User`s guide
Table Of Contents
- Preface
- Quick Start
- LTI Models
- Introduction
- Creating LTI Models
- LTI Properties
- Model Conversion
- Time Delays
- Simulink Block for LTI Systems
- References
- Operations on LTI Models
- Arrays of LTI Models
- Model Analysis Tools
- The LTI Viewer
- Introduction
- Getting Started Using the LTI Viewer: An Example
- The LTI Viewer Menus
- The Right-Click Menus
- The LTI Viewer Tools Menu
- Simulink LTI Viewer
- Control Design Tools
- The Root Locus Design GUI
- Introduction
- A Servomechanism Example
- Controller Design Using the Root Locus Design GUI
- Additional Root Locus Design GUI Features
- References
- Design Case Studies
- Reliable Computations
- Reference
- Category Tables
- acker
- append
- augstate
- balreal
- bode
- c2d
- canon
- care
- chgunits
- connect
- covar
- ctrb
- ctrbf
- d2c
- d2d
- damp
- dare
- dcgain
- delay2z
- dlqr
- dlyap
- drmodel, drss
- dsort
- dss
- dssdata
- esort
- estim
- evalfr
- feedback
- filt
- frd
- frdata
- freqresp
- gensig
- get
- gram
- hasdelay
- impulse
- initial
- inv
- isct, isdt
- isempty
- isproper
- issiso
- kalman
- kalmd
- lft
- lqgreg
- lqr
- lqrd
- lqry
- lsim
- ltiview
- lyap
- margin
- minreal
- modred
- ndims
- ngrid
- nichols
- norm
- nyquist
- obsv
- obsvf
- ord2
- pade
- parallel
- place
- pole
- pzmap
- reg
- reshape
- rlocfind
- rlocus
- rltool
- rmodel, rss
- series
- set
- sgrid
- sigma
- size
- sminreal
- ss
- ss2ss
- ssbal
- ssdata
- stack
- step
- tf
- tfdata
- totaldelay
- zero
- zgrid
- zpk
- zpkdata
- Index
3 Operations on LTI Models
3-20
Continuous/Discrete Conversions of LTI Models
The function c2d discretizes continuous-time TF, SS, or ZPK models.
Conversely,
d2c converts discrete-time TF, SS, or ZPK models to continuous
time. Several discretization/interpolation methods are supported, including
zero-order hold (ZOH), first-order hold (FOH), Tustin approximation with or
without frequency prewarping, and matched poles and zeros.
The syntax
sysd = c2d(sysc,Ts); % Ts = sampling period in seconds
sysc = d2c(sysd);
performs ZOH conversions by default. To use alternative conversion schemes,
specifythedesiredmethodasanextrastringinput:
sysd = c2d(sysc,Ts,'foh'); % use first-order hold
sysc = d2c(sysd,'tustin'); % use Tustin approximation
The conversion methods and their limitations are discussed next.
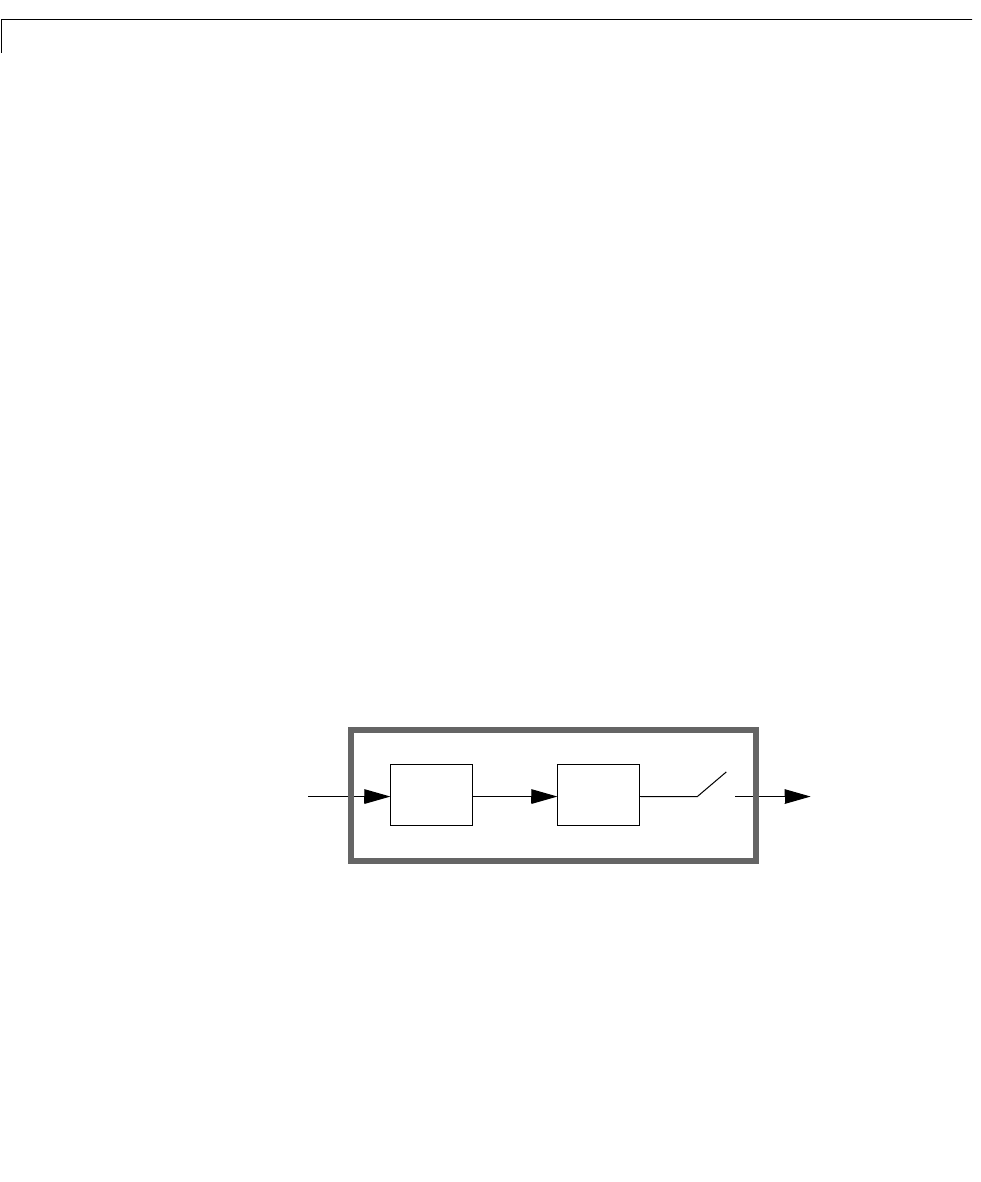
Zero-Order Hold
Zero-order hold (ZOH) devices convert sampled signals to continuous-time
signals for analyzing sampled continuous-time systems. The zero-order-hold
discretization of a continuous-time LTI model is depicted in the
following block diagram.
The ZOH device generates a continuous input signal u(t) by holding each
sample value u[k] constant over one sample period.
H
d
z
()
Hs
()
Hs()
uk[]
yk[]
ut()
yt()
ZOH
T
s
H
d
z()










