Specifications
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- LTI Models
- Operations on LTI Models
- Model Analysis Tools
- Arrays of LTI Models
- Customization
- Setting Toolbox Preferences
- Setting Tool Preferences
- Customizing Response Plot Properties
- Design Case Studies
- Reliable Computations
- GUI Reference
- SISO Design Tool Reference
- Menu Bar
- File
- Import
- Export
- Toolbox Preferences
- Print to Figure
- Close
- Edit
- Undo and Redo
- Root Locus and Bode Diagrams
- SISO Tool Preferences
- View
- Root Locus and Bode Diagrams
- System Data
- Closed Loop Poles
- Design History
- Tools
- Loop Responses
- Continuous/Discrete Conversions
- Draw a Simulink Diagram
- Compensator
- Format
- Edit
- Store
- Retrieve
- Clear
- Window
- Help
- Tool Bar
- Current Compensator
- Feedback Structure
- Root Locus Right-Click Menus
- Bode Diagram Right-Click Menus
- Status Panel
- Menu Bar
- LTI Viewer Reference
- Right-Click Menus for Response Plots
- Function Reference
- Functions by Category
- acker
- allmargin
- append
- augstate
- balreal
- bode
- bodemag
- c2d
- canon
- care
- chgunits
- connect
- covar
- ctrb
- ctrbf
- d2c
- d2d
- damp
- dare
- dcgain
- delay2z
- dlqr
- dlyap
- drss
- dsort
- dss
- dssdata
- esort
- estim
- evalfr
- feedback
- filt
- frd
- frdata
- freqresp
- gensig
- get
- gram
- hasdelay
- impulse
- initial
- interp
- inv
- isct, isdt
- isempty
- isproper
- issiso
- kalman
- kalmd
- lft
- lqgreg
- lqr
- lqrd
- lqry
- lsim
- ltimodels
- ltiprops
- ltiview
- lyap
- margin
- minreal
- modred
- ndims
- ngrid
- nichols
- norm
- nyquist
- obsv
- obsvf
- ord2
- pade
- parallel
- place
- pole
- pzmap
- reg
- reshape
- rlocus
- rss
- series
- set
- sgrid
- sigma
- sisotool
- size
- sminreal
- ss
- ss2ss
- ssbal
- ssdata
- stack
- step
- tf
- tfdata
- totaldelay
- zero
- zgrid
- zpk
- zpkdata
- Index
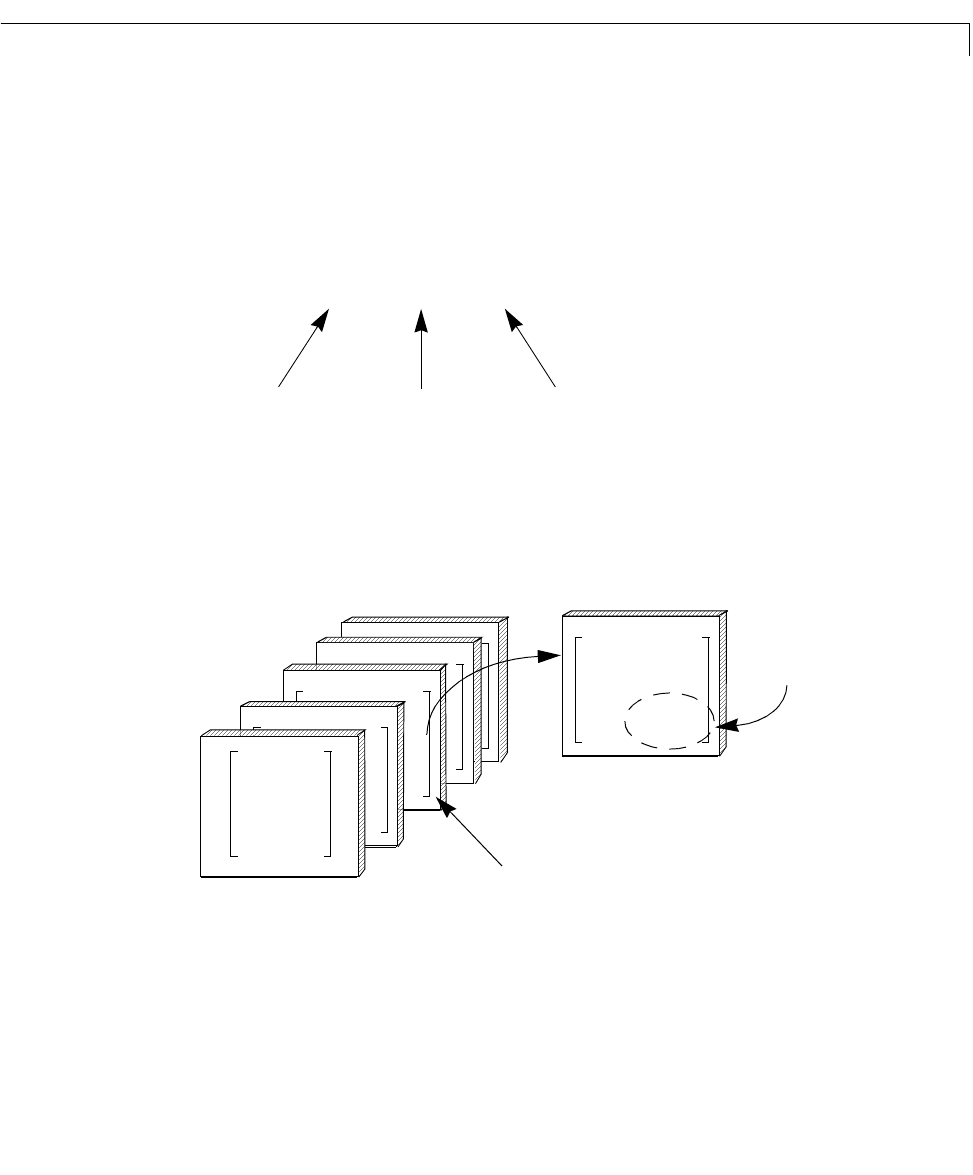
The Concept of an LTI Array
5-5
Just as you might collect a set of two-by-two matrices in a multidimensional
array, you can collect this set offive transfer function models as a list in an LTI
array under one variable name, say,
sys. Each element of the LTI array is an
LTI model.
Individual models in the LTI array
sys are accessed via indexing. The general
form for the syntax you use to access data in an LTI array is
For example, you can access the third model in
sys with sys(:,:,3).The
following illustrates how you can use indexing to select models or their
components from
sys.
Figure 5-3: Using Indices to Select Models and Their Components
See “Indexing Into LTI Arrays” for more information on indexing.
sysa(Outputs,Inputs,Models)
The first index
selects the output
channels.
The second index
selects the input
channels.
The remaining indices select particular
models in the LTI array by their array
coordinates.
1.11
s 1.2+
-----------------
0
0
1
s 5.4+
-----------------
sysa(:,:,3) selects the third model in the array.
sysa(2,2,3) selects
the (2,2) entry of the
third model in the array.
1.09
s 1.4+
-----------------
0
0
1
s 5.8+
-----------------
1.15
s 1.3+
-----------------
0
0
1
s 5.6+
-----------------
1.11
s 1.2+
-----------------
0
0
1
s 5.4+
-----------------
1.3
s 1.1+
-----------------
0
0
1
s 5.2+
-----------------
1.1
s 1+
------------
0
0
1
s 5+
------------










