Datasheet
LUXEON LED Assembly and Handling Application Brief AB32 20121217 8
1.3 Lens Handling
A LUXEON LED is designed to maximize light output and reliability. However, improper handling of a LUXEON LED may damage the silicone lens
and affect the overall light performance and reliability.
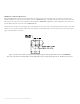
To minimize the risk of damage to the silicone lens during manual handling, only pick up LUXEON LEDs from the sides of the ceramic substrate and
never from the silicone lens itself (see Figure 7).
Due to its small size, the silicone lens of a LUXEON LED can only withstand a limited amount of force. In order to avoid any mechanical damage to
the silicone lens of a LUXEON LED or to the LED chip inside the LUXEON LED, do not apply more than 3N of shear force (300g) directly onto the
lens. When utilizing a pick and place machine, always ensure that the pick and place nozzle does not place excessive pressure onto the silicone lens
of a LUXEON LED. For more information see section 5.3 Pick and Place Nozzle of this document. Similar restrictions exist for manual handling.
1.4 Lens cleaning
The silicone lens of a LUXEON LED should not be exposed to dust and debris. Excessive dust and debris may cause a drastic decrease in optical
output. In the event that an emitter requires cleaning, first try a gentle swabbing using a lint-free swab. If needed, a lint-free swab and isopropyl
alcohol (IPA) can be used to gently remove dirt from the lens. Do not use other solvents as they may adversely react with a LUXEON LED. For
more information regarding chemical compatibility, see section 7. Product Packaging Considerations—Chemical Compatibility.
1.5 Electrical Isolation
The ceramic substrate of a LUXEON LED electrically isolates the thermal pad from the LED cathode and anode (see the cross sections in
Figure 1). Consequently, a high voltage difference between the electrical and thermal metallization may occur in applications where multiple
LUXEON LEDs are connected in series. As a reference, the minimum distance between the top electrical metallization and the bottom thermal
metallization of a LUXEON LED, considering x, y and z dimensions, is > 0.35 mm.
In order to avoid any electrical shocks and/or damage to LUXEON LEDs, each design needs to comply with the appropriate standards of safety and
isolation distances, known as clearance and creepage distances, respectively. Compliance with appropriate standards is application and design specific.
Examples of standards are IEC 60065 for audio/video equipment and IEC 60598 for general lighting applications.
With proper use of electrical isolation and circuitry (e.g. short-circuits protection) the length of a series of LUXEON LEDs can be many tens of
units long.
Figure 7. Correct handling (left) and incorrect handling (right) of a LUXEON LED.