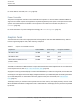
Specifications
Sound System Overview
The sound circuitry is connected to the K2 IC by a standard I2S (inter-IC sound) bus. The K2 IC provides DB-DMA
(descriptor-based direct memory access) support for the I2S port.
The Power Mac G5 circuitry consists of two main components: an analog audio CODEC IC and a digital audio
CODEC IC. The analog audio CODEC IC includes an A/D converter, a D/A converter, and digital audio processing
functions. The digital audio processing functions include output equalization, dynamic range compression,
and volume control. The equalization and dynamic range control functions are set to fixed values to equalize
the internal speaker. Those functions are bypassed for signals sent to the audio output jacks.
Stereo signals from the audio input jack are routed to an analog line input buffer that drives the internal A/D
converter in the analog CODEC. The output of the A/D converter is routed to the K2 IC over the I2S bus.
Digital audio data from the K2 IC is routed to the D/A converter on the analog audio CODEC over the I2S bus.
The analog audio output from the D/A converter is routed to separate amplifiers that drive the line output,
headphone output, and internal speaker.
The digital audio CODEC IC includes an S/PDIF (Sony/Phillips Digital Interface) digital audio receiver, a sample
rate converter (SRC), a phase-locked loop (PLL), and an S/PDIF digital audio transmitter.
The S/PDIF input can operate in synchronous and asynchronous modes. In synchronous mode, the PLL in the
digital audio CODEC locks on to the incoming S/PDIF data rate and drives the audio system clocks in the Power
Mac G5, allowing bit-accurate data processing of the S/PDIF input data. In asynchronous mode, the incoming
S/PDIF data passes through the SRC, where it is converted to the output sample rate of the Power Mac G5,
allowing the Power Mac G5 to play audio at a fixed output sample rate while accepting S/PDIF input data over
a wide frequency range. The audio data from the S/PDIF receiver is routed to the K2 IC over the I2S bus.
Digital audio data from the K2 chip is routed to the S/PDIF output transmitter in the digital audio CODEC over
the I2S bus. The Power Mac G5 sends and receives S/PDIF audio data over TOSLink optical connectors.
Analog audio I/O is not independent of digital audio I/O on the Power Mac G5. Audio input can come from
either the line input or the S/PDIF input, but not both at the same time. Audio output can be played
simultaneously on the line out, headphones output, and S/PDIF output. However, these audio streams are not
independent.
The speaker output is mutually exclusive from the line out, headphones out and S/PDIF outputs. If the speaker
output is selected, the line output, the headphones output and the S/PDIF output are disabled. If any of the
line output, the headphones output, or the S/PDIF output are selected, the speaker output is disabled.
When the speaker output is active, the digital audio processing functions in the analog CODEC are used to
implement output equalization for the internal speaker, resulting in improved sound quality from the internal
speaker.
Architecture
K2 I/O Controller
Retired Document | 2005-04-29 | Copyright © 2003, 2005 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
27