User`s guide
Table Of Contents
- Preface
- Quick Start
- LTI Models
- Introduction
- Creating LTI Models
- LTI Properties
- Model Conversion
- Time Delays
- Simulink Block for LTI Systems
- References
- Operations on LTI Models
- Arrays of LTI Models
- Model Analysis Tools
- The LTI Viewer
- Introduction
- Getting Started Using the LTI Viewer: An Example
- The LTI Viewer Menus
- The Right-Click Menus
- The LTI Viewer Tools Menu
- Simulink LTI Viewer
- Control Design Tools
- The Root Locus Design GUI
- Introduction
- A Servomechanism Example
- Controller Design Using the Root Locus Design GUI
- Additional Root Locus Design GUI Features
- References
- Design Case Studies
- Reliable Computations
- Reference
- Category Tables
- acker
- append
- augstate
- balreal
- bode
- c2d
- canon
- care
- chgunits
- connect
- covar
- ctrb
- ctrbf
- d2c
- d2d
- damp
- dare
- dcgain
- delay2z
- dlqr
- dlyap
- drmodel, drss
- dsort
- dss
- dssdata
- esort
- estim
- evalfr
- feedback
- filt
- frd
- frdata
- freqresp
- gensig
- get
- gram
- hasdelay
- impulse
- initial
- inv
- isct, isdt
- isempty
- isproper
- issiso
- kalman
- kalmd
- lft
- lqgreg
- lqr
- lqrd
- lqry
- lsim
- ltiview
- lyap
- margin
- minreal
- modred
- ndims
- ngrid
- nichols
- norm
- nyquist
- obsv
- obsvf
- ord2
- pade
- parallel
- place
- pole
- pzmap
- reg
- reshape
- rlocfind
- rlocus
- rltool
- rmodel, rss
- series
- set
- sgrid
- sigma
- size
- sminreal
- ss
- ss2ss
- ssbal
- ssdata
- stack
- step
- tf
- tfdata
- totaldelay
- zero
- zgrid
- zpk
- zpkdata
- Index
The Right-Click Menus
6-37
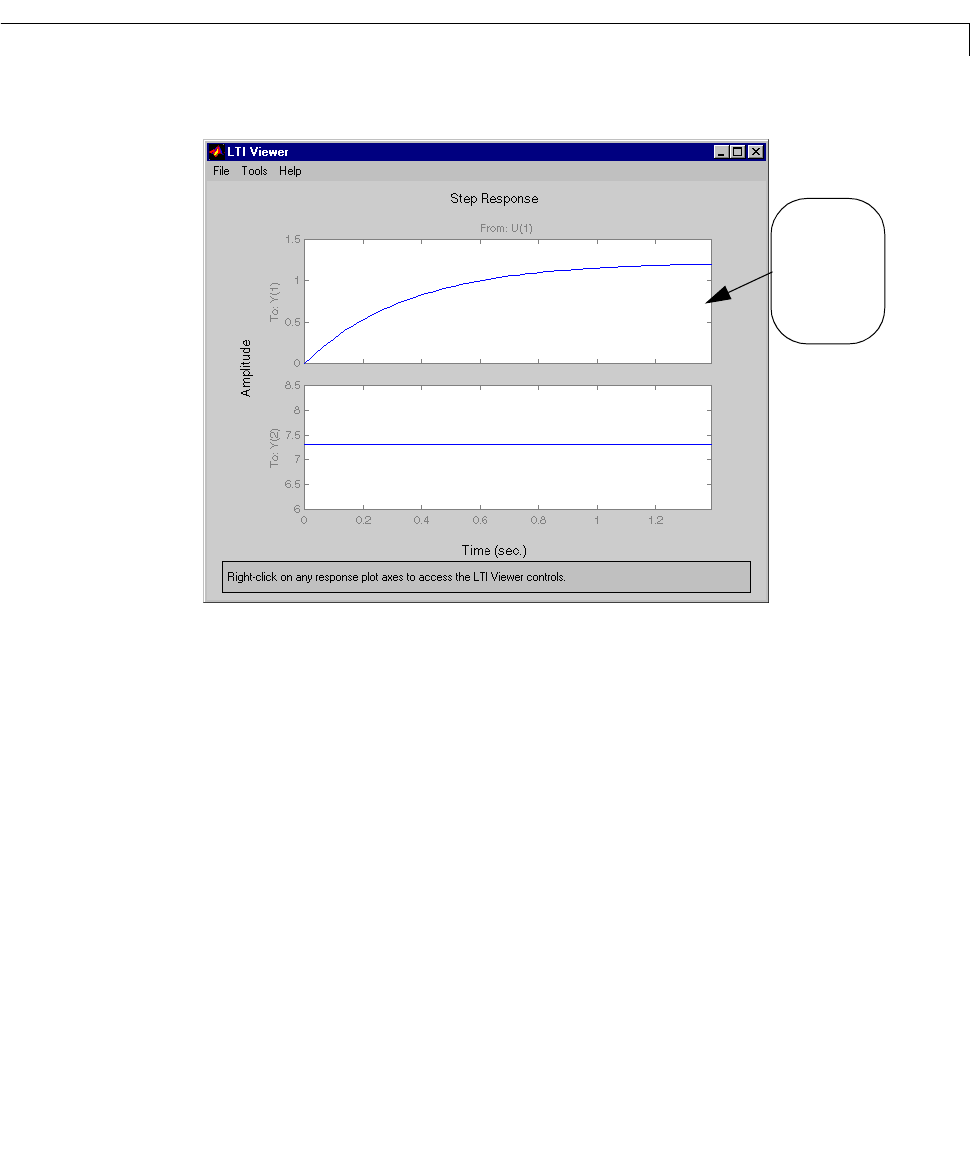
Figure 6-19: Step Response of the Model with the Maximum Rise Time
You can also use any logical expression in variables defined in the MATLAB
workspace to i ndex into a specific design criterion. For example, typing
$(2,1) < 7.25 & $(1,1) > 1.2
next to Steady State (after unchecking Rise Time), displays the responses of
any models for which the steady-state response has a value less than 7 .25 for
in the second I/O channel, a nd g reater than 1.2 in the first.
Suppose you have a design specification requirement for each I/O map of each
model of the L TI array, and store this requirement in a matrix
q in the
MATLAB workspace. For example, if
q is an Ny-by-Nu matrix (2-by-1, in this
case), and
N is the number of models in the LTI array (6, in this case), then you
can type
N = 6;
Q = repmat(q,[1,1,N]);
The step response
of the model in
the (2,3) position
of the LTI array is
displayed.










