User`s guide
Table Of Contents
- Preface
- Quick Start
- LTI Models
- Introduction
- Creating LTI Models
- LTI Properties
- Model Conversion
- Time Delays
- Simulink Block for LTI Systems
- References
- Operations on LTI Models
- Arrays of LTI Models
- Model Analysis Tools
- The LTI Viewer
- Introduction
- Getting Started Using the LTI Viewer: An Example
- The LTI Viewer Menus
- The Right-Click Menus
- The LTI Viewer Tools Menu
- Simulink LTI Viewer
- Control Design Tools
- The Root Locus Design GUI
- Introduction
- A Servomechanism Example
- Controller Design Using the Root Locus Design GUI
- Additional Root Locus Design GUI Features
- References
- Design Case Studies
- Reliable Computations
- Reference
- Category Tables
- acker
- append
- augstate
- balreal
- bode
- c2d
- canon
- care
- chgunits
- connect
- covar
- ctrb
- ctrbf
- d2c
- d2d
- damp
- dare
- dcgain
- delay2z
- dlqr
- dlyap
- drmodel, drss
- dsort
- dss
- dssdata
- esort
- estim
- evalfr
- feedback
- filt
- frd
- frdata
- freqresp
- gensig
- get
- gram
- hasdelay
- impulse
- initial
- inv
- isct, isdt
- isempty
- isproper
- issiso
- kalman
- kalmd
- lft
- lqgreg
- lqr
- lqrd
- lqry
- lsim
- ltiview
- lyap
- margin
- minreal
- modred
- ndims
- ngrid
- nichols
- norm
- nyquist
- obsv
- obsvf
- ord2
- pade
- parallel
- place
- pole
- pzmap
- reg
- reshape
- rlocfind
- rlocus
- rltool
- rmodel, rss
- series
- set
- sgrid
- sigma
- size
- sminreal
- ss
- ss2ss
- ssbal
- ssdata
- stack
- step
- tf
- tfdata
- totaldelay
- zero
- zgrid
- zpk
- zpkdata
- Index
3 Operations on LTI Models
3-6
Note:
•
sys, the LTI model that has had a portion reassigned, retains its original
model type (TF, ZPK, SS, or FRD) regardless of the model type of
NewSubSys.
• If
NewSubSys is an FRD model, then sys must also be an FRD model.
Furthermore, their frequencies must match.
• Subsystem assignment does not reassign any I/O names or I/O group names
of
NewSubSys that are already assigned to NewSubSys.
• Reassig n ing parts of a MIMO state-space model general ly increases its
order.
Other sta ndard matrix subindexing extends to LTI objects as well. For
exampl e,
sys(3,1:2)
extracts the subsystem mapping the first two inputs to the third output.
sys(:,1)
selects the first input and all outputs, a nd
sys([1 3],:)
extractsa subsystemwith the sameinputs, but only thefirst and third outputs.
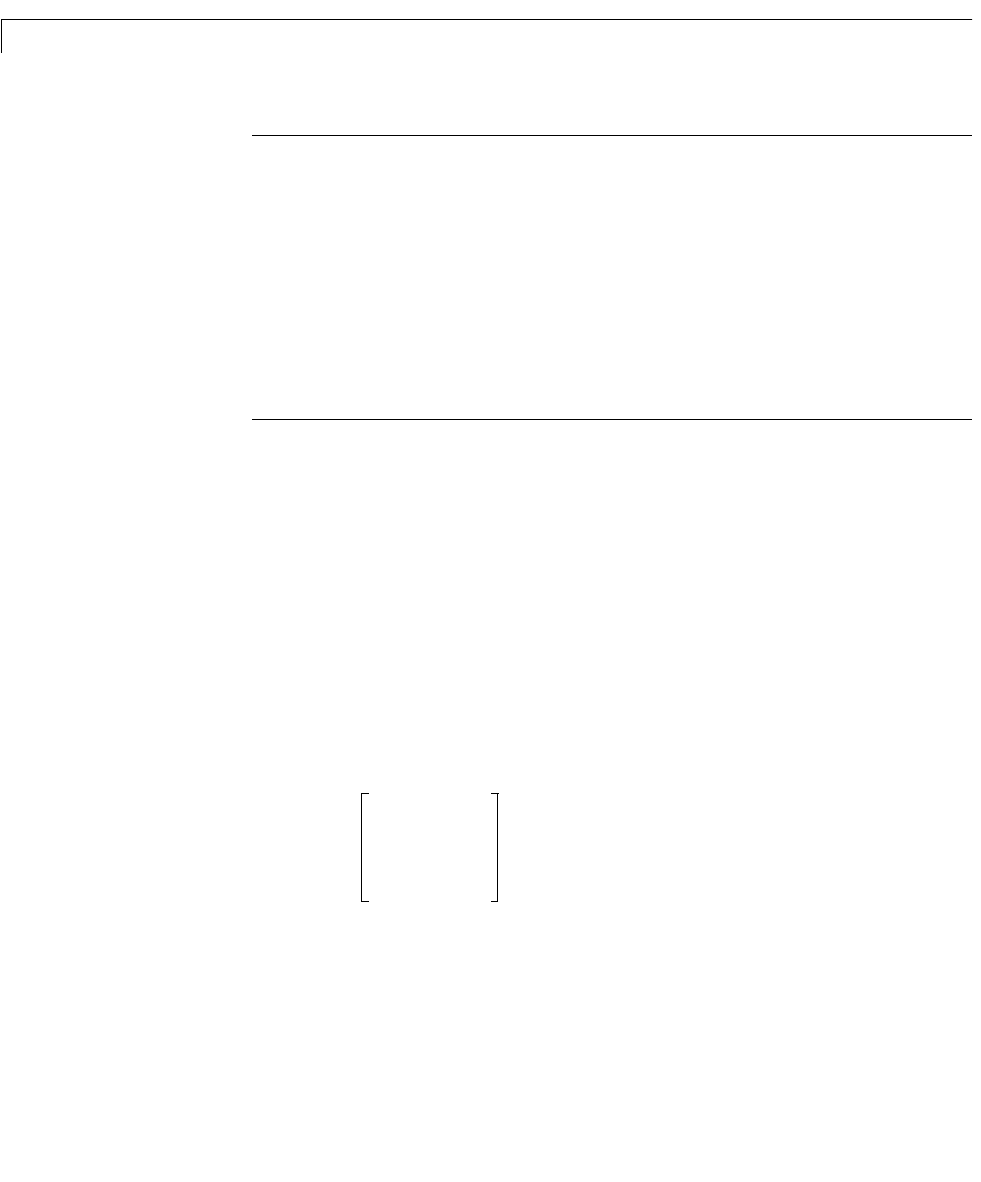
For example, consider the two-input/two-output transfer function
.Ts()
1
s 0.1+
-----------------
0
s 1–
s
2
2 s 2++
----------------------------
1
s
---
=










