Users Guide: DS80C390 Supplement Manual
High-Speed Microcontroller User’s Guide: DS80C390 Supplement
124 of 158
CAN MOVX REGISTER DESCRIPTION
Most of the SRAM control registers, including the message centers proper, are mapped into a special
location in the MOVX SRAM space. The specific location of the registers is a function of the module
number (CAN 0 or CAN 1) and the CMA bit that controls whether the CAN SRAM begins at location
401xxxh or 00Exxxh.
The MOVX CAN Registers consist of a set of one Control/Status/Mask register and 15 message centers.
Write access to the Control/Status/Mask registers is only possible when the SWINT bit is set to 1. All
message centers for a given CAN module are identical with the exception of 15, which has some minor
differences noted in the register descriptions. All of the CAN 1 registers are duplicates of the CAN 0
register set, differing only by address. To simplify the documentation, only one set of registers will be
shown, with the following generic notation used for register names and addresses:
n CAN number (0 or 1)
xxxx First four hexadecimal digits of register address
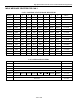
CMA
CAN 0
CAN 1
0 00EE 00EF
1 4010 4011
y Address based on message center number
y Message center number
1 1
2 2
. .
A 10
F 15
CAN Media ID Mask Register 0 (CnMID0)
MOVX
Address
1
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
xxxx00h
CAN Media ID Mask Register 1 (CnMID1)
MOVX
Address
1
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
xxxx02h
CAN Media ID Mask Registers 1-0. These registers function as the mask when
performing the Media Identification test. This register can only be modified
during a software initialization (SWINT=1). If MDME=0, the Media
Identification test will not be performed and the contents of these registers is
ignored. If MDME=1, the CAN module will perform an additional qualifying test
on Data Bytes 0 and 1 of the incoming message, regardless of the state of the
EX/
ST bit. Data byte 1 will be compared against CAN Media Byte Arbitration
Register 1 utilizing CnMID1 as a mask, and Data byte 0 will be compared against
CAN Media Byte Arbitration Register 0 utilizing CnMID0 as a mask. Any bit in
the CnMID1, CnMID0 masks programmed to 0 will ignore the state of the
corresponding Data Byte bit when performing the test. Any bit in the CnMID1,