User`s guide
Table Of Contents
- Getting Started
- Using the IQmath Library
- Block Reference
- Blocks — Alphabetical List
- Absolute IQN
- Arctangent IQN
- C24x ADC
- C24x CAN Receive
- C24x CAN Transmit
- C24x From Memory
- C24x PWM
- C24x To Memory
- C28x ADC
- C28x eCAN Receive
- C28x eCAN Transmit
- C28x From Memory
- C28x PWM
- C28x To Memory
- Division IQN
- F2812 eZdsp
- Float to IQN
- Fractional part IQN
- Fractional part IQN x int32
- Integer part IQN
- Integer part IQN x int32
- IQN to Float
- IQN x int32
- IQN x IQN
- IQN1 to IQN2
- IQN1 x IQN2
- LF2407 eZdsp
- Magnitude IQN
- Saturate IQN
- Square Root IQN
- Trig Fcn IQN
- Index
Fixed-Point Numbers
2-3
Fixed-Point Numbers
In digital hardware, numbers are stored in binary words. A binary word is a
fixed-length sequence of binary digits (1’s and 0’s). How hardware components
or software functions interpret this sequence of 1’s and 0’s is defined by the
data type.
Binary numbers are used to represent either fixed-point or floating-point data
types. A fixed-point data type is characterized by the word size in bits, the
binary point, and whether it is signed or unsigned. The position of the binary
point is the means by which fixed-point values are scaled and interpreted.
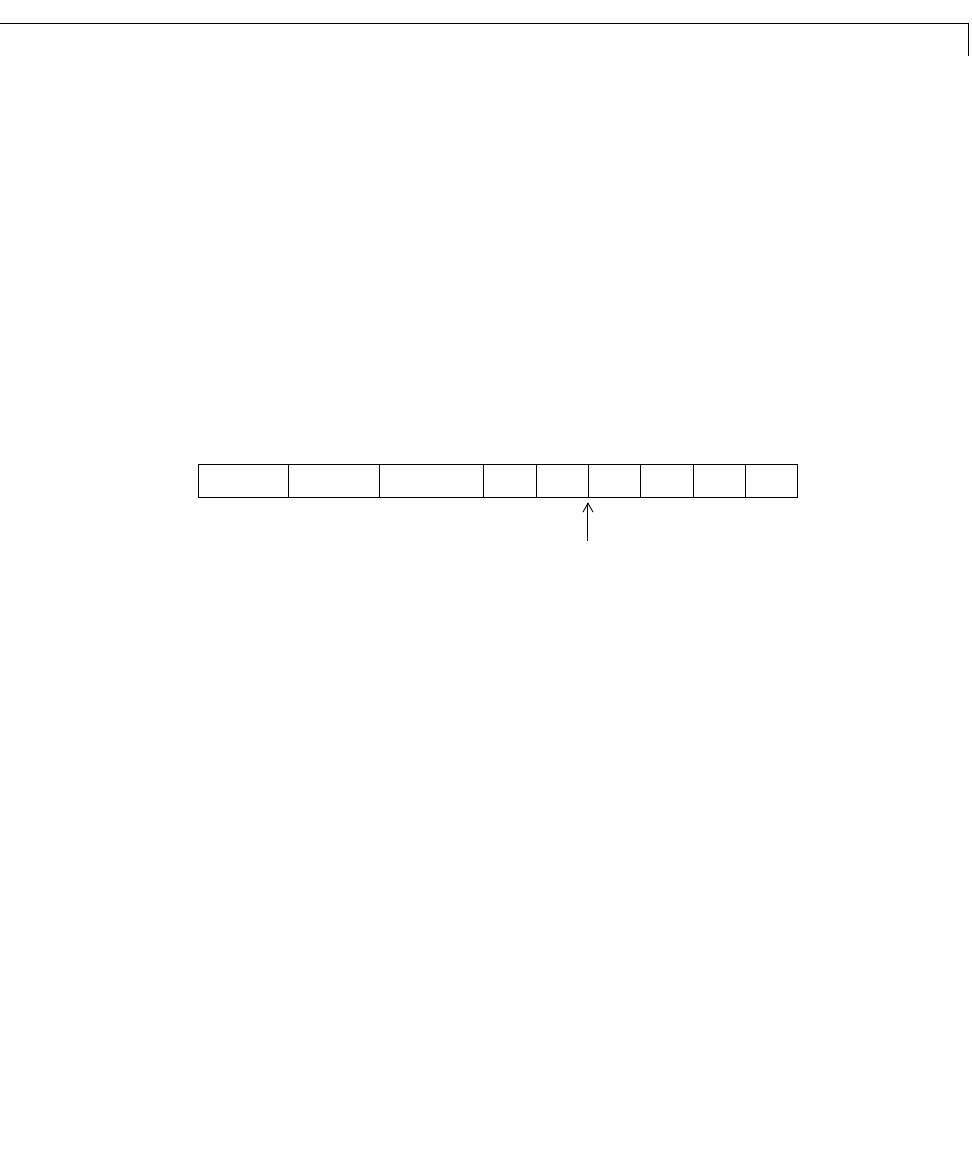
For example, a binary representation of a fractional fixed-point number (either
signed or unsigned) is shown below.
where
• is the ith binary digit.
• is the word size in bits.
• is the location of the most significant (highest) bit (MSB).
• is the location of the least significant (lowest) bit (LSB).
• The binary point is shown four places to the left of the LSB. In this example,
therefore, the number is said to have four fractional bits, or a fraction length
of four.
Signed Fixed-Point Numbers
Signed binary fixed-point numbers are typically represented in one of three
ways:
• Sign/magnitude
• One’s complement
• Two’s complement
•
…
b
0
b
1
b
ws 2–
b
5
b
3
b
4
b
2
b
ws 1–
MSB LSB
binary point
b
i
ws
b
ws 1–
b
0










