Specifications
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- LTI Models
- Operations on LTI Models
- Model Analysis Tools
- Arrays of LTI Models
- Customization
- Setting Toolbox Preferences
- Setting Tool Preferences
- Customizing Response Plot Properties
- Design Case Studies
- Reliable Computations
- GUI Reference
- SISO Design Tool Reference
- Menu Bar
- File
- Import
- Export
- Toolbox Preferences
- Print to Figure
- Close
- Edit
- Undo and Redo
- Root Locus and Bode Diagrams
- SISO Tool Preferences
- View
- Root Locus and Bode Diagrams
- System Data
- Closed Loop Poles
- Design History
- Tools
- Loop Responses
- Continuous/Discrete Conversions
- Draw a Simulink Diagram
- Compensator
- Format
- Edit
- Store
- Retrieve
- Clear
- Window
- Help
- Tool Bar
- Current Compensator
- Feedback Structure
- Root Locus Right-Click Menus
- Bode Diagram Right-Click Menus
- Status Panel
- Menu Bar
- LTI Viewer Reference
- Right-Click Menus for Response Plots
- Function Reference
- Functions by Category
- acker
- allmargin
- append
- augstate
- balreal
- bode
- bodemag
- c2d
- canon
- care
- chgunits
- connect
- covar
- ctrb
- ctrbf
- d2c
- d2d
- damp
- dare
- dcgain
- delay2z
- dlqr
- dlyap
- drss
- dsort
- dss
- dssdata
- esort
- estim
- evalfr
- feedback
- filt
- frd
- frdata
- freqresp
- gensig
- get
- gram
- hasdelay
- impulse
- initial
- interp
- inv
- isct, isdt
- isempty
- isproper
- issiso
- kalman
- kalmd
- lft
- lqgreg
- lqr
- lqrd
- lqry
- lsim
- ltimodels
- ltiprops
- ltiview
- lyap
- margin
- minreal
- modred
- ndims
- ngrid
- nichols
- norm
- nyquist
- obsv
- obsvf
- ord2
- pade
- parallel
- place
- pole
- pzmap
- reg
- reshape
- rlocus
- rss
- series
- set
- sgrid
- sigma
- sisotool
- size
- sminreal
- ss
- ss2ss
- ssbal
- ssdata
- stack
- step
- tf
- tfdata
- totaldelay
- zero
- zgrid
- zpk
- zpkdata
- Index
Arithmetic Operations
3-13
Multiplication
Multiplication of two LTI models connects them in series. Specifically,
sys = sys1 * sys2
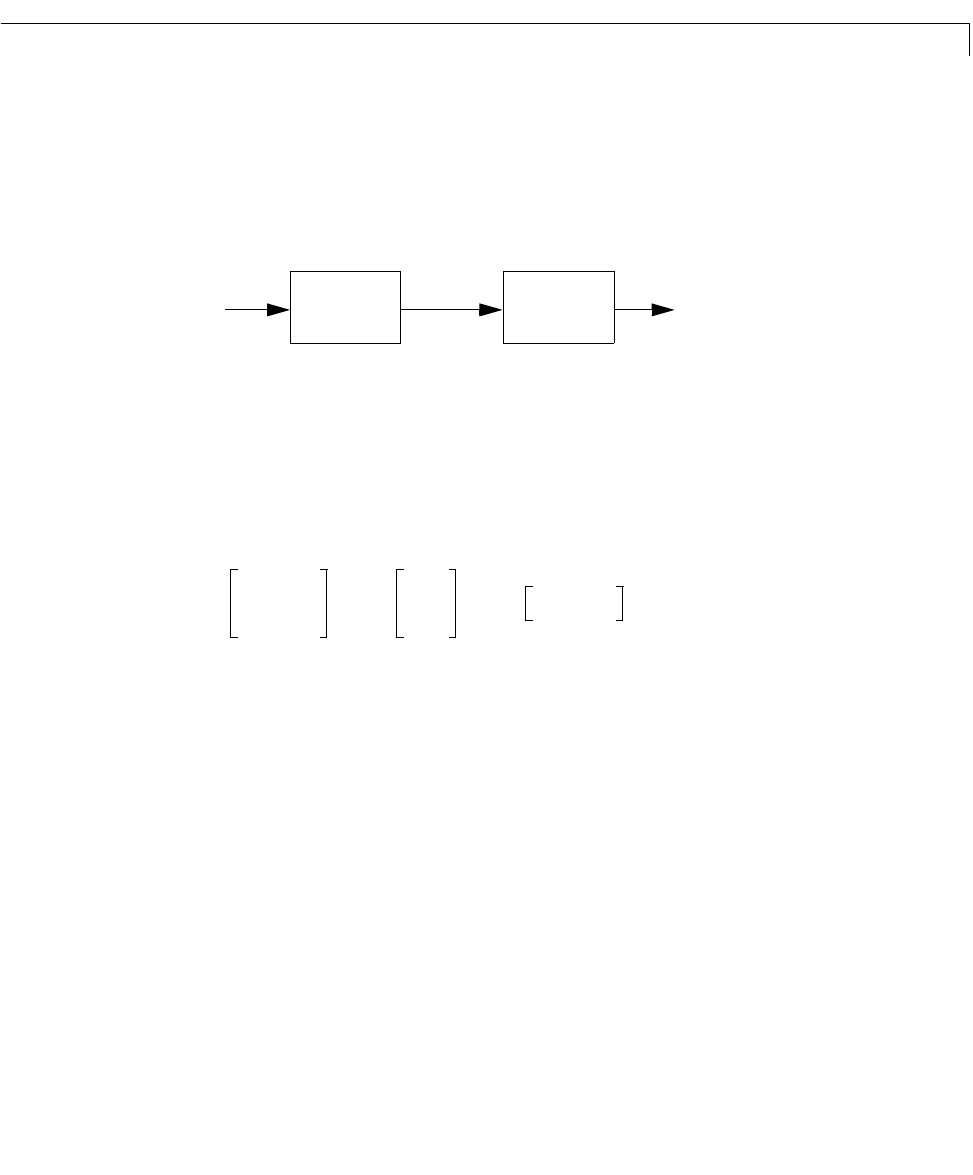
returns an LTI model sys for the series interconnection shown below.
Notice the reverse orders of
sys1 and sys2 in the multiplication and block
diagram. This is consistent with the way transfer matrices are combined in a
series connection: if
sys1 and sys2 have transfer matrices and , then
For state-space models
sys1 and sys2 with data and
, the state-space data associated with
sys1*sys2 is
Finally, if
sys1 is MIMO and sys2 is SISO, then sys1*sys2 or sys2*sys1 is
interpreted as an entry-by-entry scalar multiplication and produces a system
with the same dimensions as
sys1,whoseijth entry is sys1(i,j)*sys2.
Inversion and Related Operations
Inversion of LTI models amounts to inverting the following input/output
relationship.
This operation is defined only for square systems (that is, systems with as
many inputs as outputs) and is performed using
inv(sys)
The resulting inverse model is of the same type as sys. Related operations
include:
u
y
v
sys2 sys1
H
1
H
2
yH
1
vH
1
H
2
u
()
H
1
H
2
×()
u== =
A
1
B
1
C
1
D
1
,,,
A
2
B
2
C
2
D
2
,,,
A
1
B
1
C
2
0 A
2
,
B
1
D
2
B
2
,
C
1
D
1
C
2
, D
1
D
2
yHu=
→
uH
1–
y=