Technical data
Glossary
SINAUT MICRO SC
72 C79000-G8900-C210
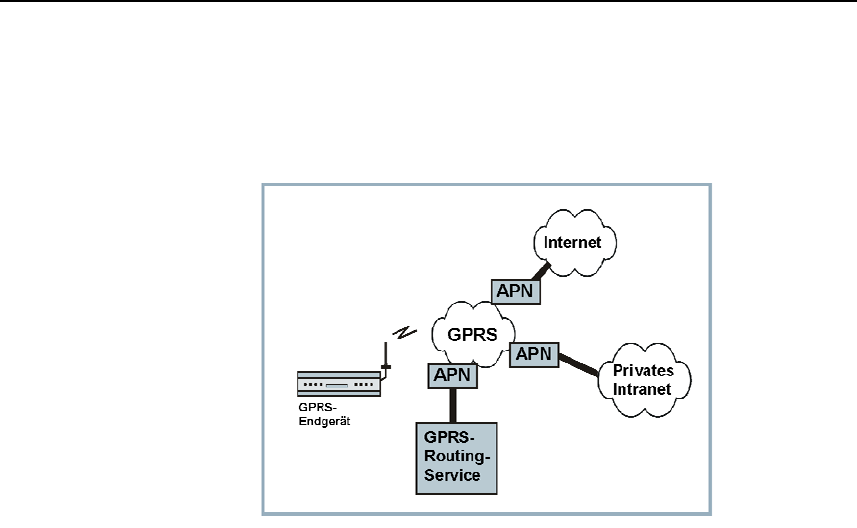
APN (Access Point
Name)
(Access Point Name). Cross-network connections, e.g. from the GPRS
network into the Internet are established in the GPRS network via so-
called APNs
During the dialling into the GPRS network the calling terminal specifies
via the APN with which network it wishes to be connected:
• the Internet,
• a private company network connected via a dedicated line.
RAS (Remote
Access Services
The designation for the Windows programming interface and its
functions which the dial-up networking makes available to the
application programs. RAS enables application programs which expect
a network, e.g. a TCP/IP network, to establish a connection via the
TAPI and a modem. The application does not notice at all that the data
are not forwarded via a network board but via the telephone network
using a modem or another transmission device. In the Windows dial-up
networking so-called connections are created. The connection data for
each of these connections is stored, for example a definition is made as
to which modem is used to establish the connection and which network
protocol is available to the application following establishment of the
connection.
TCP/IP
Two network protocols which are used for the connection of two
computers in the Internet.
IP provides the basic mechanisms for the transmission of data
packets.
UDP is based upon IP and transmits individual data packets. They
can reach the receiver in another sequence as the sequence they
have been sent. They also can get lost.
TCP serves to protect the connection and, for example, ensures that
the data packets are forwarded in the correct order to the application.
UDP and TCP also bring port numbers between 1 and 65535, in
addition to the IP addresses. These port numbers distinguish the
different services.
There are some more protocols that are based upon UDP and TCP,
e.g.: HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol), HTTPS (Secure Hyper
Text Transfer Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), POP3
(Post Office Protocol, Version 3), DNS (Domain Name System).
ICMP is based upon IP and transmits control messages.










