User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Terminology
- Introduction
- Installation
- Software configuration
- Prepare your PC to configure the WLAN Broadband Router
- Connect to the WLAN Broadband Router
- Management and configuration on the WLAN Broadband Router
- Status
- Setup Wizard
- Operation Mode
- Wireless - Basic Settings
- Wireless - Advanced Settings
- Wireless - Security Setup
- Wireless - Access Control
- WDS Settings
- Site Survey
- WPS
- LAN Interface Setup
- WAN Interface Setup
- Firewall - Port Filtering
- Firewall - IP Filtering
- Firewall - MAC Filtering
- Firewall - Port Forwarding
- Firewall - URL Filtering
- Firewall - DMZ
- Management - Statistics
- Management - DDNS
- Management - Time Zone Setting
- Management - Denial-of-Service
- Management - Log
- Management - Upgrade Firmware
- Management - Save/ Reload Settings
- Management - Password Setup
- FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQ)
- What and how to find my PC’s IP and MAC address?
- What is Wireless LAN?
- What are ISM bands?
- How does wireless networking work?
- What is BSSID?
- What is ESSID?
- What are potential factors that may causes interference?
- What are the Open System and Shared Key authentications?
- What is WEP?
- What is Fragment Threshold?
- What is RTS (Request To Send) Threshold?
- What is Beacon Interval?
- What is Preamble Type?
- What is SSID Broadcast?
- What is Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)?
- What is WPA2?
- What is 802.1x Authentication?
- What is Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)?
- What is Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)?
- What is Inter-Access Point Protocol (IAPP)?
- What is Wireless Distribution System (WDS)?
- What is Universal Plug and Play (uPNP)?
- What is Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) Size?
- What is Clone MAC Address?
- What is DDNS?
- What is NTP Client?
- What is VPN?
- What is IPSEC?
- What is WLAN Block Relay Between Clients?
- What is WMM?
- What is WLAN ACK TIMEOUT?
- What is Modulation Coding Scheme (MCS)?
- What is Frame Aggregation?
- What is Guard Intervals (GI)?
- Configuration examples
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQ)
-55-
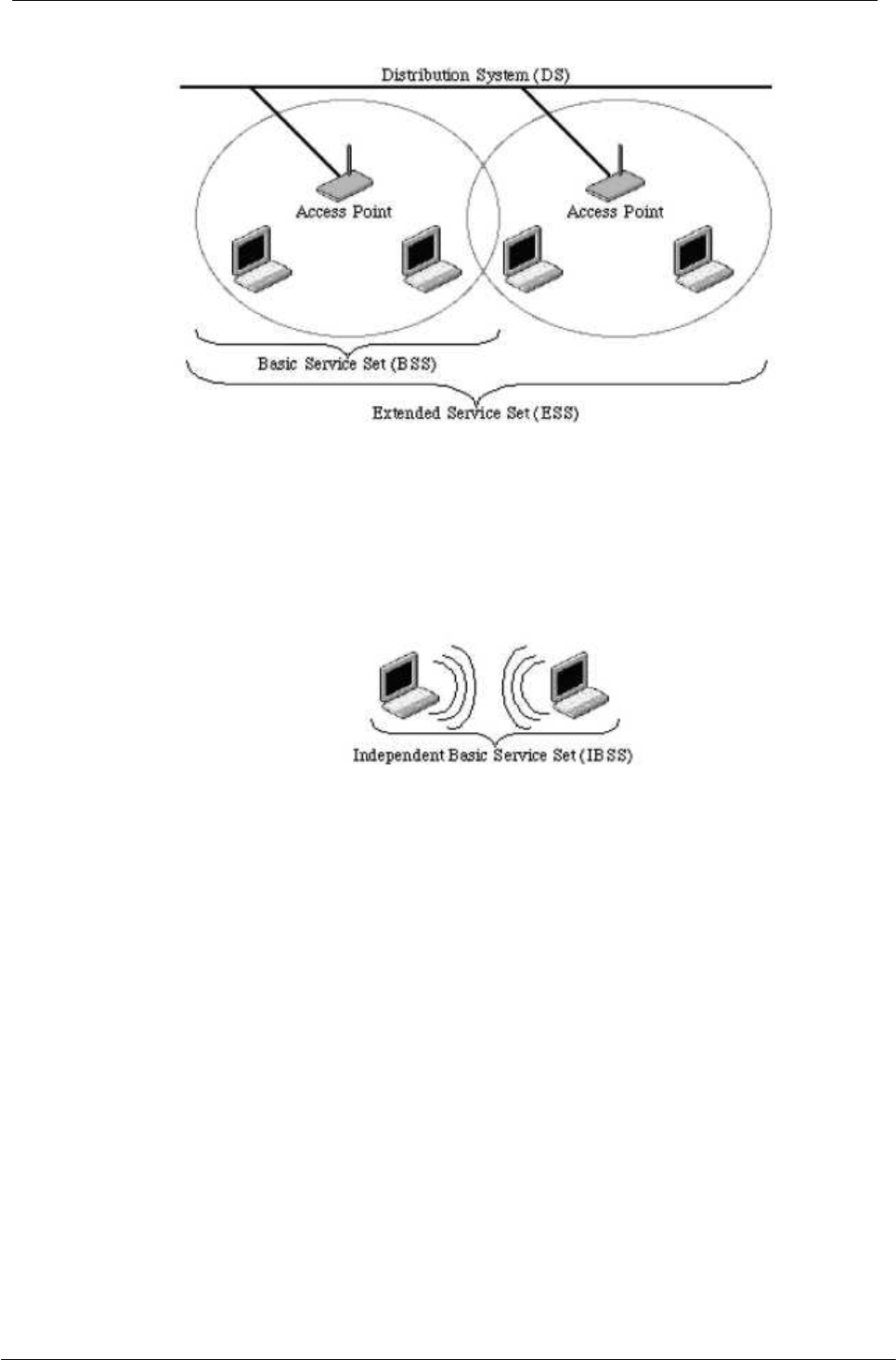
Example 1: wireless Infrastructure Mode
Ad hoc mode (also called peer-to-peer mode or an Independent Basic Service Set, or IBSS) is
simply a set of 802.11 wireless stations that communicate directly with one another without using an
access point or any connection to a wired network. This mode is useful for quickly and easily setting
up a wireless network anywhere that a wireless infrastructure does not exist or is not required for
services, such as a hotel room, convention center, or airport, or where access to the wired network
is barred (such as for consultants at a client site).
Example 2: wireless Ad Hoc Mode
5.5 What is BSSID?
A six-byte address that distinguishes a particular a particular access point from others. Also know
as just SSID. Serves as a network ID or name.
5.6 What is ESSID?
The Extended Service Set ID (ESSID) is the name of the network you want to access. It is used to
identify different wireless networks.
5.7 What are potential factors that may causes interference?
Factors of interference:
O Obstacles: walls, ceilings, furniture… etc.
O Building Materials: metal door, aluminum studs.
O Electrical devices: microwaves, monitors and electrical motors.
Solutions to overcome the interferences:










