Specifications
MCU slave software
Developer’s Serial Bootloader, Rev. 13
Freescale Semiconductor 43
TXA ;FEW CYCLES THAN EXPECTED, SO TRIM BY SPEEDING
BEQ SLOW ;UP f OP .
FAST: CMP #$40 ;SEE IF BREAK IS WITHIN TOLERANCE
BGE OOR ;DON'T TRIM IF OUT OF RANGE
ASLA ;multiply by two to get right range
ADD #$80 ;BREAK LONGER THAN EXPECTED, SO SLOW DOWN f OP
BRA ICGDONE
SLOW: CMP #$C0 ;SEE IF BREAK IS WITHIN TOLERANCE
BLT OOR ;DON'T TRIM IF OUT OF RANGE
ASLA ;multiply by two to get right range
SUB #$80
ICGDONE:
STA ICGTR
OOR:
RTS
The complete explanation of the trimming procedure can be found in AN1831/D. See References.
8.2 MC68HC908JK/JL
MC68HC908JK/JL MCUs are among the least expensive in the M68HC08 Family, and they have no
hardware SCI. Therefore, a software SCI must be implemented. This allows the unrestricted selection of
which pins are used for serial communication (the provisions are made in the code so an IRQ pin can also
be used as an input serial line).
The MC68HC908JK/JL Family has a RC version (an RC oscillator is used instead of a crystal). The
bootloader’s calibration compensates for any speed variation. If the desired clock frequency is outside the
specified range covered by the calibration system, the code must be modified.
The MC68HC908JK/JL Family has on-chip FLASH programming routines. Using FLASH programming
saves memory.
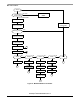
The main program flowchart (Figure 27) is very similar to the previous case. The following figure
represents the MC68HC908JK/JL Bootloader flowchart: