User`s guide
Table Of Contents
- Preface
- Quick Start
- LTI Models
- Introduction
- Creating LTI Models
- LTI Properties
- Model Conversion
- Time Delays
- Simulink Block for LTI Systems
- References
- Operations on LTI Models
- Arrays of LTI Models
- Model Analysis Tools
- The LTI Viewer
- Introduction
- Getting Started Using the LTI Viewer: An Example
- The LTI Viewer Menus
- The Right-Click Menus
- The LTI Viewer Tools Menu
- Simulink LTI Viewer
- Control Design Tools
- The Root Locus Design GUI
- Introduction
- A Servomechanism Example
- Controller Design Using the Root Locus Design GUI
- Additional Root Locus Design GUI Features
- References
- Design Case Studies
- Reliable Computations
- Reference
- Category Tables
- acker
- append
- augstate
- balreal
- bode
- c2d
- canon
- care
- chgunits
- connect
- covar
- ctrb
- ctrbf
- d2c
- d2d
- damp
- dare
- dcgain
- delay2z
- dlqr
- dlyap
- drmodel, drss
- dsort
- dss
- dssdata
- esort
- estim
- evalfr
- feedback
- filt
- frd
- frdata
- freqresp
- gensig
- get
- gram
- hasdelay
- impulse
- initial
- inv
- isct, isdt
- isempty
- isproper
- issiso
- kalman
- kalmd
- lft
- lqgreg
- lqr
- lqrd
- lqry
- lsim
- ltiview
- lyap
- margin
- minreal
- modred
- ndims
- ngrid
- nichols
- norm
- nyquist
- obsv
- obsvf
- ord2
- pade
- parallel
- place
- pole
- pzmap
- reg
- reshape
- rlocfind
- rlocus
- rltool
- rmodel, rss
- series
- set
- sgrid
- sigma
- size
- sminreal
- ss
- ss2ss
- ssbal
- ssdata
- stack
- step
- tf
- tfdata
- totaldelay
- zero
- zgrid
- zpk
- zpkdata
- Index
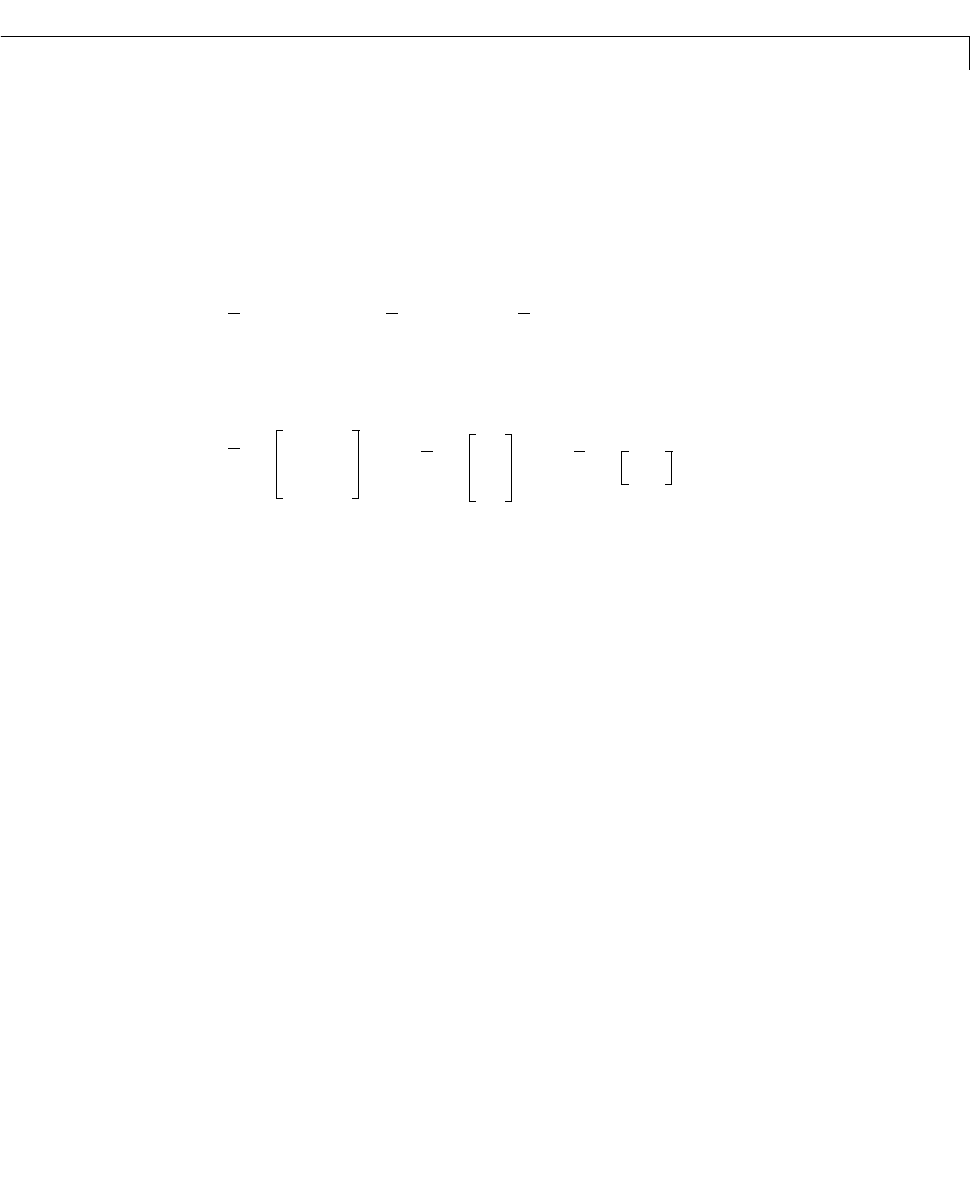
obsvf
11-161
11obsvf
Purpose Compute the observability staircase form
Syntax [Abar,Bbar,Cbar,T,k] = obsvf(A,B,C)
[Abar,Bbar,Cbar,T,k] = obsvf(A,B,C,tol)
Description If theobservabilitymatrixof (A,C) ha s rank ,wheren isthesizeofA,then
there exists a similarity trans formation such that
where is unitary and the transformed system has a staircase form with the
unobservable modes, if any, in the upper left corner.
where is observable, and the eigenvalues of are the unobservable
modes.
[Abar,Bbar,Cbar,T,k] = obsvf(A,B,C) decomposes the state-space system
with matrices
A, B,andCinto the observability staircase form Abar, Bbar,and
Cbar, as described above. T is the similarity transformation matrix and k is a
vector of length n,whereni s t he number of stat es in
A.Eachentryofk
representsthe number ofobservable states factored outduring each step ofthe
transformation matrix calculation [1]. The number of nonzero elements in
k
indicates how many iterations were necess ary to calculate T,andsum(k) is the
number of states in , the observable portion of
Abar.
obsvf(A,B,C,tol) uses the tolerance tol when calculating the observable/
unobservable s ubspaces. When the tolerance is not specified, it defaults to
10*n*norm(a,1)*eps.
rn
≤
ATAT
T
,= BTB,= CCT
T
=
T
A
A
no
A
12
0 A
o
,=
B
B
no
B
o
,= C 0 C
o
=
C
o
A
o
,()
A
no
A
o










