Specifications
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- LTI Models
- Operations on LTI Models
- Model Analysis Tools
- Arrays of LTI Models
- Customization
- Setting Toolbox Preferences
- Setting Tool Preferences
- Customizing Response Plot Properties
- Design Case Studies
- Reliable Computations
- GUI Reference
- SISO Design Tool Reference
- Menu Bar
- File
- Import
- Export
- Toolbox Preferences
- Print to Figure
- Close
- Edit
- Undo and Redo
- Root Locus and Bode Diagrams
- SISO Tool Preferences
- View
- Root Locus and Bode Diagrams
- System Data
- Closed Loop Poles
- Design History
- Tools
- Loop Responses
- Continuous/Discrete Conversions
- Draw a Simulink Diagram
- Compensator
- Format
- Edit
- Store
- Retrieve
- Clear
- Window
- Help
- Tool Bar
- Current Compensator
- Feedback Structure
- Root Locus Right-Click Menus
- Bode Diagram Right-Click Menus
- Status Panel
- Menu Bar
- LTI Viewer Reference
- Right-Click Menus for Response Plots
- Function Reference
- Functions by Category
- acker
- allmargin
- append
- augstate
- balreal
- bode
- bodemag
- c2d
- canon
- care
- chgunits
- connect
- covar
- ctrb
- ctrbf
- d2c
- d2d
- damp
- dare
- dcgain
- delay2z
- dlqr
- dlyap
- drss
- dsort
- dss
- dssdata
- esort
- estim
- evalfr
- feedback
- filt
- frd
- frdata
- freqresp
- gensig
- get
- gram
- hasdelay
- impulse
- initial
- interp
- inv
- isct, isdt
- isempty
- isproper
- issiso
- kalman
- kalmd
- lft
- lqgreg
- lqr
- lqrd
- lqry
- lsim
- ltimodels
- ltiprops
- ltiview
- lyap
- margin
- minreal
- modred
- ndims
- ngrid
- nichols
- norm
- nyquist
- obsv
- obsvf
- ord2
- pade
- parallel
- place
- pole
- pzmap
- reg
- reshape
- rlocus
- rss
- series
- set
- sgrid
- sigma
- sisotool
- size
- sminreal
- ss
- ss2ss
- ssbal
- ssdata
- stack
- step
- tf
- tfdata
- totaldelay
- zero
- zgrid
- zpk
- zpkdata
- Index
5 Arrays of LTI Models
5-6
Higher Dimensional Arrays of LTI Models
You can also collect a set of models in a two-dimensional array. The following
diagram illustrates a 2-by-3 array of six, two-output, one-input models called
m2d.
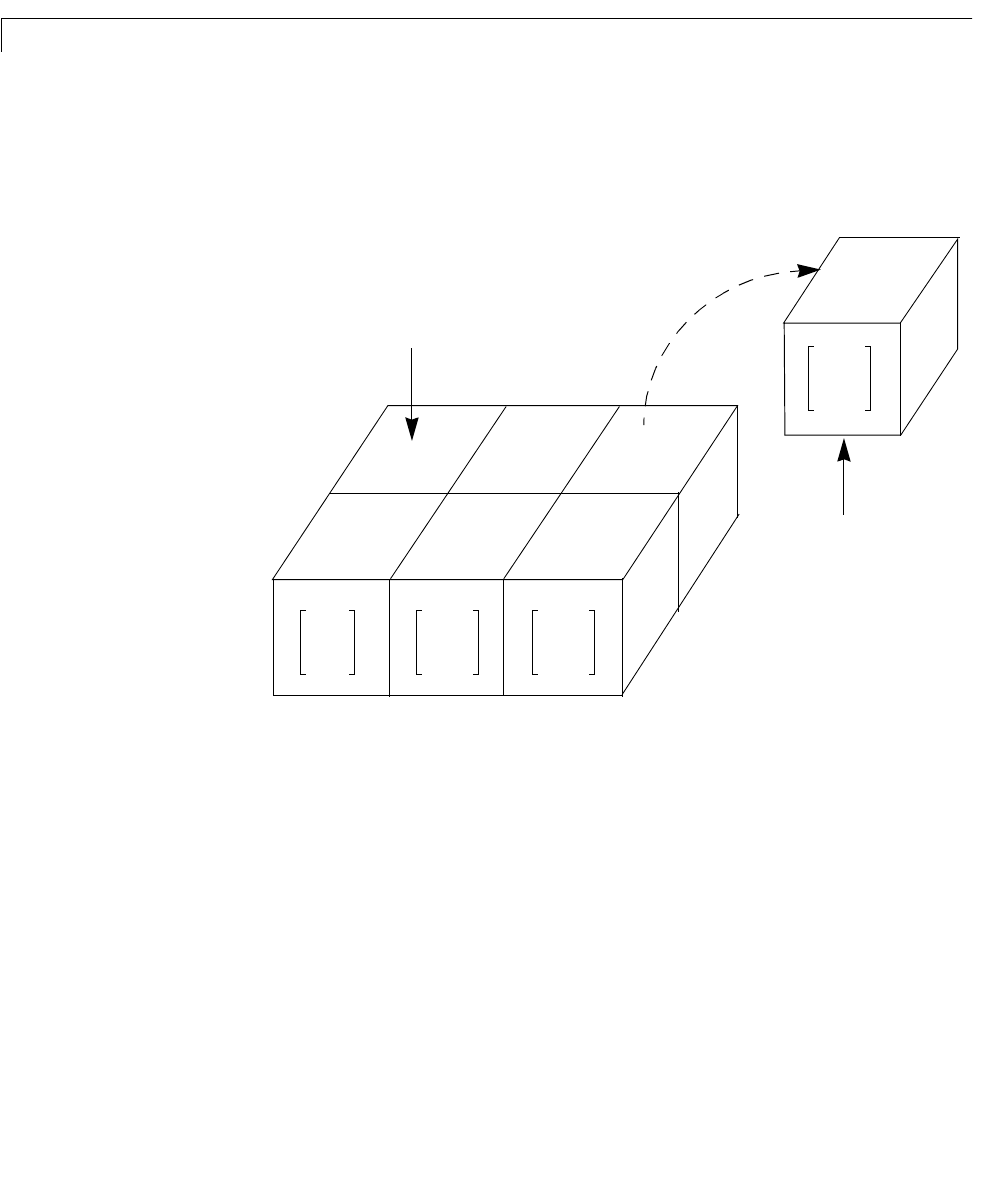
Figure 5-4: m2d: A 2-by-3 Array of Two-Output, One-Input Models
More generally, you can organize models into a 3-D or higher-dimensional
array, in much the same way you arrange numerical data into
multidimensional arrays (see “Multidimensional Arrays” in Using MATLAB).
m2d(:,:,2,1)
m2d(:,:,1,2) m2d(:,:,1,3)
m2d(:,:,2,2) m2d(:,:,2,3)
m2d(:,:,1,3)
m2d(:,:,1,1)
m2d(:,:,1,3) extracts the model in
the (1,3) position of the array.
3.36
s 2.9+
-----------------
7.23
3.4
s 2.86+
--------------------
7.27
3.45
s 2.81+
--------------------
7.32
3.42
s 2.84+
--------------------
7.29
Each entry in this 2-by-3 array of
models is a two-output, one-input
transfer function.










