h) following address = BLOB + 1000h.
BOOT_MEMEND—pointer to the ending address of network stack buffers and heap memory. The user may define this ending address
as an input parameter to the rom_init function call or may allow a default assignment to be made by rom_init. The default ending
address for heap memory is 00FFFFh.
autobaud—The same autobaud procedure is executed as can be executed during the boot process. Please reference the earlier text
for a description of the autobaud function.
216
Maxim Integrated