Specifications
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- LTI Models
- Operations on LTI Models
- Model Analysis Tools
- Arrays of LTI Models
- Customization
- Setting Toolbox Preferences
- Setting Tool Preferences
- Customizing Response Plot Properties
- Design Case Studies
- Reliable Computations
- GUI Reference
- SISO Design Tool Reference
- Menu Bar
- File
- Import
- Export
- Toolbox Preferences
- Print to Figure
- Close
- Edit
- Undo and Redo
- Root Locus and Bode Diagrams
- SISO Tool Preferences
- View
- Root Locus and Bode Diagrams
- System Data
- Closed Loop Poles
- Design History
- Tools
- Loop Responses
- Continuous/Discrete Conversions
- Draw a Simulink Diagram
- Compensator
- Format
- Edit
- Store
- Retrieve
- Clear
- Window
- Help
- Tool Bar
- Current Compensator
- Feedback Structure
- Root Locus Right-Click Menus
- Bode Diagram Right-Click Menus
- Status Panel
- Menu Bar
- LTI Viewer Reference
- Right-Click Menus for Response Plots
- Function Reference
- Functions by Category
- acker
- allmargin
- append
- augstate
- balreal
- bode
- bodemag
- c2d
- canon
- care
- chgunits
- connect
- covar
- ctrb
- ctrbf
- d2c
- d2d
- damp
- dare
- dcgain
- delay2z
- dlqr
- dlyap
- drss
- dsort
- dss
- dssdata
- esort
- estim
- evalfr
- feedback
- filt
- frd
- frdata
- freqresp
- gensig
- get
- gram
- hasdelay
- impulse
- initial
- interp
- inv
- isct, isdt
- isempty
- isproper
- issiso
- kalman
- kalmd
- lft
- lqgreg
- lqr
- lqrd
- lqry
- lsim
- ltimodels
- ltiprops
- ltiview
- lyap
- margin
- minreal
- modred
- ndims
- ngrid
- nichols
- norm
- nyquist
- obsv
- obsvf
- ord2
- pade
- parallel
- place
- pole
- pzmap
- reg
- reshape
- rlocus
- rss
- series
- set
- sgrid
- sigma
- sisotool
- size
- sminreal
- ss
- ss2ss
- ssbal
- ssdata
- stack
- step
- tf
- tfdata
- totaldelay
- zero
- zgrid
- zpk
- zpkdata
- Index
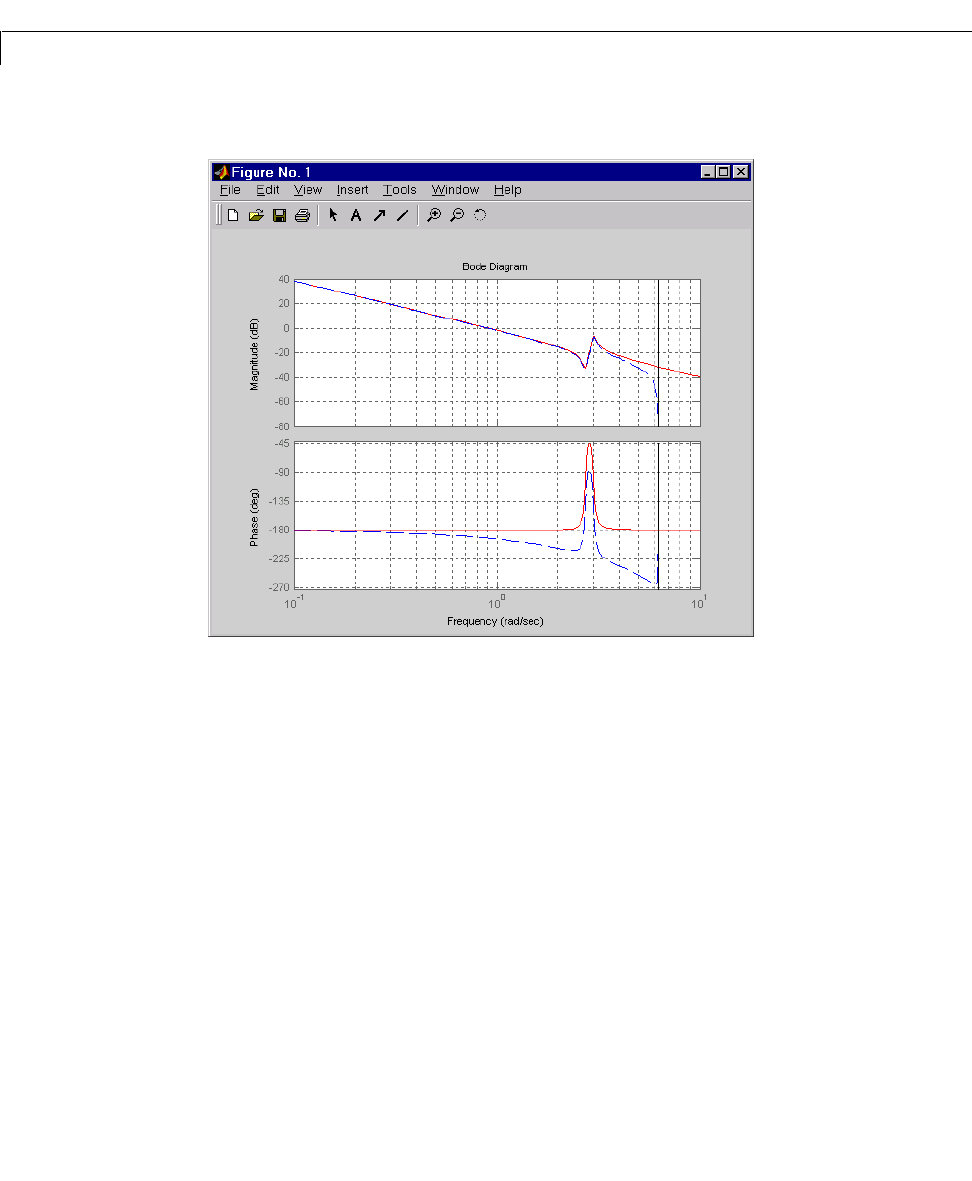
bode
16-24
bode(g,'r',gd,'b--')
Algorithm For continuous-time systems, bode computes the frequency response by
evaluating the transfer function on the imaginary axis . Only
positive frequencies are considered. For state-space models, the frequency
response is
When numerically safe, is diagonalized for maximum speed. Otherwise,
is reduced to upper Hessenberg form and the linear equation
is solved at each frequency point, taking advantage of the Hessenberg
structure. The reduction to Hessenberg form provides a good compromise
between efficiency and reliability. See [1] for more details on this technique.
For discrete-time systems, the frequency response is obtained by evaluating
the transfer function on the unit circle. To facilitate interpretation, the
upper-half of the unit circle is parametrized as
Hs
()
sj
ω
=
ω
DCj
ω
A–
()
1–
B+ ,
ω
0
≥
AA
j
ω
A–
()
XB=
Hz()
ze
j
ω
T
s
= ,0ωω
N
≤≤
π
T
s
------
=










